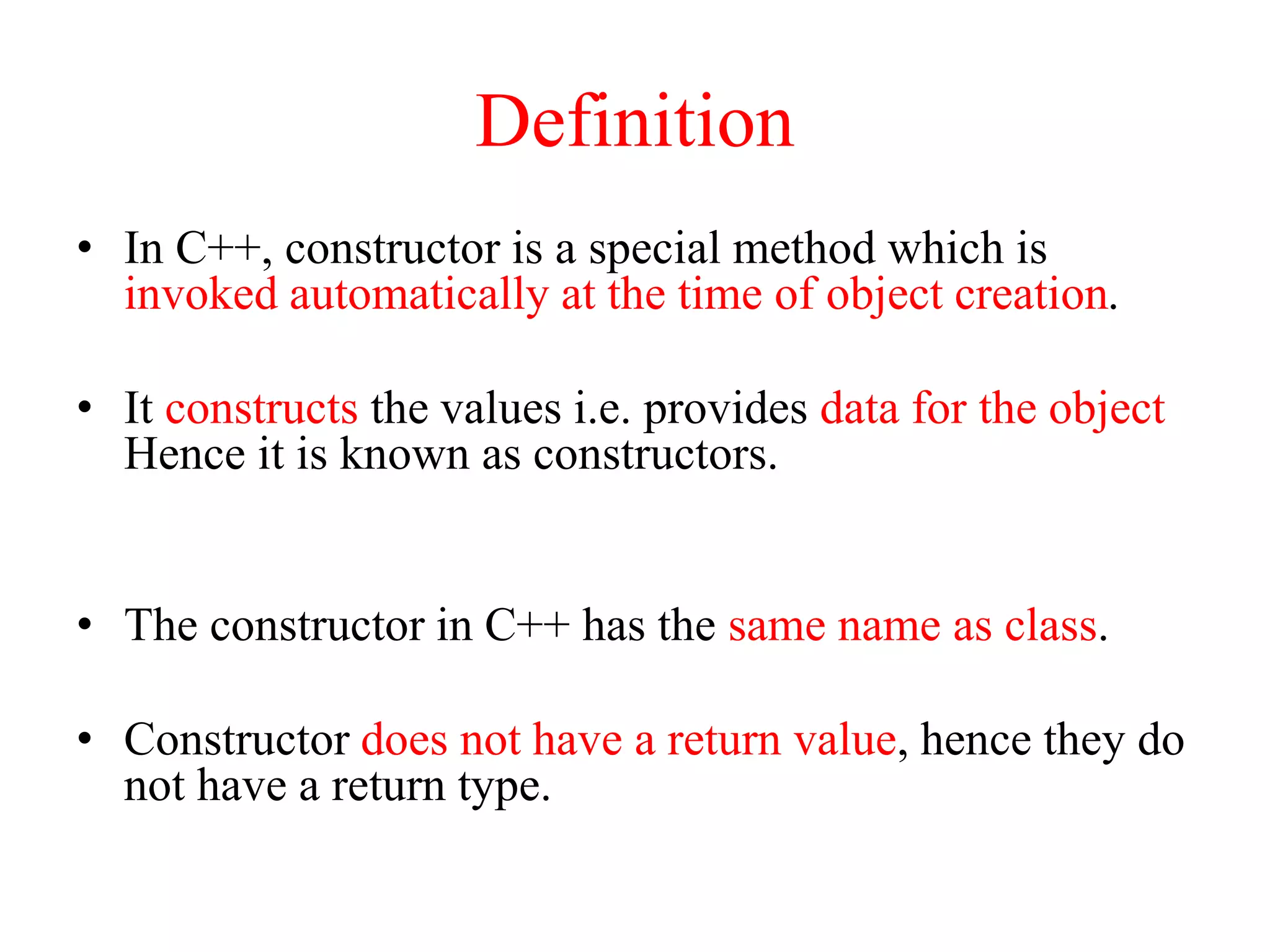
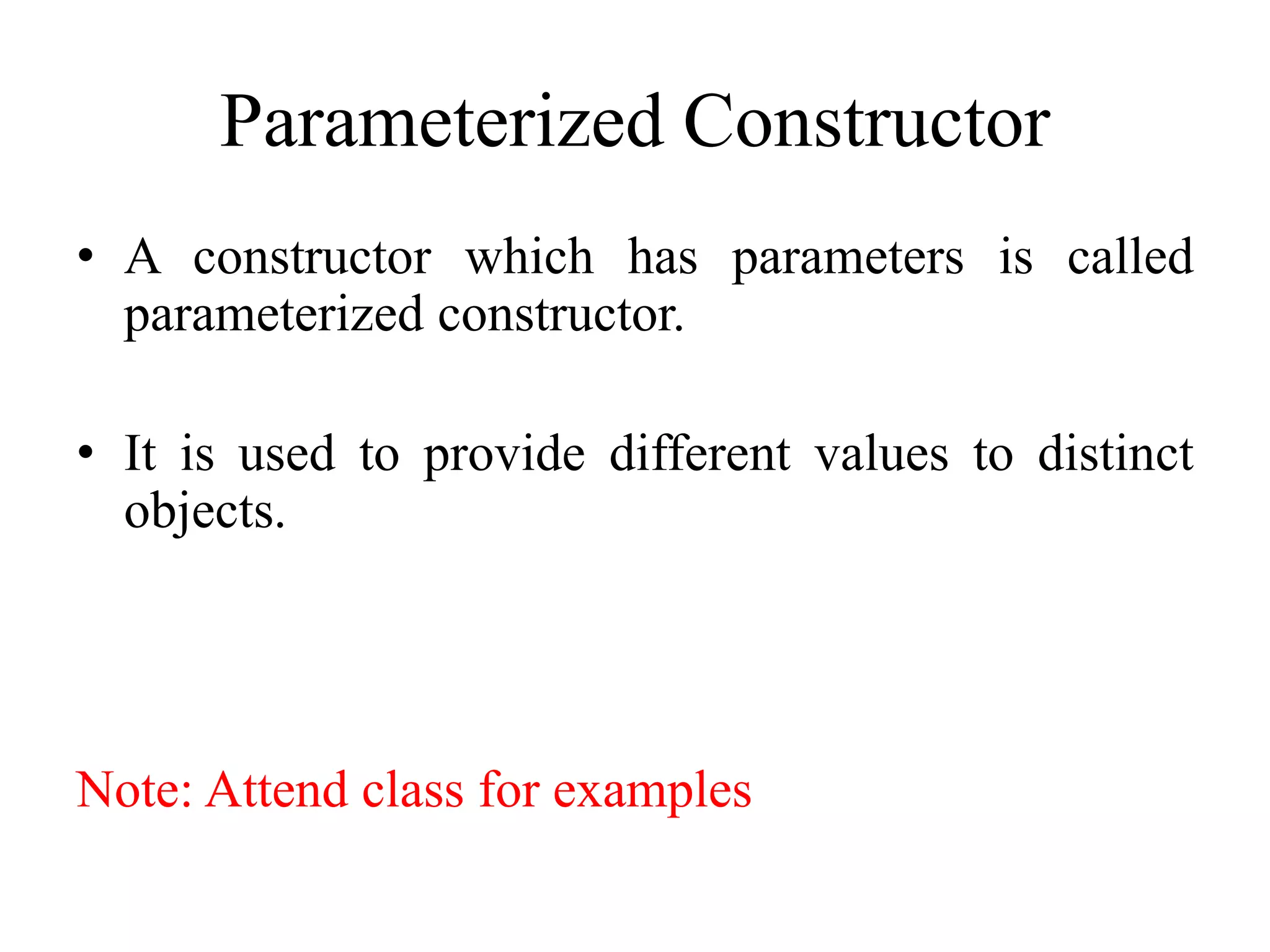
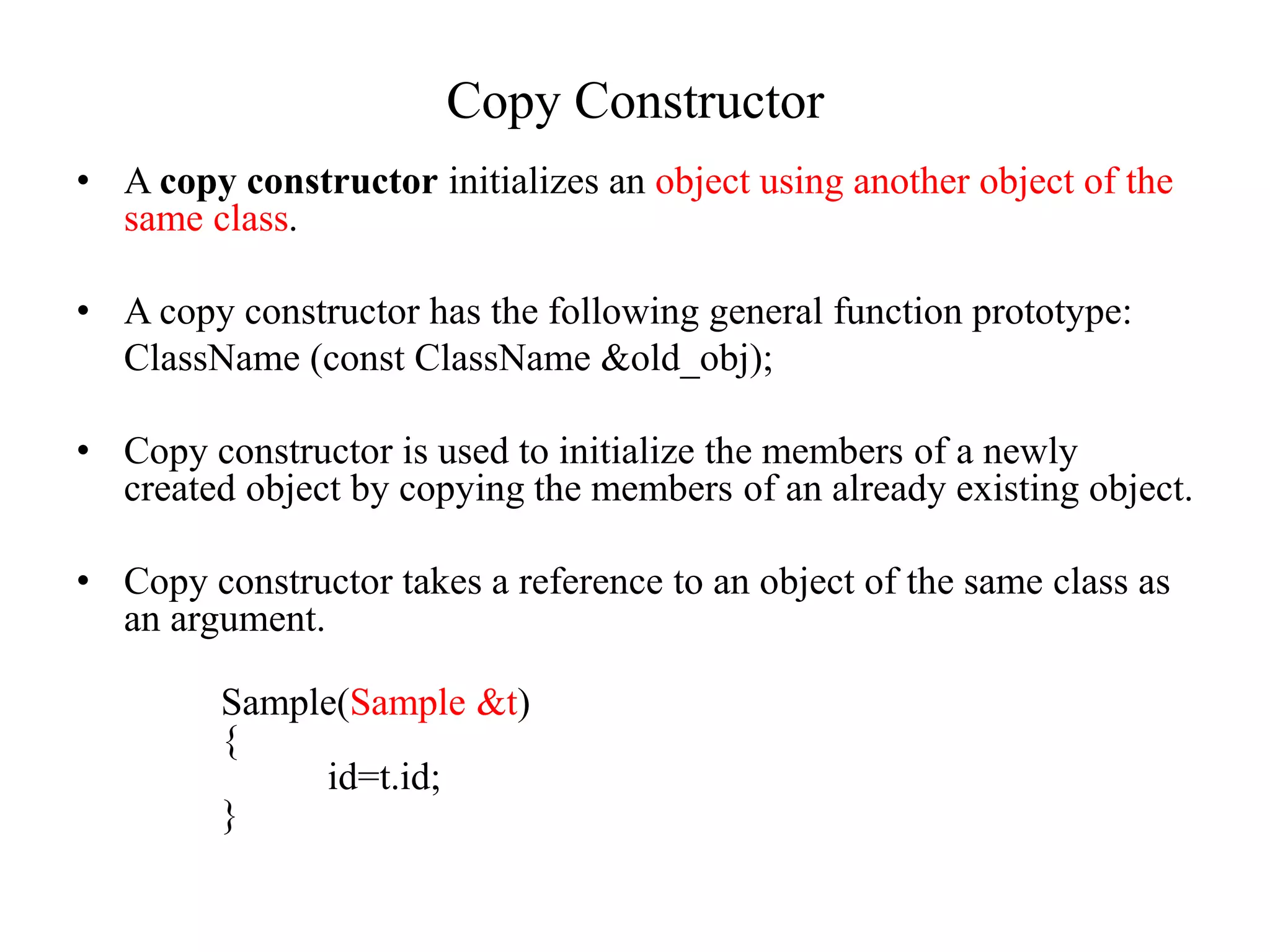
C++ constructors initialize objects and provide data when objects are created. There are three types of constructors: default constructors which have no parameters, parameterized constructors which initialize objects with different values, and copy constructors which initialize a new object using an existing object of the same class. Destructors destroy objects and free memory when objects go out of scope or are destroyed. Destructors have the same name as the class preceded by a tilde and are automatically called when objects are destroyed.