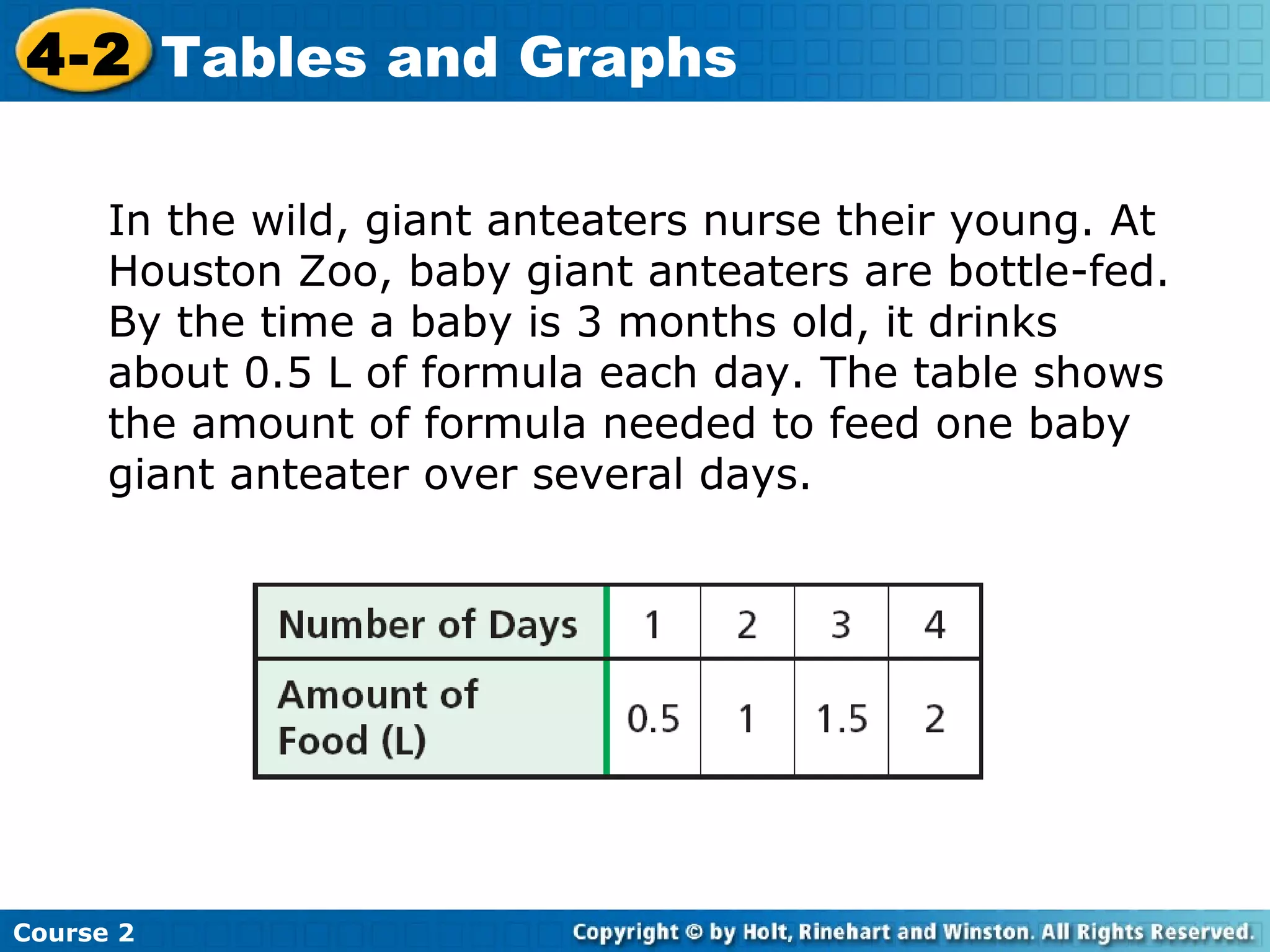
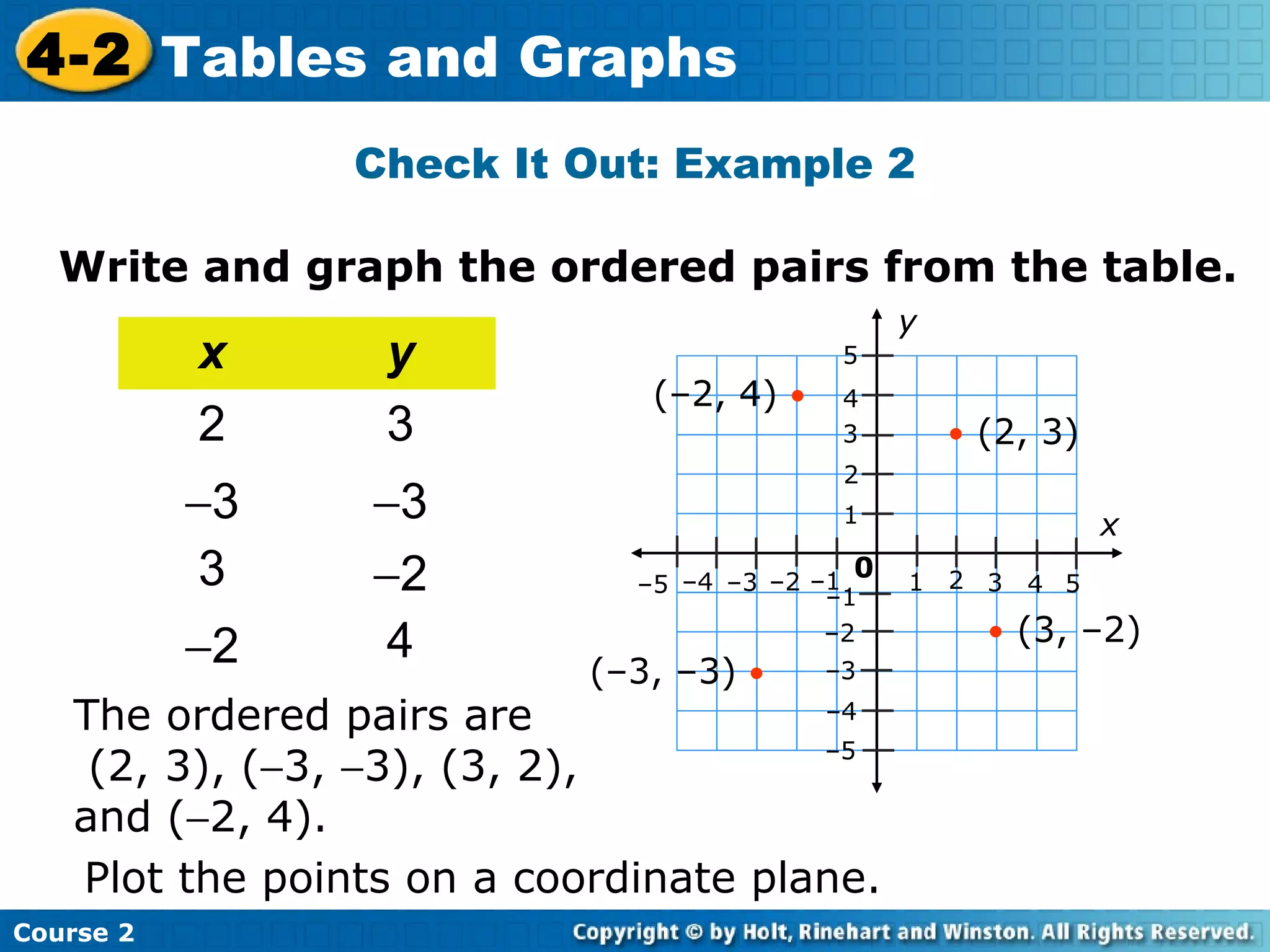
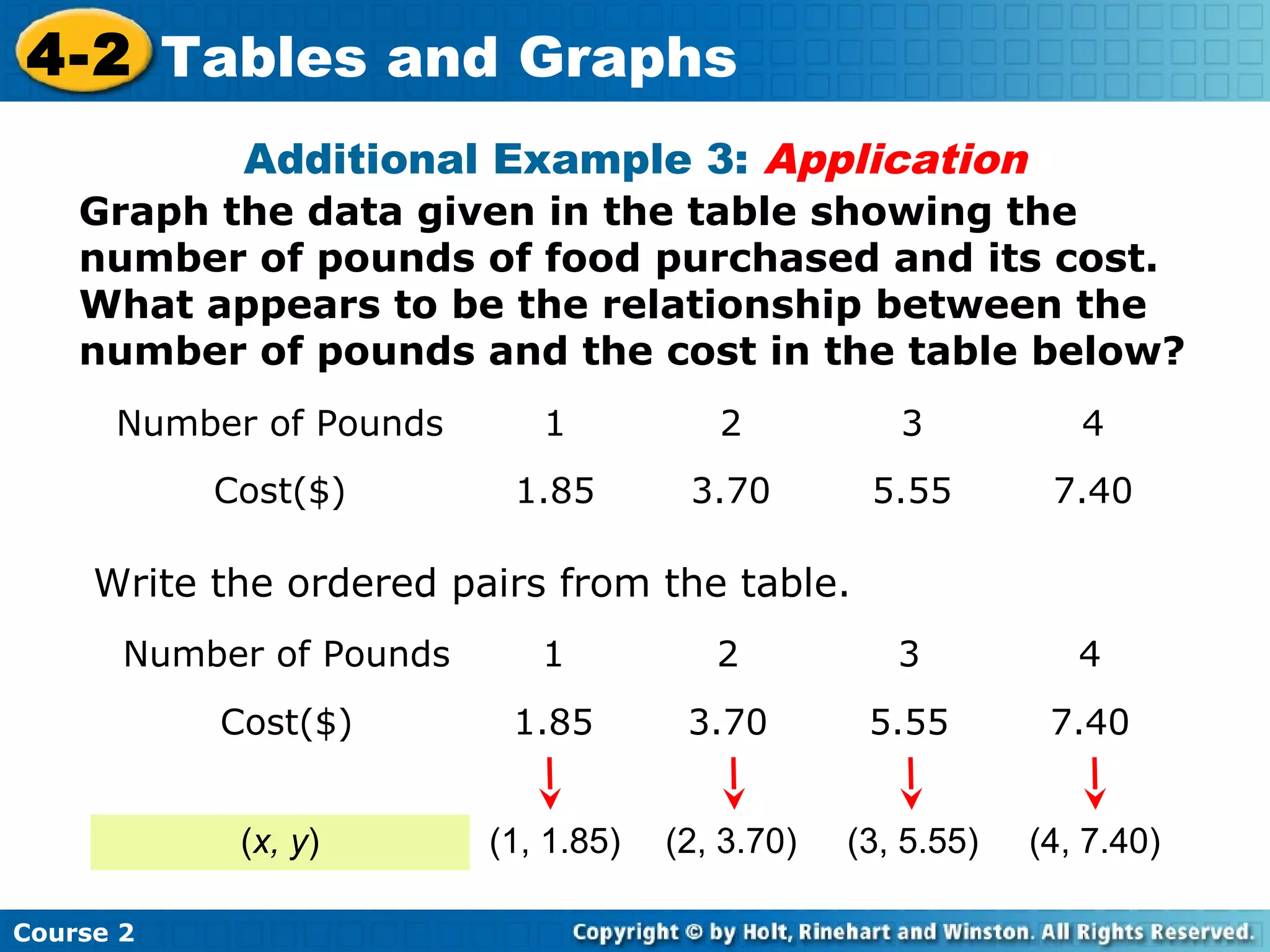
