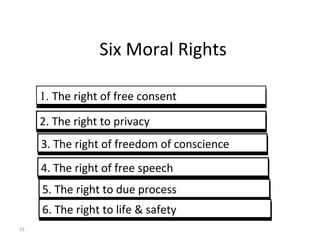
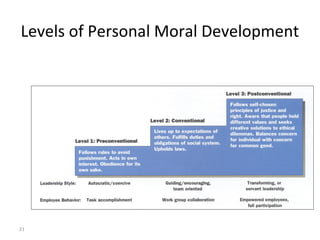
This document provides an overview of business ethics. It discusses the definition of ethics as the study of right and wrong in the workplace. Common forms of unethical behavior in businesses are described, such as misrepresenting work hours or lying. Pressure, fear, greed, and convenience are cited as common causes of unethical actions. The document recommends that organizations develop ethics codes, communicate them clearly, and lead by example. Managing ethics benefits businesses by improving culture, reputation, and risk management. Ethical dilemmas are complex situations without clear answers, and decision-making approaches like utilitarianism, individualism, and moral rights are examined.