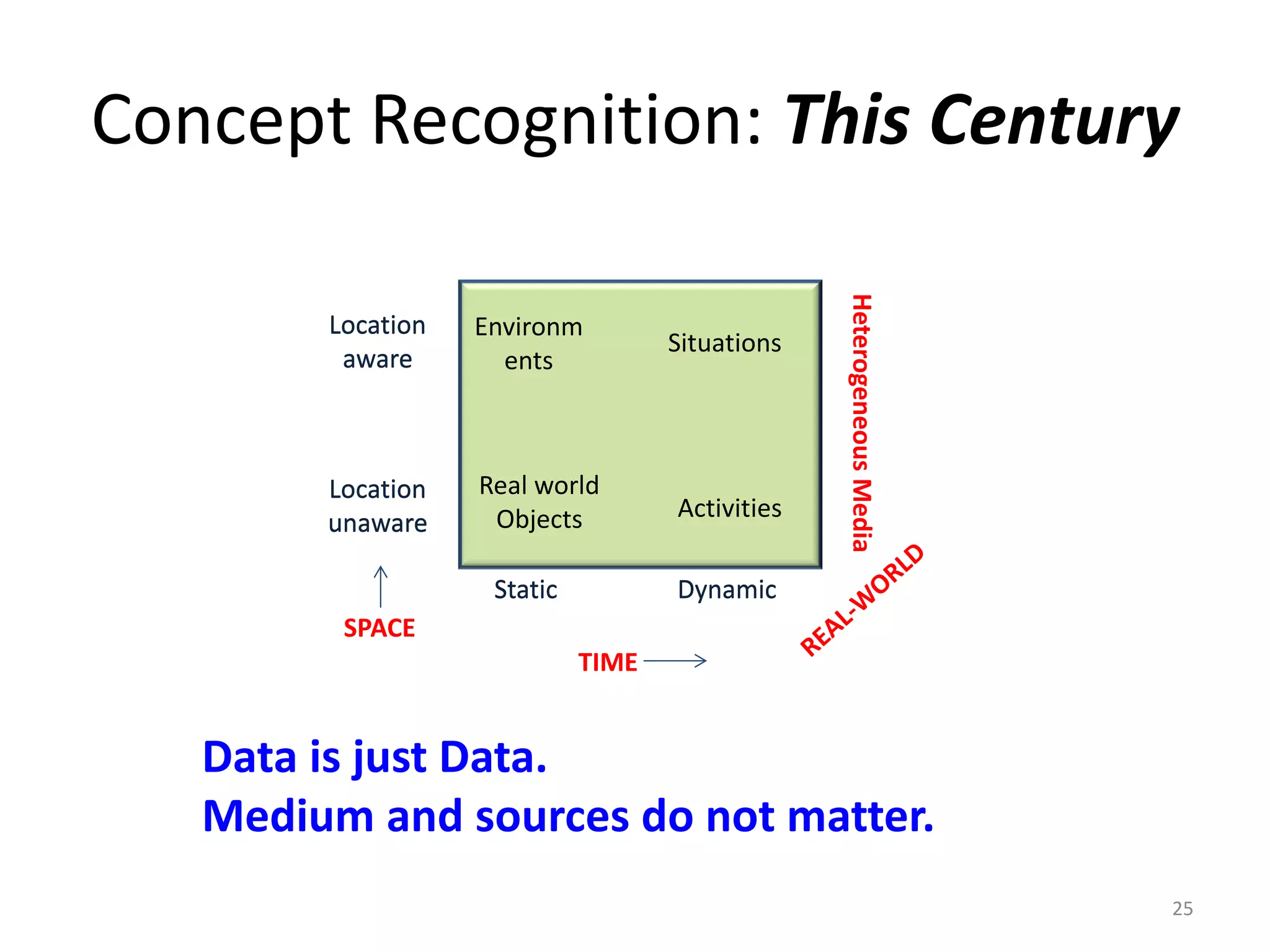
