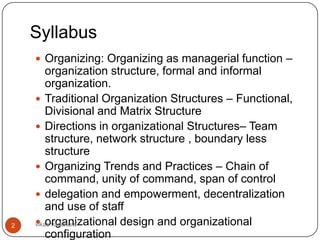
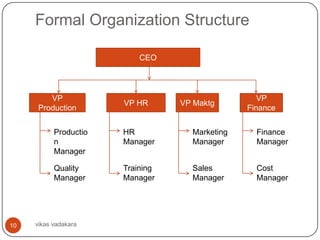
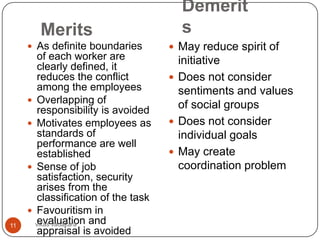
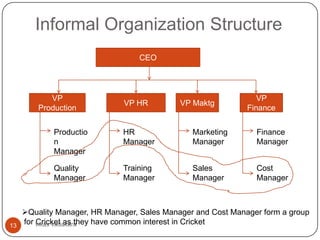
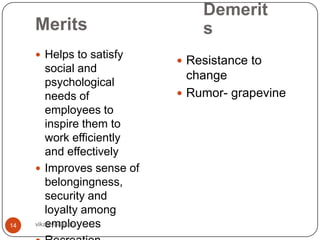
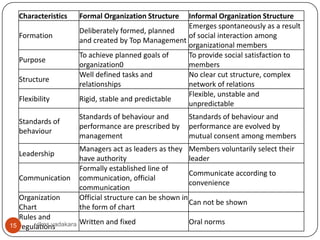
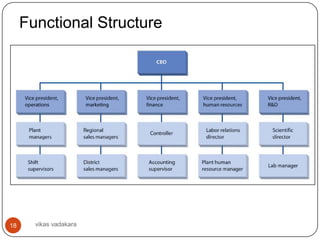
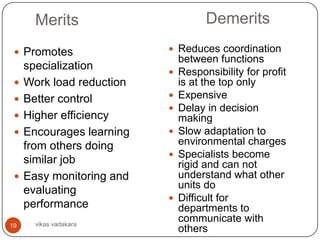
This document discusses organizing as a managerial function and different organization structures. It covers traditional structures like functional, divisional, and matrix structures. It also discusses trends like team structures, network structures, and boundaryless structures. Key aspects of organizing covered include departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, and delegation. Traditional and informal organization structures are defined and compared.


![Organizing involves:
The identification and classification of required
activities
The Grouping of activities necessary to attain
objectives
The assignment of each group to a manager with
the authority necessary to supervise it
The provision for coordination horizontally [on the
same or a similar organizational level] and
vertically [ between various departments which
are not on a similar organizational level] in the
organization structure
4 vikas vadakara](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-4-320.jpg)








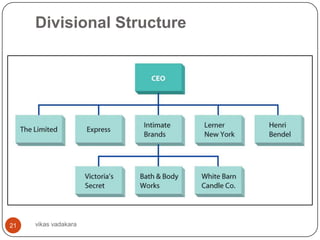
![Divisional Structure
Also known as M Form- M means Multidivisional
It’s a structure made up of separate, semi autonomous
units or multiple divisions in related industry
Ex: 1] HP: computers, scanners, printers, electronic
medical equipments. Ex 2] Walt Disney: Theme parks,
Movies
A structure composed of separate business units within
which are the functions that work together to produce a
specific product for a specific customer
Create smaller, manageable teams
Develop a business unit level strategy to compete
Divisions have marketing, finance, HR and other functions
Functional managers report to divisional managers who
report to corporate heads
20 vikas vadakara](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-20-320.jpg)
![Conglomerate Structure or H
Form
H stands for HOLDING
It’s a structure made up of multiple divisions in unrelated
businesses/industry
Ex: Samsung Electrics Co uses H Form or conglomerate
structure. – Semiconductors, Telecommunications,
Appliances, Media
Ex: General Electric- aircraft engines, appliances,
broadcasting, financial services, lighting products,
plastics, etc]
It is essentially a holding company that results from
unrelated diversification
This design which results from a strategy of unrelated
diversification, is a complex to manage
Managers find that comparing & integrating activities
among the dissimilar operations are difficlut
23 vikas vadakara](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-23-320.jpg)
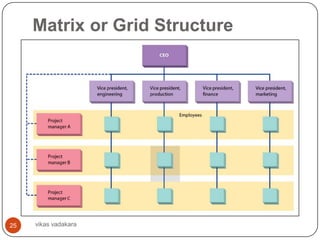
![Matrix or Grid Structure
Combines two organization structures; functional
and project structures [based on projects
organizational activities are grouped]
Functional departments create vertical chain of
command
Project or product types form horizontal chain
This type used to efficiently execute multiple
project operations of enterprise
Project managers coordinate teams of employees
drawn from different functional departments
Matrix organization relies on multiple command
structure
24 Ex: General Motors, Prudential, American
vikas vadakara
Cyanamid, NCR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-24-320.jpg)


