This document contains C code examples for various programming concepts like functions, loops, arrays, structures, pointers etc. There are a total of 40 code snippets showing how to use different features in C like printing output, taking input, if-else conditions, switch case, loops (while, for, do-while), functions (call by value, call by reference), arrays (single, multi-dimensional), structures, pointers etc. Each code snippet is commented and labeled to explain the concept demonstrated in that section.













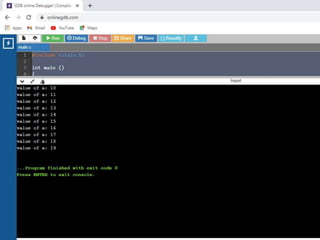

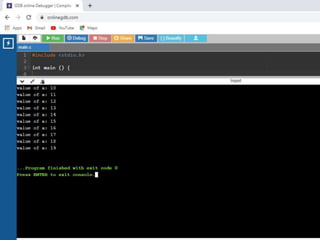







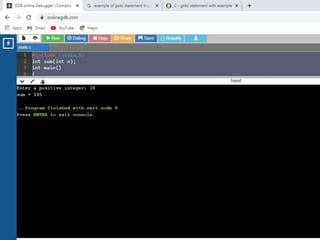



![• /* C - Arrays*/
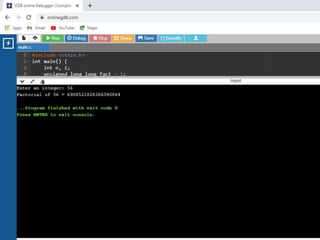
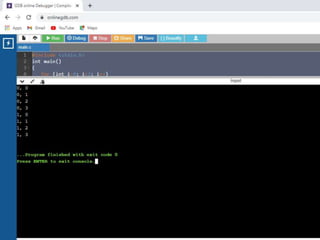
1. #include <stdio.h>
2.
3. int main () {
4.
5. int n[ 10 ]; /* n is an array of 10 integers */
6. int i,j;
7.
8. /* initialize elements of array n to 0 */
9. for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) {
10. n[ i ] = i + 100; /* set element at location i to i + 100 */
11. }
12.
13. /* output each array element's value */
14. for (j = 0; j < 10; j++ ) {
15. printf("Element[%d] = %dn", j, n[j] );
16. }
17.
18. return 0;
19. }
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-42-320.jpg)
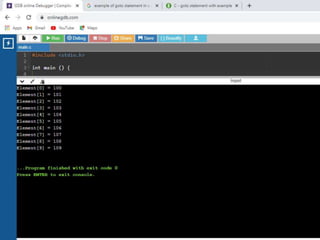
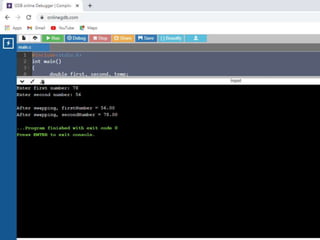
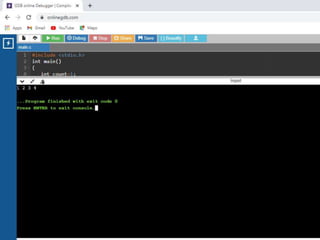
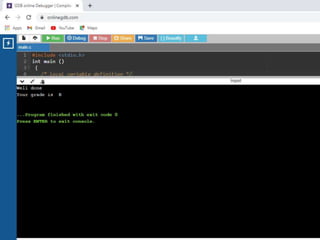
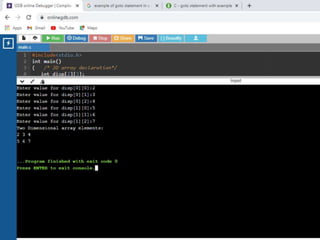
![• /* Simple Two dimensional (2D) Array Example*/
1. #include<stdio.h>
2. int main()
3. { /* 2D array declaration*/
4. int disp[2][3];
5. /*Counter variables for the loop*/
6. int i, j;
7. for(i=0; i<2; i++) {
8. for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
9. printf("Enter value for disp[%d][%d]:", i, j);
10. scanf("%d", &disp[i][j]);
11. } }
12. //Displaying array elements
13. printf("Two Dimensional array elements:n");
14. for(i=0; i<2; i++) {
15. for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
16. printf("%d ", disp[i][j]);
17. if(j==2){
18. printf("n");
19. } } }
20. return 0;
21. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-44-320.jpg)
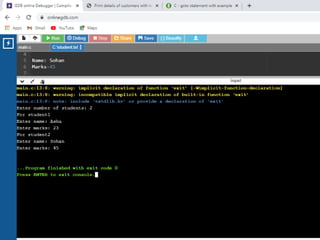
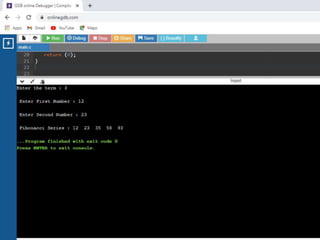
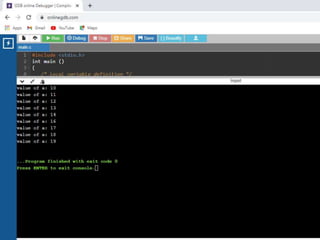
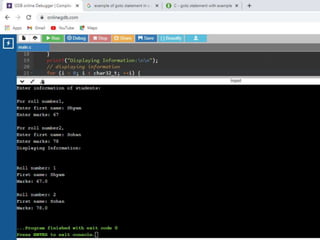
![/* Store Information in Structure and Display it*/
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. struct student {
3. char firstName[50];
4. int roll;
5. float marks; } s[10];