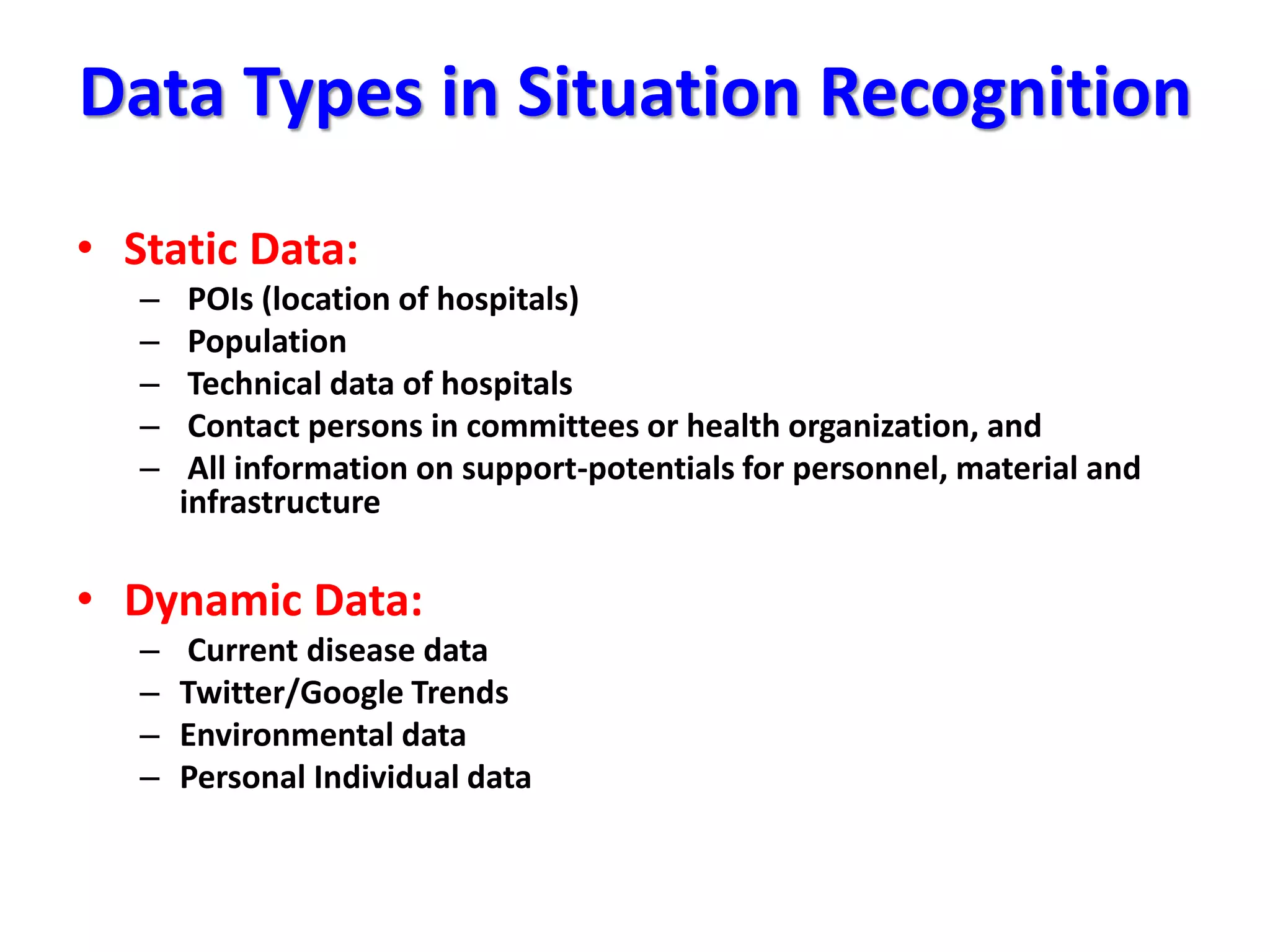
