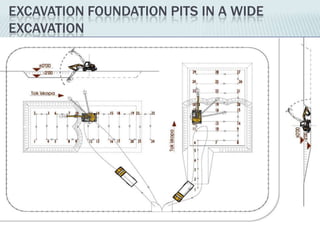
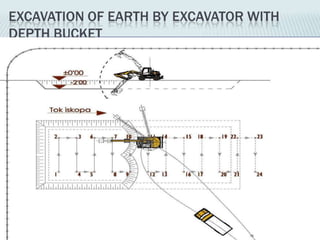
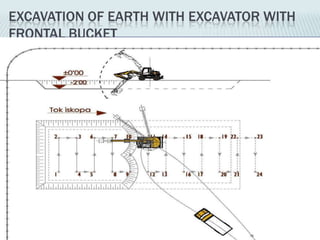
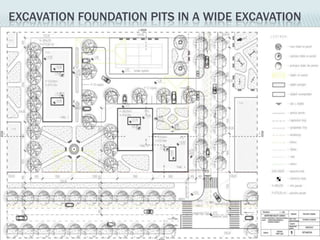
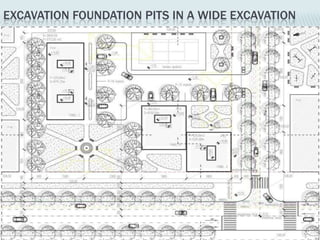
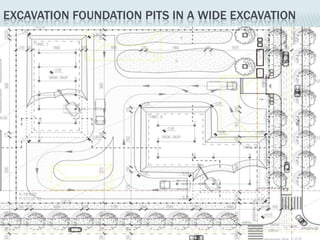
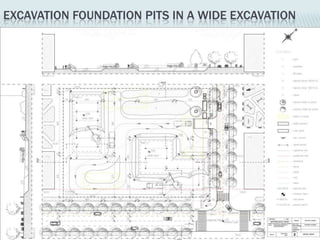
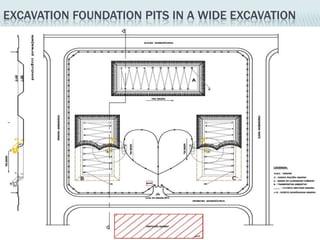
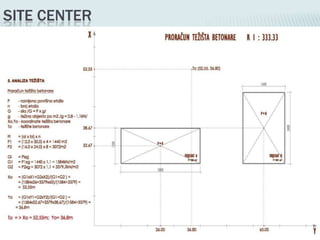
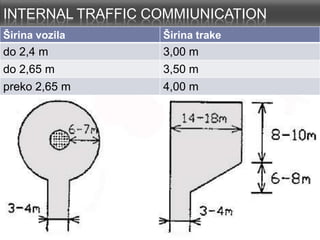
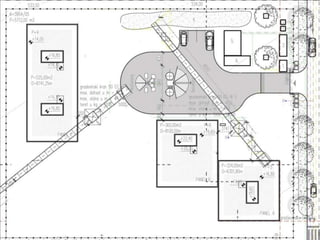
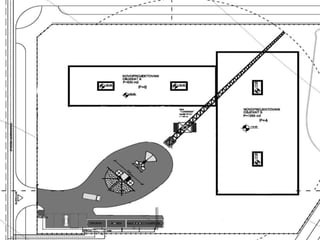
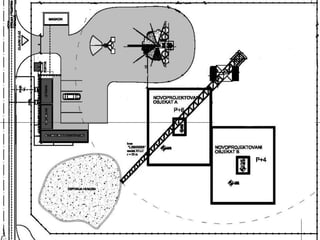
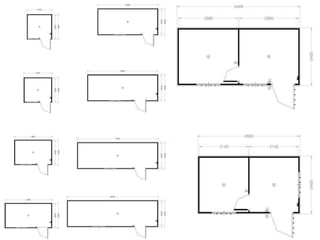
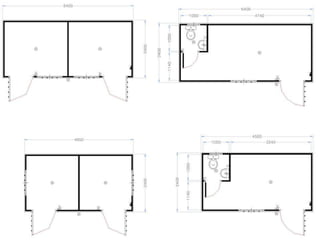
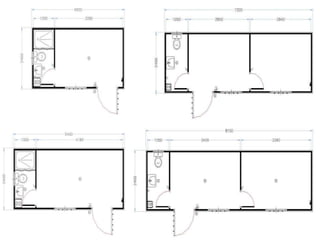
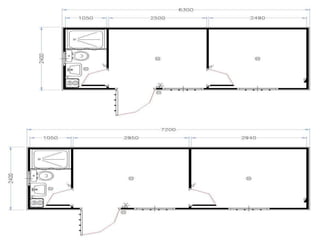
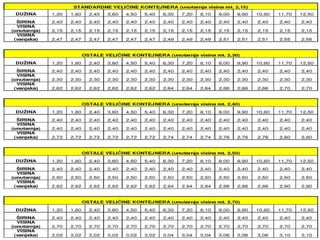
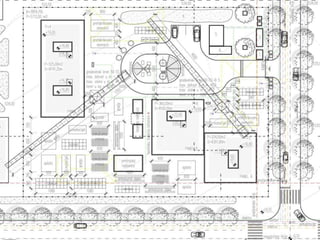
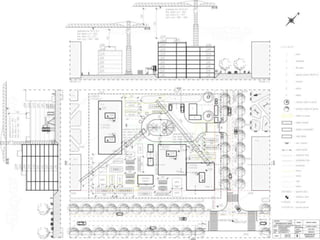
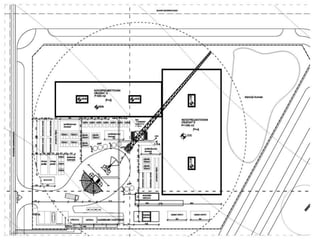
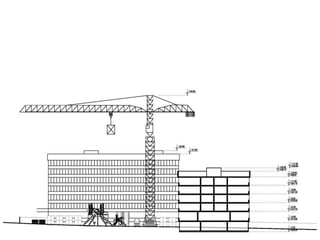