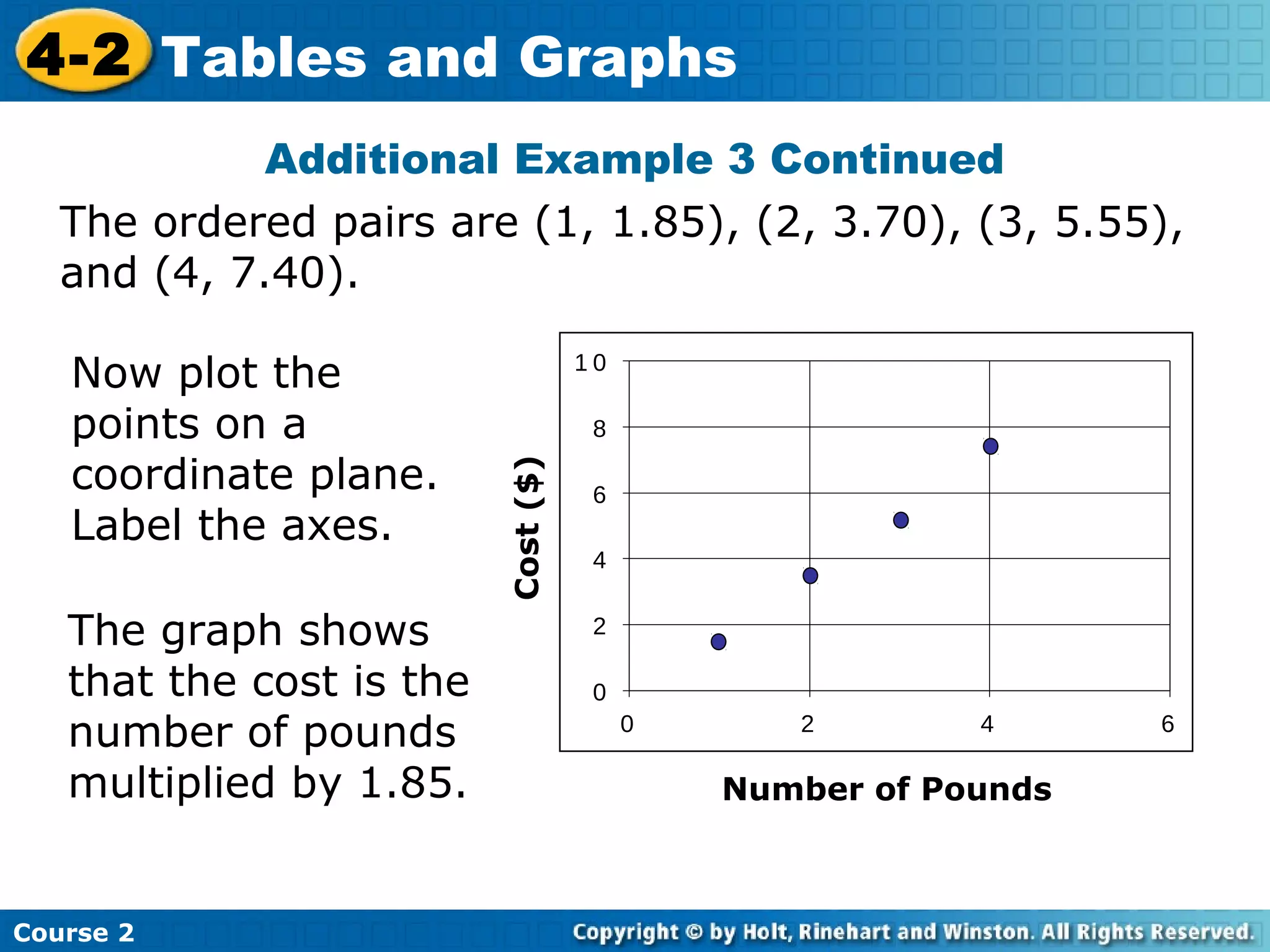
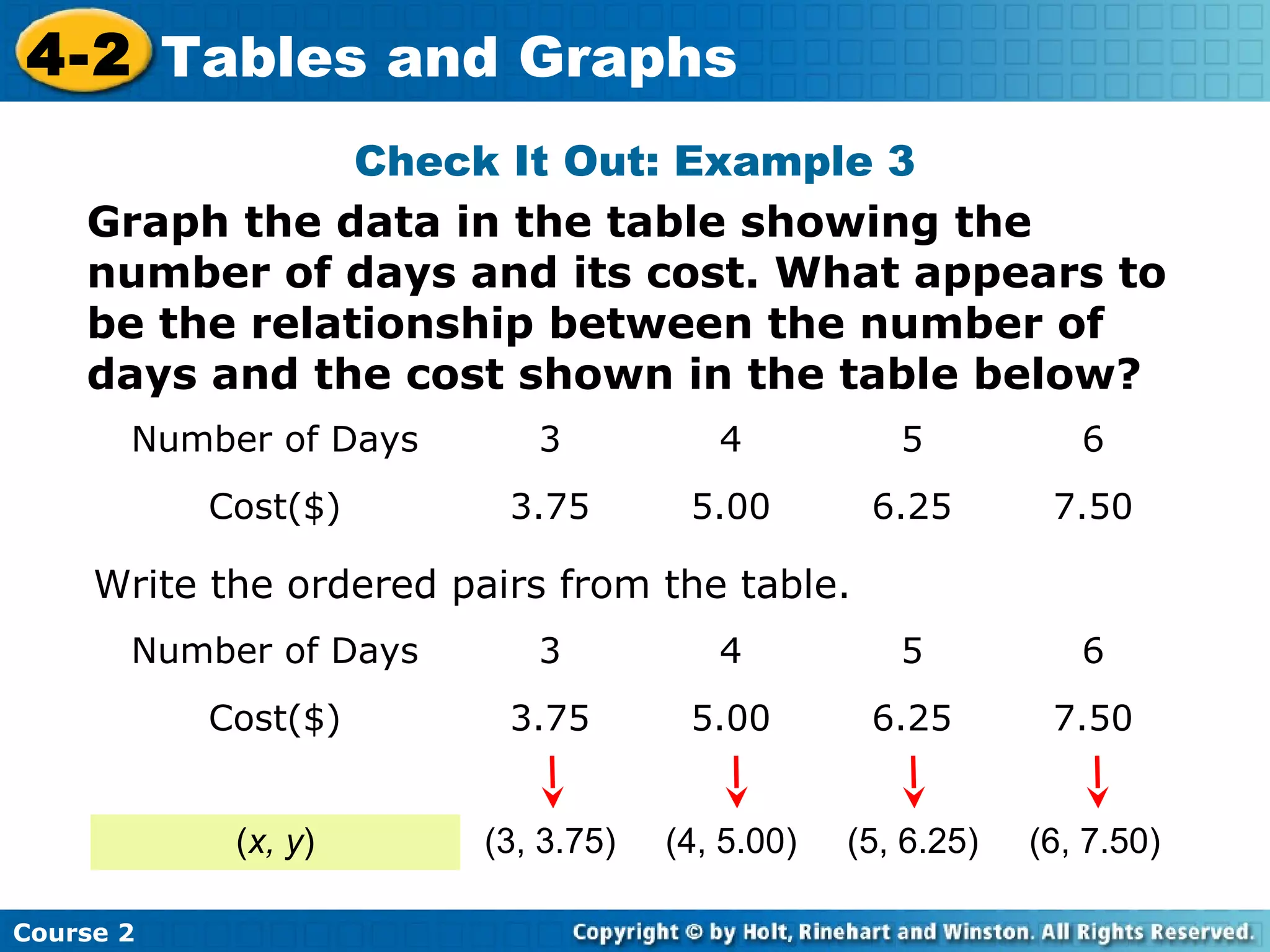
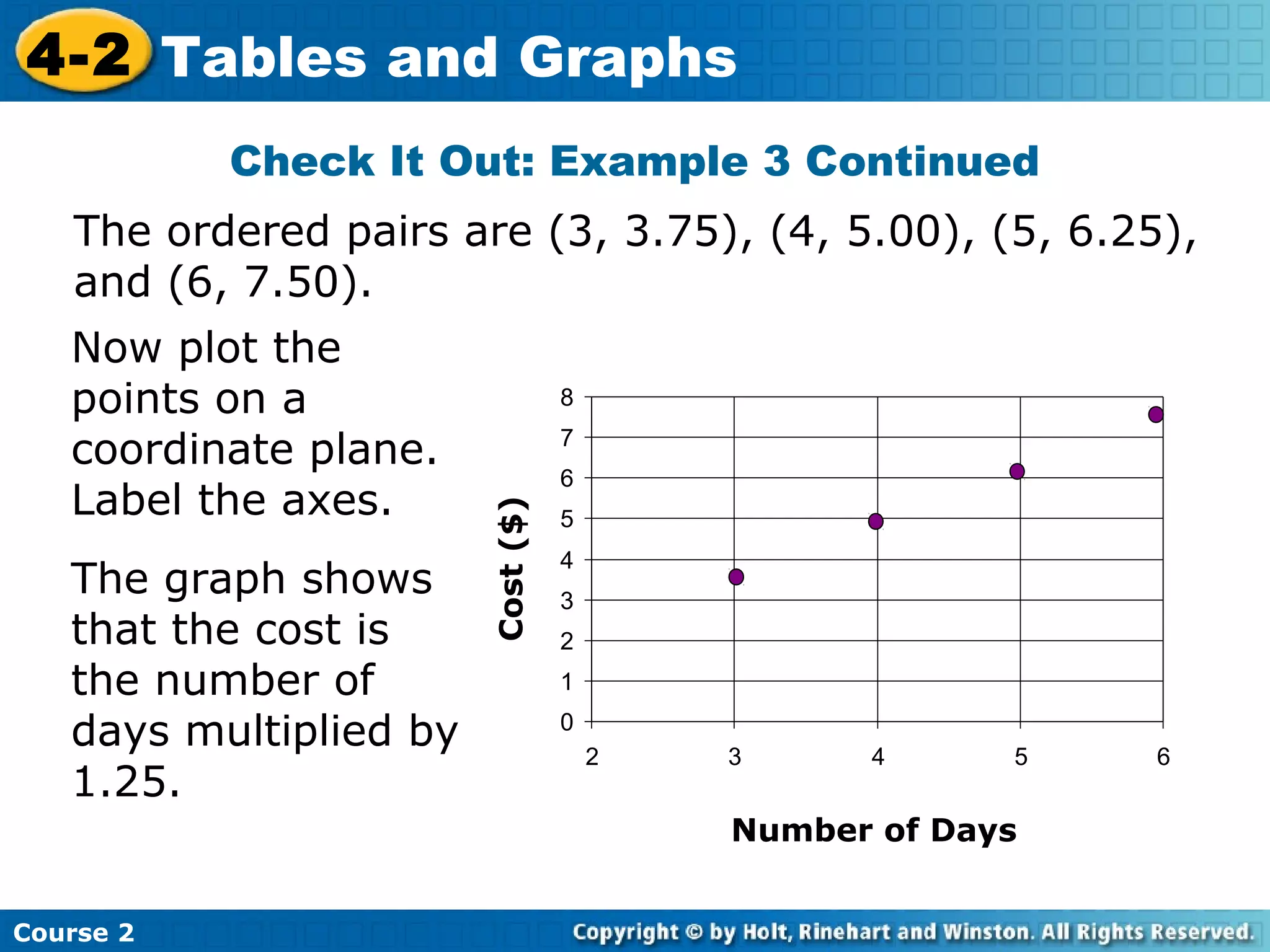