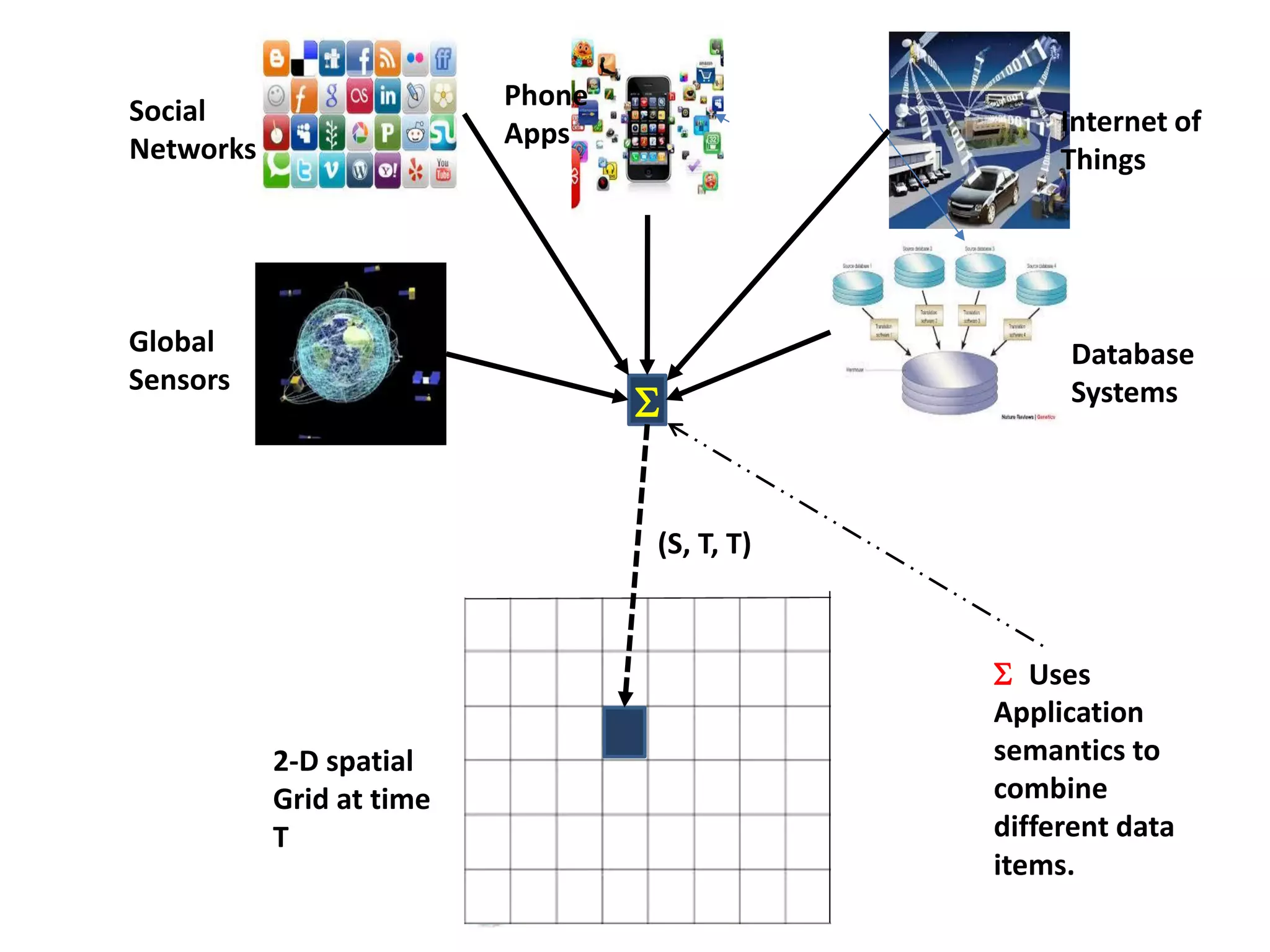
