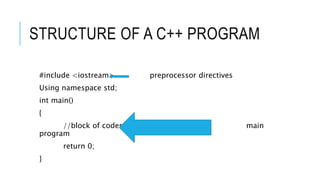
C++ is an object-oriented programming language used to create a wide range of applications. It was created in the 1980s by Bjarne Stroustrup at AT&T Bell Laboratories by adding object-oriented programming capabilities to the C language. C++ supports features like classes, inheritance, and templates which allow for modular and reusable code. A C++ program consists of preprocessor directives, namespaces, a main function which contains the main logic, and utilizes variables, data types, operators, and control structures like if/else statements and loops to control program flow.






![BASIC OPERATORS IN C++
<< - extraction
>> - insertion
+ - Addition
- - Subtraction
* - Multiplication
/ - Division
; - end of statement
// - single line commenting
/* */ - multiple line
commenting
|| - OR
&& - AND
< - Less than
<= - Less than or equal to]
> - Greater than
>= - Greater than or equal to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-170726135832/85/C-An-Introduction-8-320.jpg)