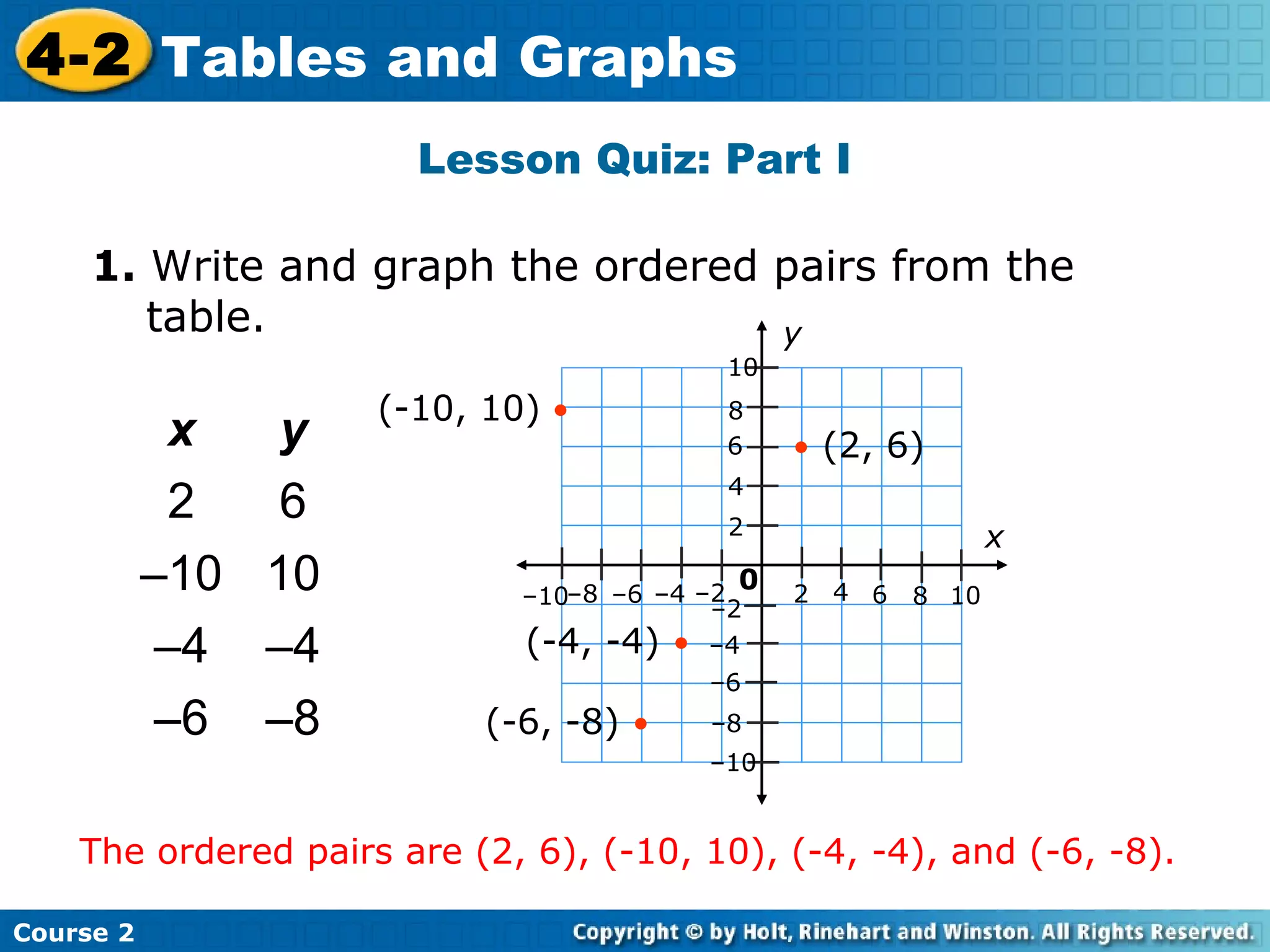
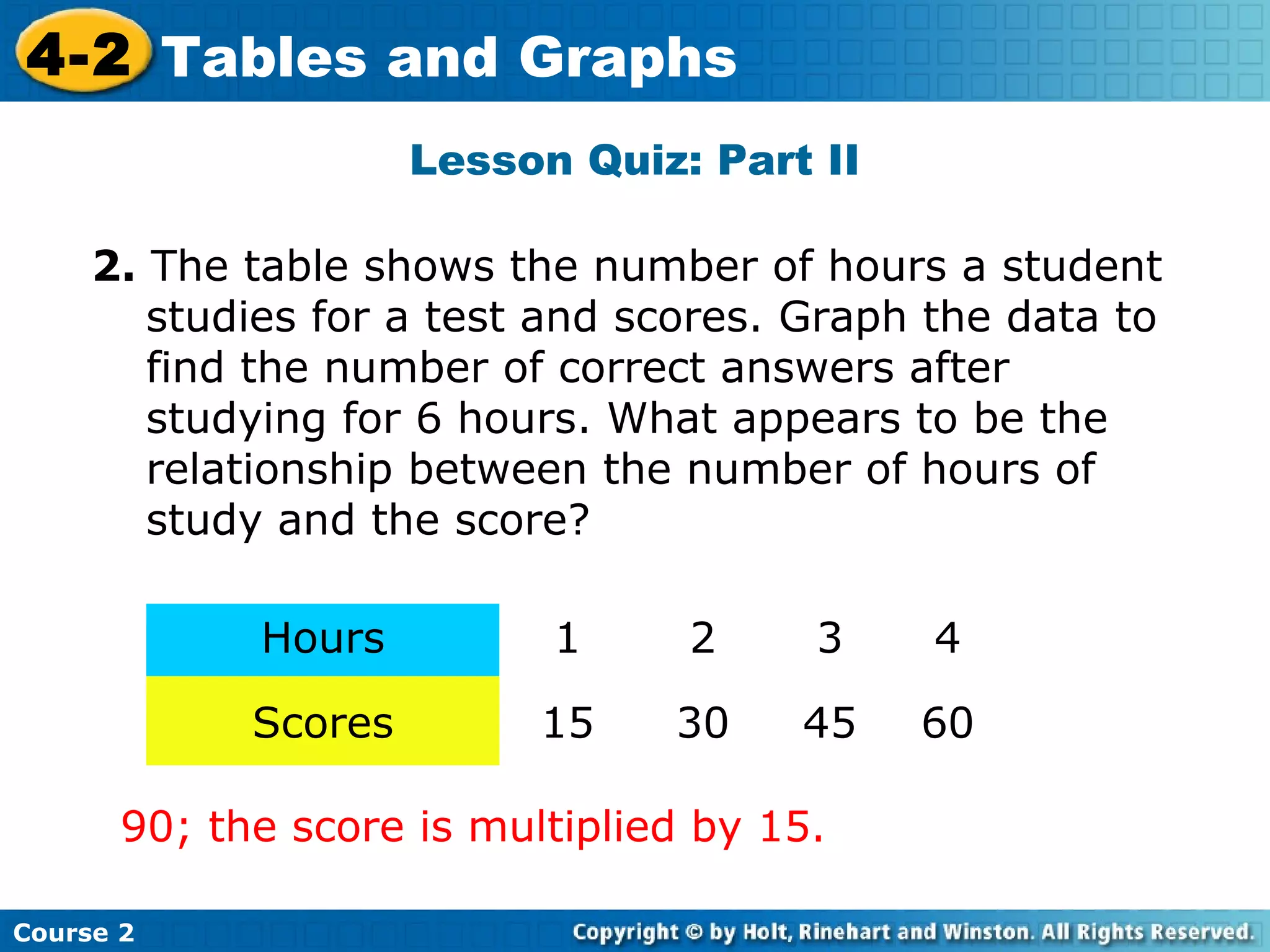
The document provides lesson materials on tables