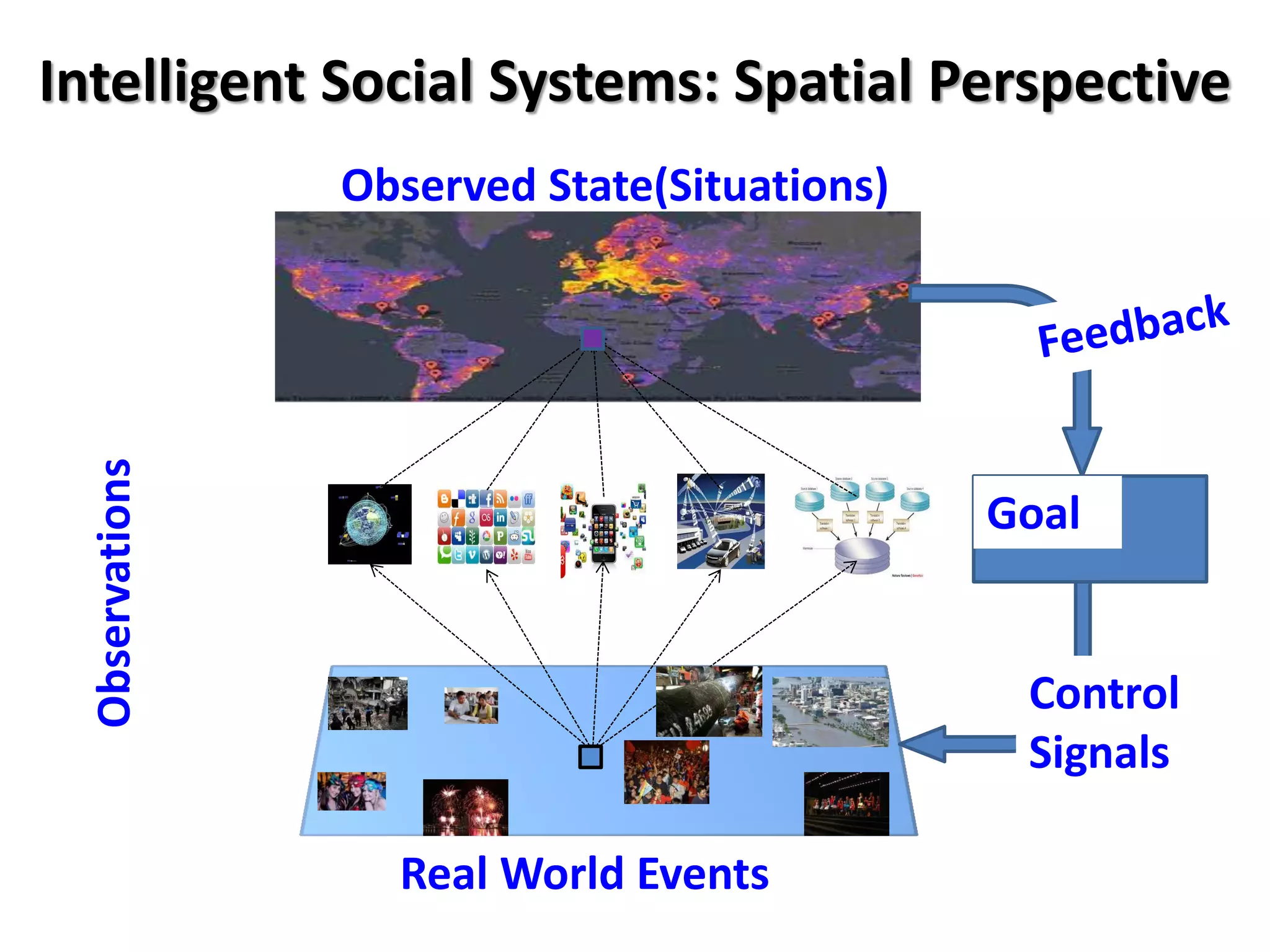