6. int main()
7. {
8. int i;
9. printf("Enter information of
students:n");
10. // storing information
11. for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
12. s[i].roll = i + 1;
13. printf("nFor roll
number%d,n", s[i].roll);
14. printf("Enter first name: ");
15. scanf("%s", s[i].firstName);
16. printf("Enter marks: ");
17. scanf("%f", &s[i].marks);
18. }
19. printf("Displaying
Information:nn");
20. // displaying information
21. for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
22. printf("nRoll number:
%dn", i + 1);
23. printf("First name: ");
24. puts(s[i].firstName);
25. printf("Marks: %.1f",
s[i].marks);
26. printf("n");
27. }
28. return 0;
29. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-46-320.jpg)
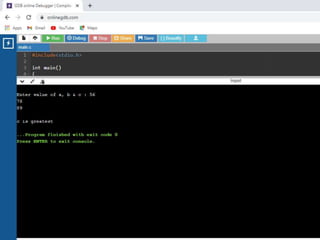
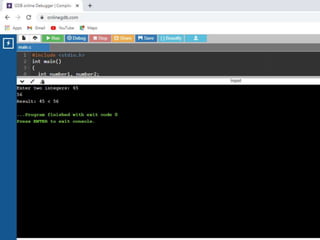
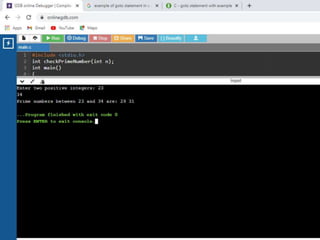
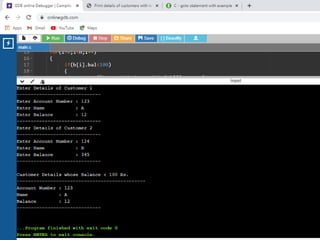
![Write a 'C' program to accept customer details such as: Account_no, Name, Balance using structure. Assume
3 customers in the bank. Write a function to print the account no. and name of each customer whose balance
< 100 Rs.
#include<stdio.h>
/* Defining Structre*/
struct bank
{
int acc_no;
char name[20];
int bal;
}b[3];
/*Function to find the details of customer whose
balance < 100.*/
void check(struct bank b[],int n)
/*Passing Array of structure to function*/
{
int i;
printf("nCustomer Details whose Balance < 100
Rs. n");
printf("----------------------------------------------n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i].bal<100)
{
printf("Account Number :
%dn",b[i].acc_no);
printf("Name : %sn",b[i].name);
printf("Balance : %dn",b[i].bal);
printf("------------------------------n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("Enter Details of Customer %dn",i+1);
printf("------------------------------n");
printf("Enter Account Number : ");
scanf("%d",&b[i].acc_no);
printf("Enter Name : ");
scanf("%s",b[i].name);
printf("Enter Balance : ");
scanf("%d",&b[i].bal);
printf("------------------------------n");
}
check(b,3); //call function check
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-48-320.jpg)
![/* C - Unions*/
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. #include <string.h>
3. union Data
4. {
5. int i;
6. float f;
7. char str[20];
8. };
9. int main( )
10. {
11. union Data data;
12. printf( "Memory size occupied by data : %dn", sizeof(data));
13. return 0;
14. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-50-320.jpg)

