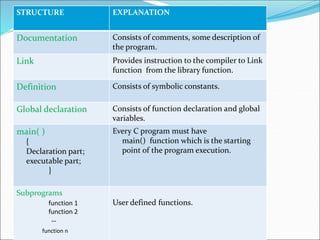
A programming language is a formal set of instructions for computers, used to create programs that solve problems. The document discusses the evolution of programming languages, focusing on 'C' developed by Dennis Ritchie in 1972, and explains its structure, components, and provides a sample program to calculate the area of a circle. It also covers tokens, keywords, data types, operators, and constants in 'C'.




![---continued
Strings
Sequence of characters (E.g “welcome”)
Operators
8 types of operators
Arithmetic operator-( +, -,*,/)
Relational operator-(<,>,<=,>=,==,!=)
Logical operator (AND &&,OR ||,NOT !)
Assignment operator(=)
Increment & decrement operator(++,- -)
Conditional operator(?,: )
Bit wise operator (bit wise&, bit wise |)
Special operator (sizeof)
Special symbols({ },[ ], ( ) )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-191121041358/85/C-programming-6-320.jpg)