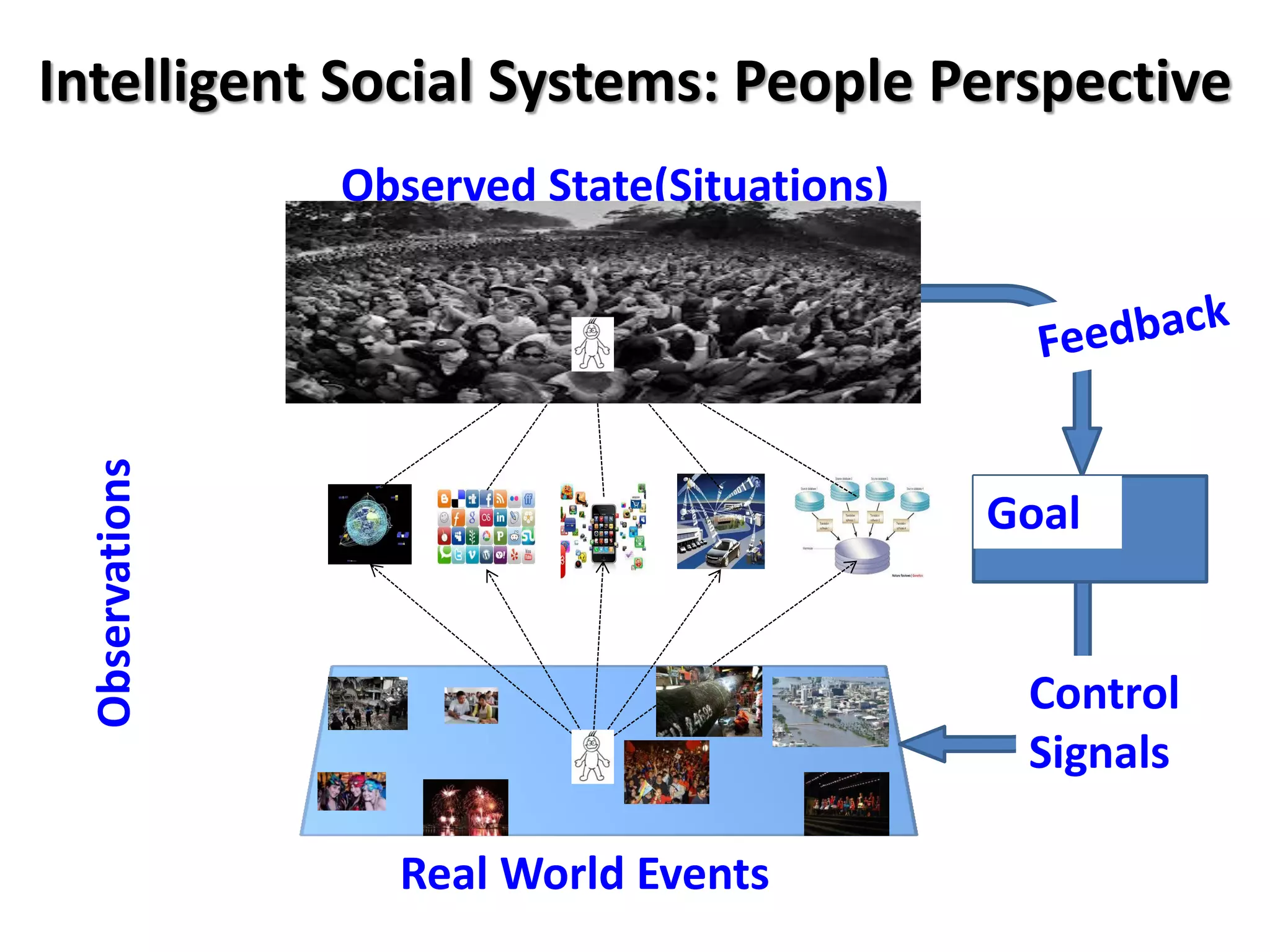
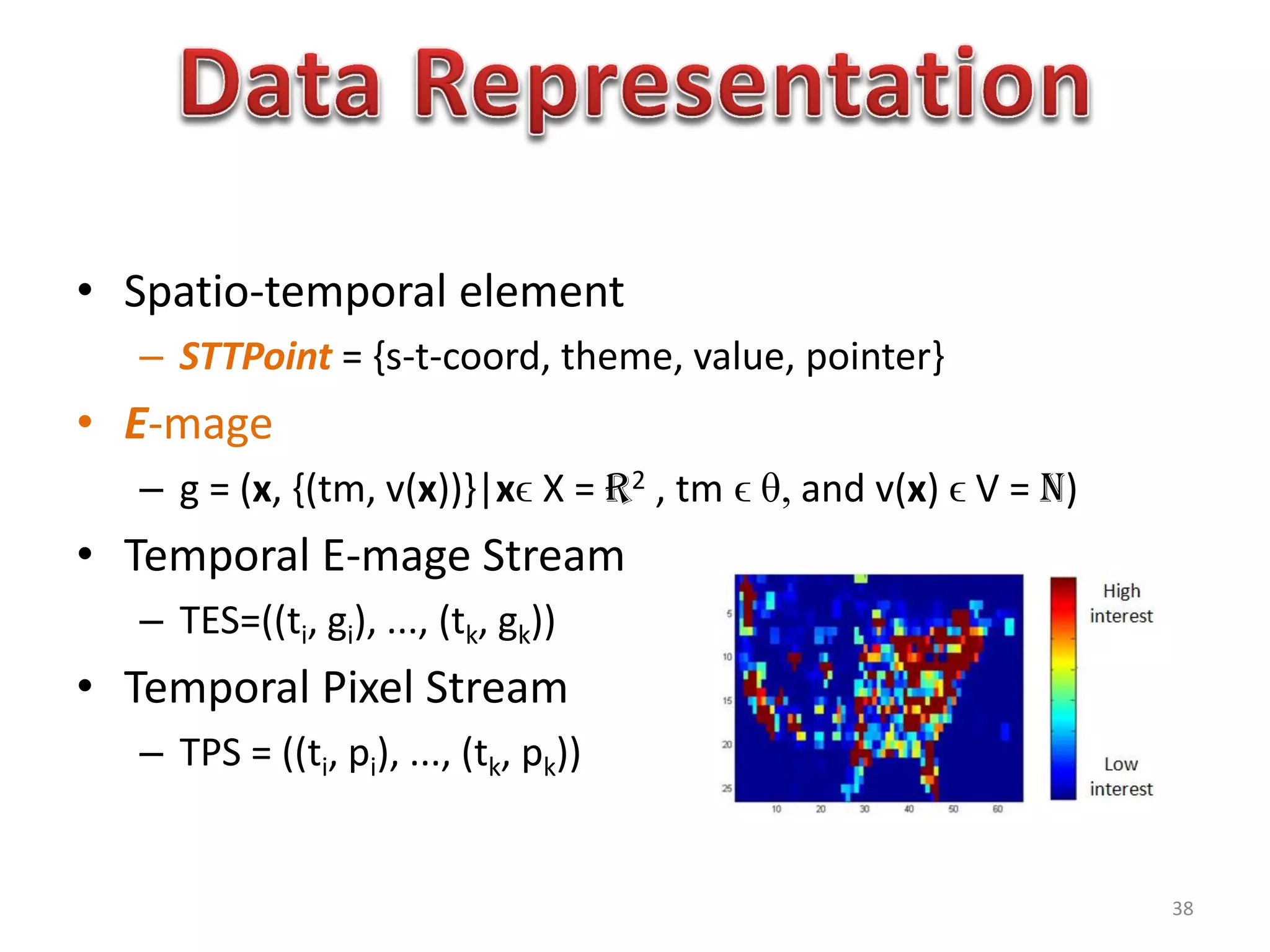