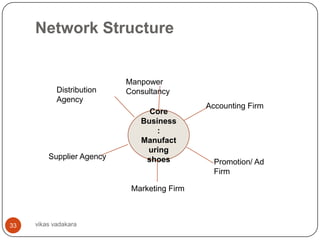
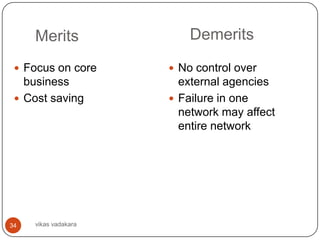
![Network Structure
Company keeps core business and through
contacts with external agencies runs business
[outsourcing]
Also known as modular organization-
especially in manufacturing firms
Companies like NIKE & REEBOK, concentrate
on their core strengths in product development
and marketing and contracted all their
footwear manufacturing to outside suppliers
Sweden's Ericsson contracts its manufacturing
and even some of its R&D to more cost
effective contractors in New Delhi, Singapore,
California and other global locations
32 vikas vadakara](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-32-320.jpg)









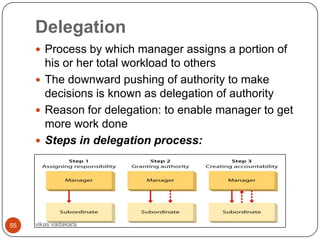
![Gangplank principle
In certain special situations the scalar chain/ chain of
command should be avoided [ Fayol]
To facilitate speed and efficiency in administrative matters,
communication through the formal chain can be avoided
and lateral communication permitted
A If D has to communicate
B E with G, the message has
to travel through formal
C F chain CBAEFG. This
involves delay and hence,
D
G D may be permitted to
communicate directly to G
[which forms lateral
communication] on
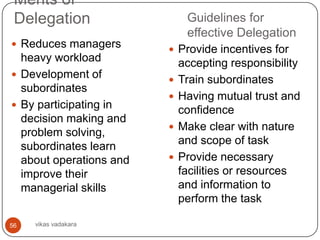
important matters.
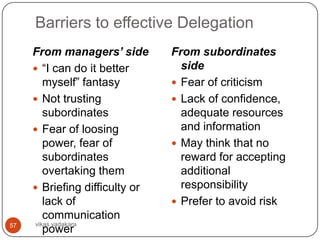
47 vikas vadakara](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-47-320.jpg)


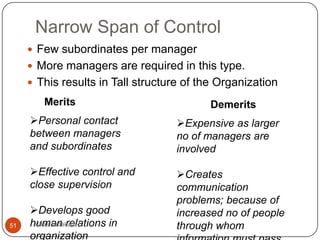
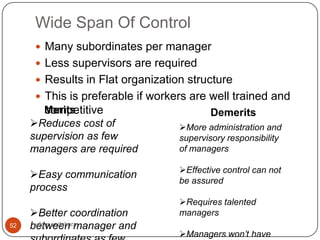
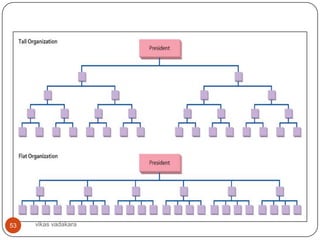
![Span of Control contd..
No of possible interactions of all types between
manager and subordinates can be determined as
follow: ( 2 N / 2 N 1)
I N
I= total no of possible interactions
N= no of subordinates
Ex: if N [ no of subordinates] = 2, the no of
possible interactions are 6.
If N= 5, I or no of possible interactions are 100.
Manager has to determine optimal span of
control. This is nothing but deciding whether it
50 vikas vadakara be narrow or wide span of management/
should
control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-50-320.jpg)





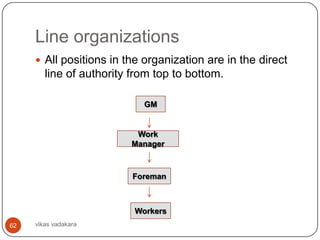
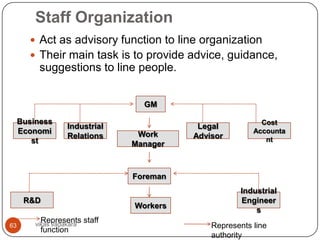



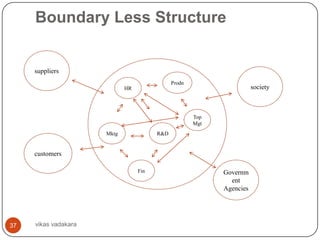
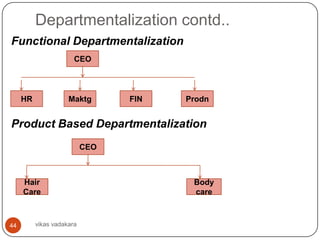
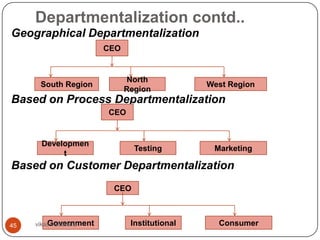
![Organization Configuration
This is nothing but creating departments in the
organization based on some logic arrangement;
based on functions, products, processes,
geography and customers.
[refer slide 43, departmentalization, 2nd element of
organization structure]
67 vikas vadakara](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessorganizing-120904084347-phpapp01/85/Business-organizing-67-320.jpg)
