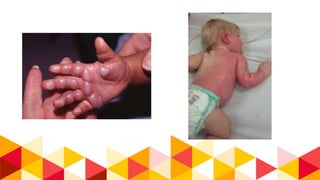
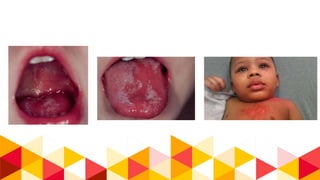
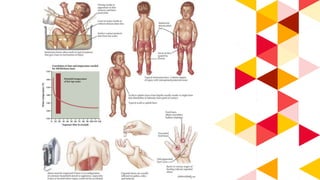
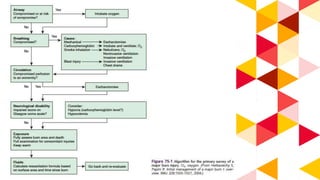
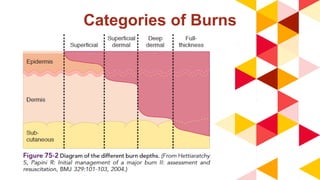
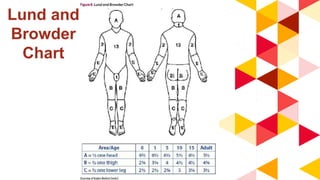
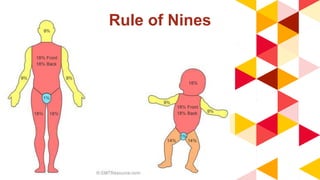
This document provides information about burn injuries, including prevention, first aid, and emergency care. It discusses common causes of burns like cooking and smoking, and recommends precautions like never leaving cooking unattended. For first aid of burns, it advises stopping the burning by smothering flames, removing clothing, and applying cold compresses. Significant burns require emergency care and fluid resuscitation based on the Parkland formula to replace lost fluids. The document also covers burn classifications and charts for determining percentage of total body surface area burned.