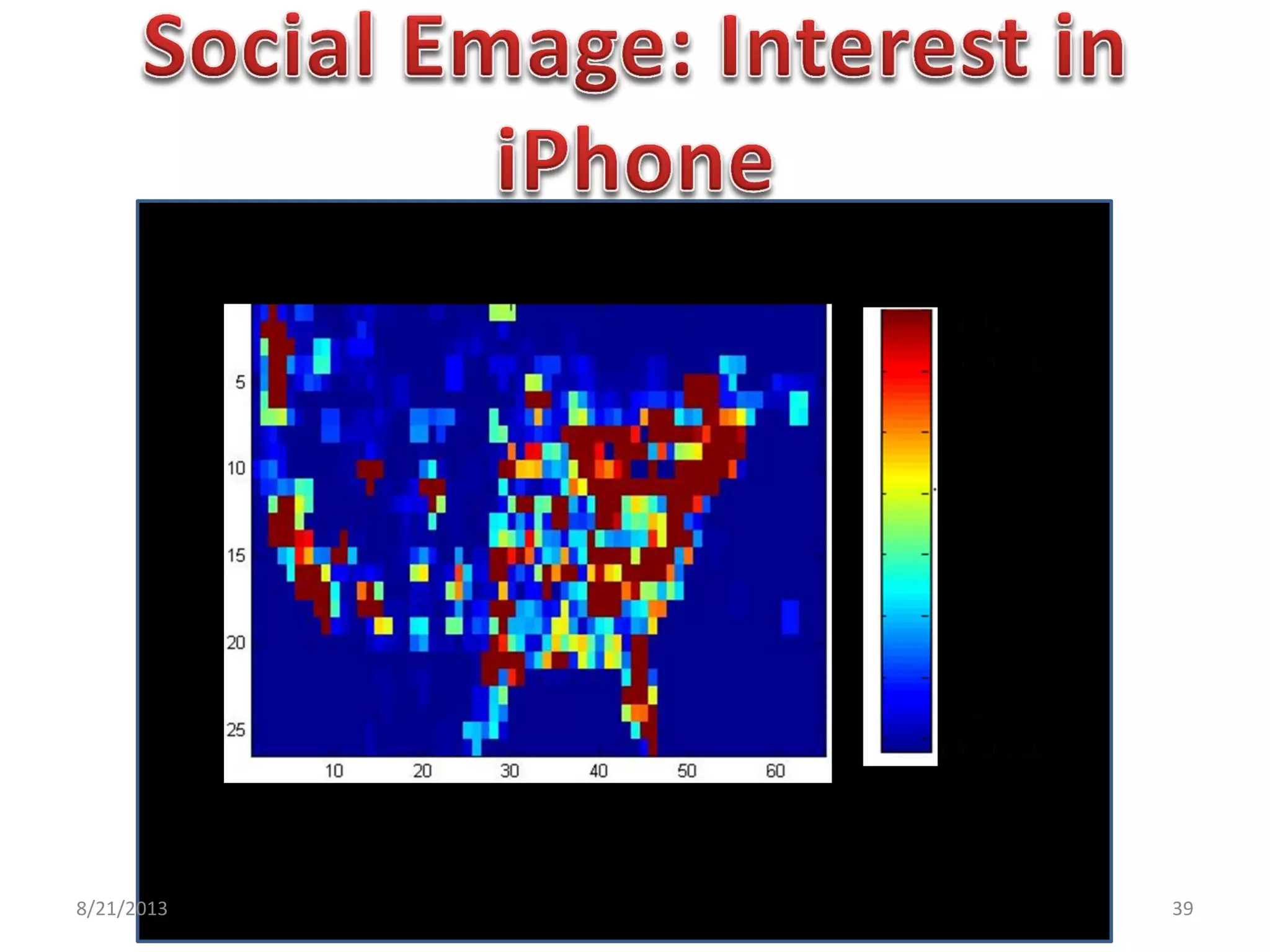