and graphs, including:
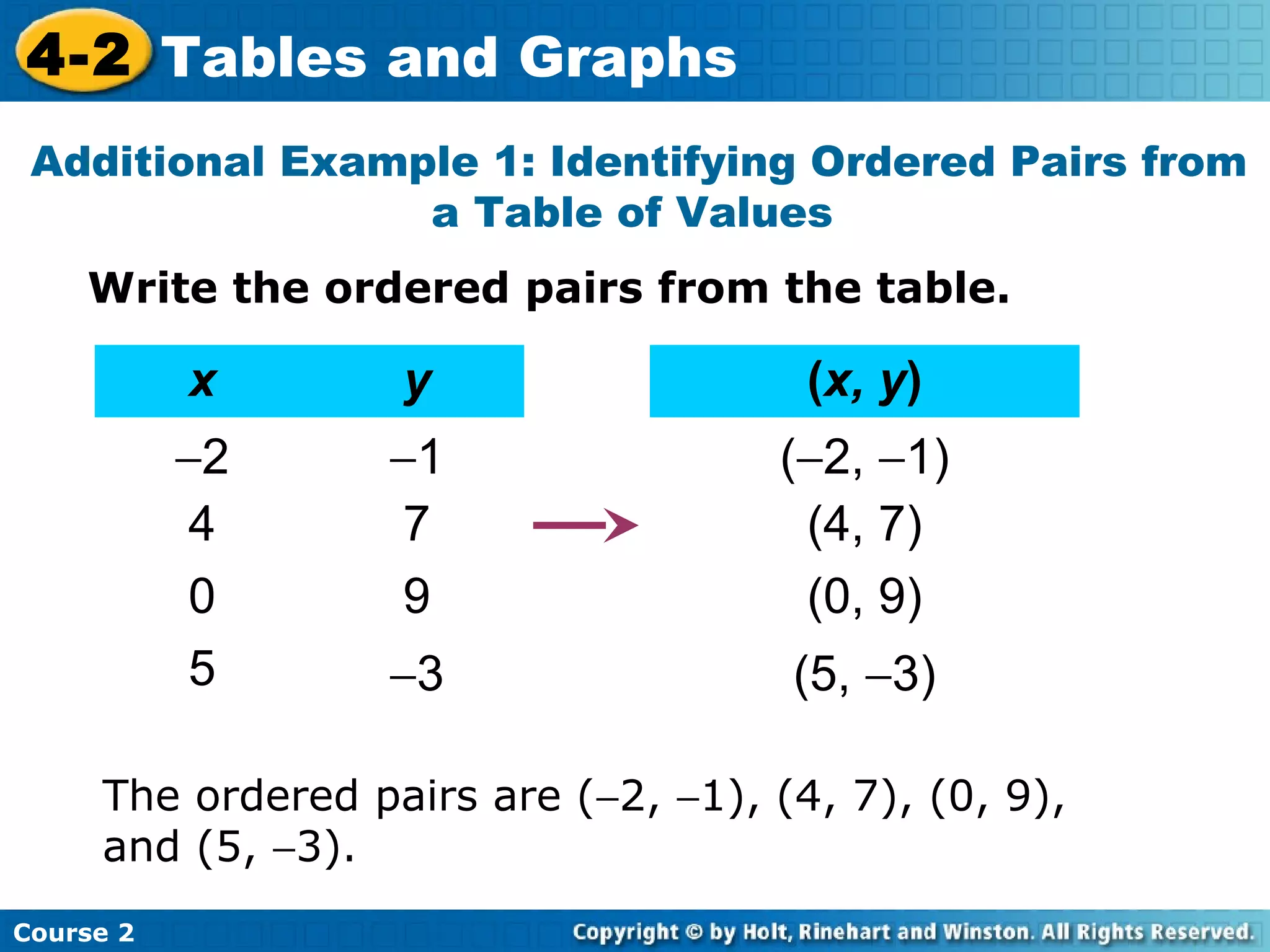
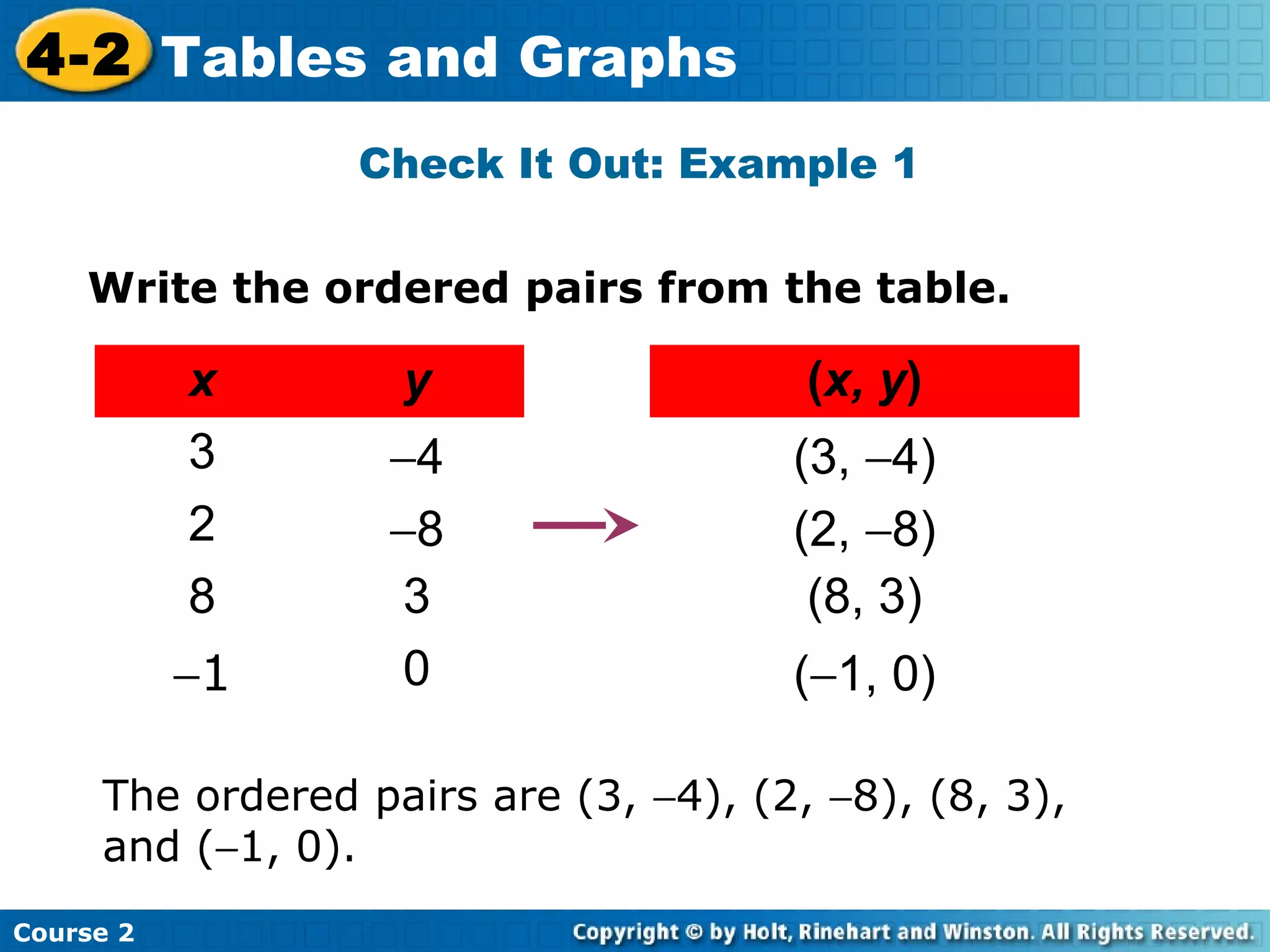