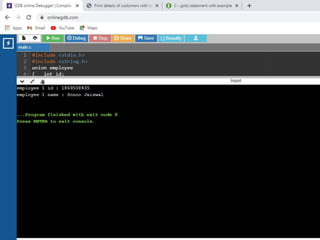
![/* example to define union for an employee in c*/
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. #include <string.h>
3. union employee
4. { int id;
5. char name[50];
6. }e1; //declaring e1 variable for union
7. int main( )
8. {
9. //store first employee information
10. e1.id=101;
11. strcpy(e1.name, "Sonoo Jaiswal");//copying string into char
array
12. //printing first employee information
13. printf( "employee 1 id : %dn", e1.id);
14. printf( "employee 1 name : %sn", e1.name);
15. return 0;
16. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-52-320.jpg)
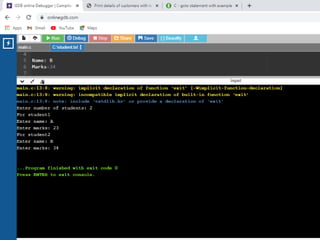
![/* C program to read name and marks of n number of students and store them in a file.*/
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. int main()
3. {
4. char name[50];
5. int marks, i, num;
6. printf("Enter number of students: ");
7. scanf("%d", &num);
8. FILE *fptr;
9. fptr = (fopen("C:student.txt", "w"));
10. if(fptr == NULL)
11. {
12. printf("Error!");
13. exit(1);
14. }
15. for(i = 0; i < num; ++i)
16. {
17. printf("For student%dnEnter name: ", i+1);
18. scanf("%s", name);
19. printf("Enter marks: ");
20. scanf("%d", &marks);
21. fprintf(fptr,"nName: %s nMarks=%d n", name, marks);
22. }
23. fclose(fptr);
24. return 0;
25. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-54-320.jpg)
![/* C program to read name and marks of n number of students from and store them in a file. If the file
previously exits, add the information to the file.*/
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. int main()
3. {
4. char name[50];
5. int marks, i, num;
6. printf("Enter number of students: ");
7. scanf("%d", &num);
8. FILE *fptr;
9. fptr = (fopen("C:student.txt", "a"));
10. if(fptr == NULL)
11. {
12. printf("Error!");
13. exit(1);
14. }
15. for(i = 0; i < num; ++i)
16. {
17. printf("For student%dnEnter name: ", i+1);
18. scanf("%s", name);
19. printf("Enter marks: ");
20. scanf("%d", &marks);
21. fprintf(fptr,"nName: %s nMarks=%d n", name, marks);
22. }
23. fclose(fptr);
24. return 0;
25. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clab-210129150456/85/C-lab-programs-56-320.jpg)