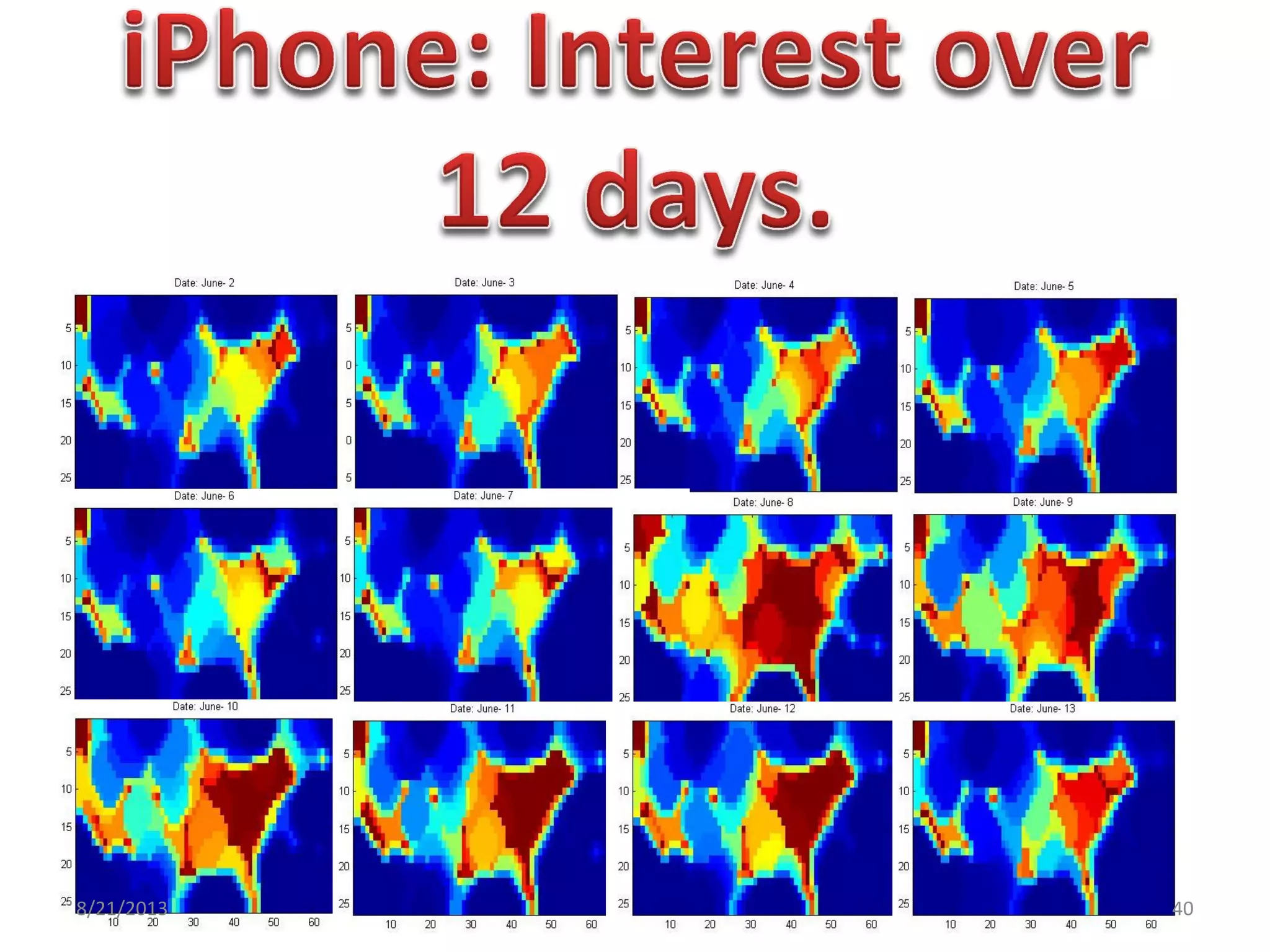
