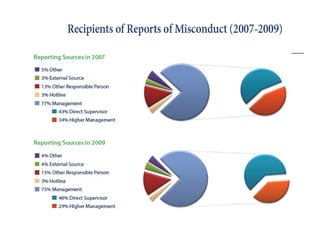
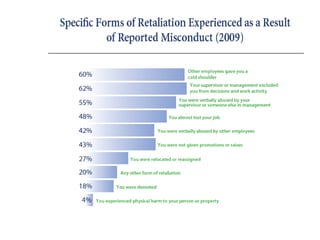
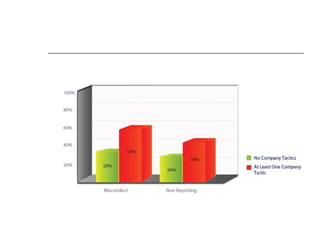
This document discusses the history and development of business ethics from ancient Greece to modern times. It defines business ethics as the study of applying moral standards to business decisions and behaviors. The document outlines increasing ethical issues businesses have faced such as scandals, fraud, environmental concerns, and privacy issues. It also discusses the development of ethics programs, codes of conduct, and laws to improve ethical standards and accountability in business over the decades.