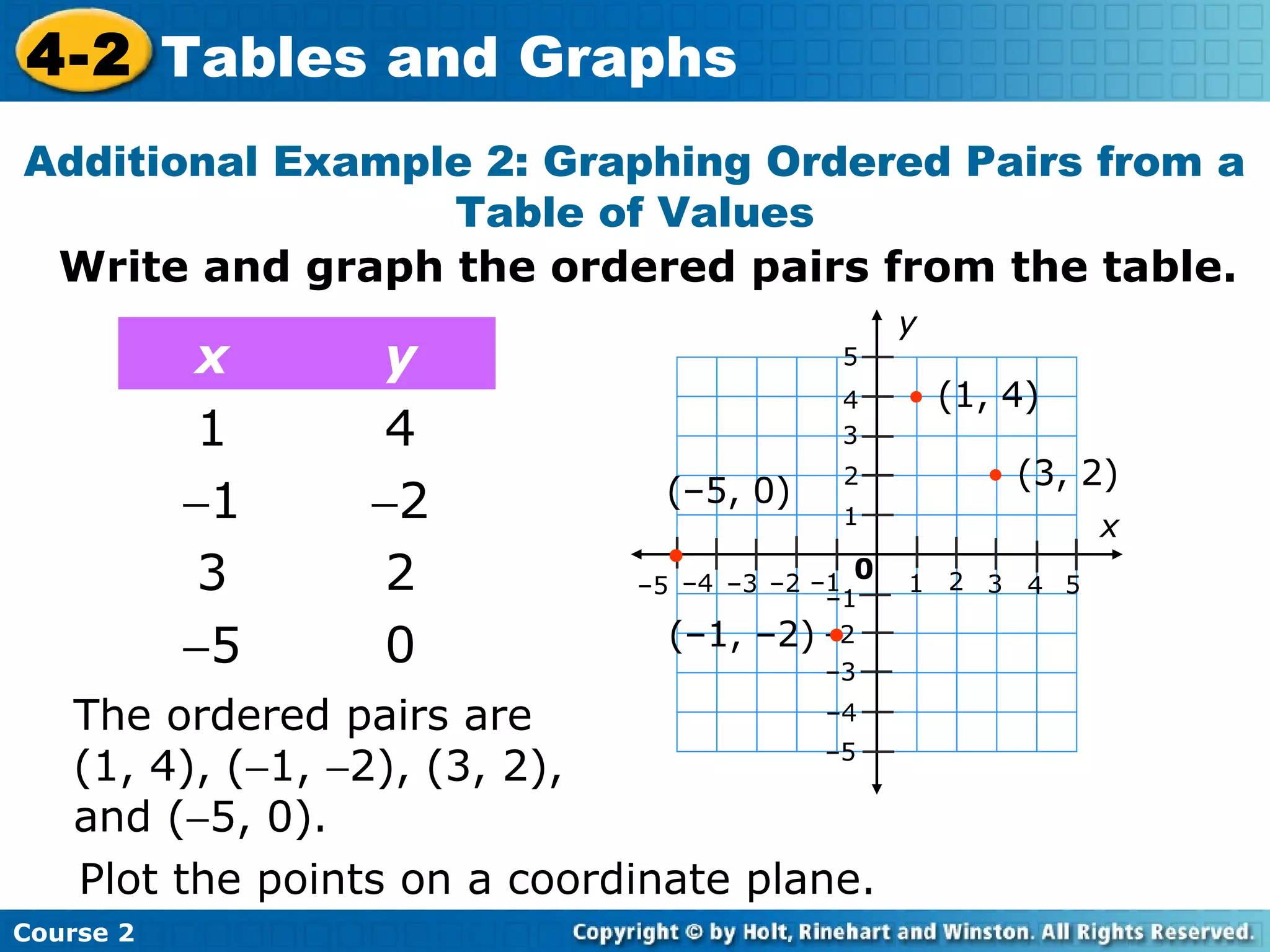
- Examples of identifying ordered pairs from tables and graphing the points on a coordinate plane. The