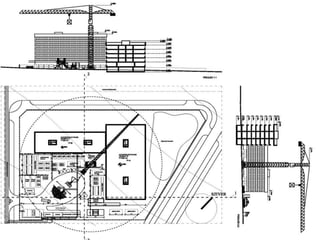
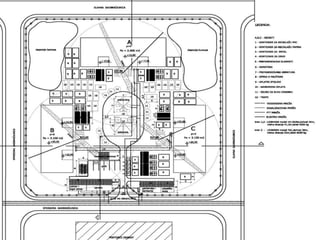
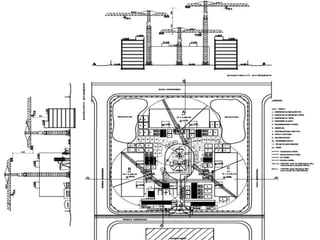
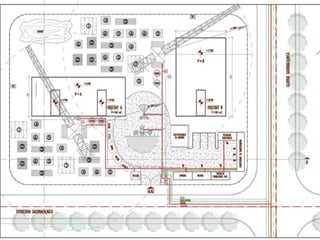
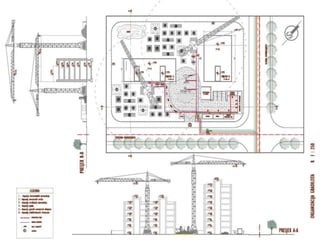
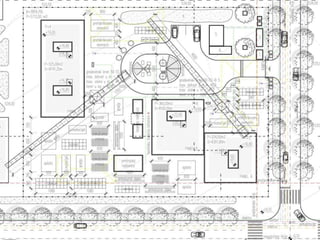
This document provides an overview of construction site organization for a building project. It discusses preparing for the site by collecting technical, geographic, climatic and other relevant data. It describes the initial site work of establishing fences, access roads and excavating foundation pits. The document outlines considerations for on-site logistics like traffic flow, materials storage, temporary buildings and transport of workers, equipment and materials. Proper planning of construction site organization is emphasized as important for efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the building process.