examples show a direct relationship between variables.
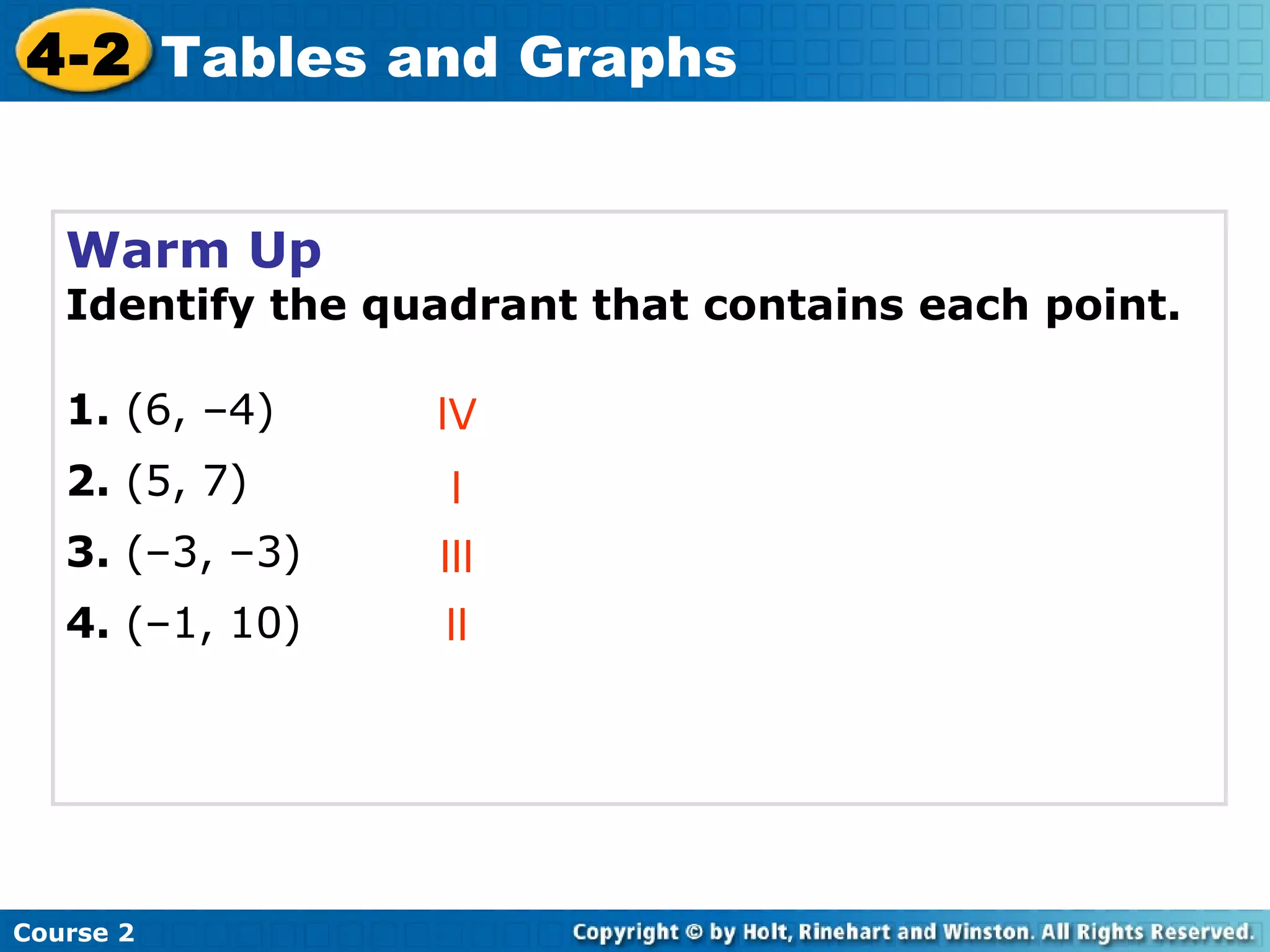
- A warm up on identifying points in quadrants.
- An example application showing pounds of food purchased and its cost, with the relationship that cost is pounds multiplied by a rate.
- A lesson quiz testing the skills of writing ordered pairs from a table and graphing the points.