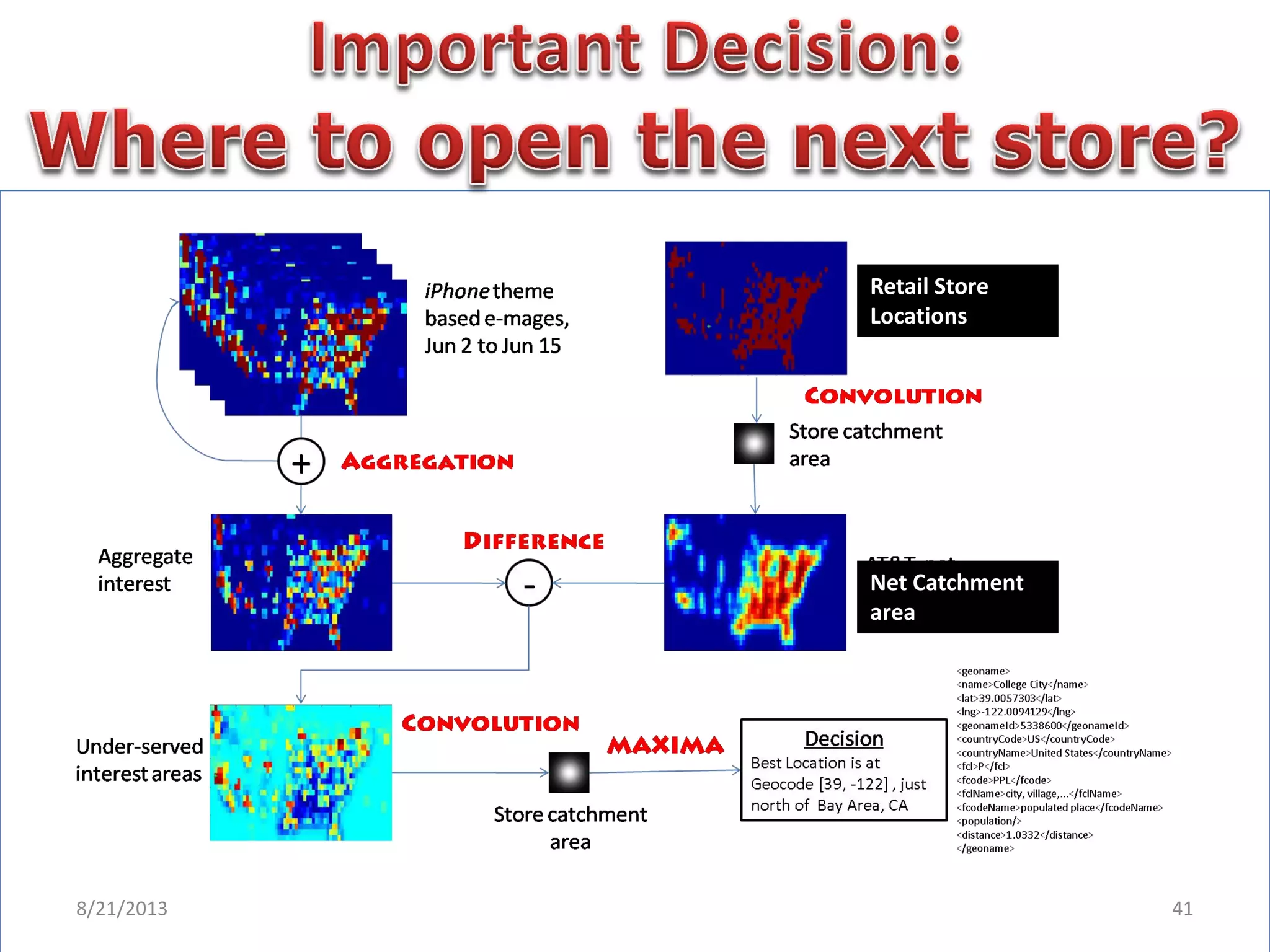
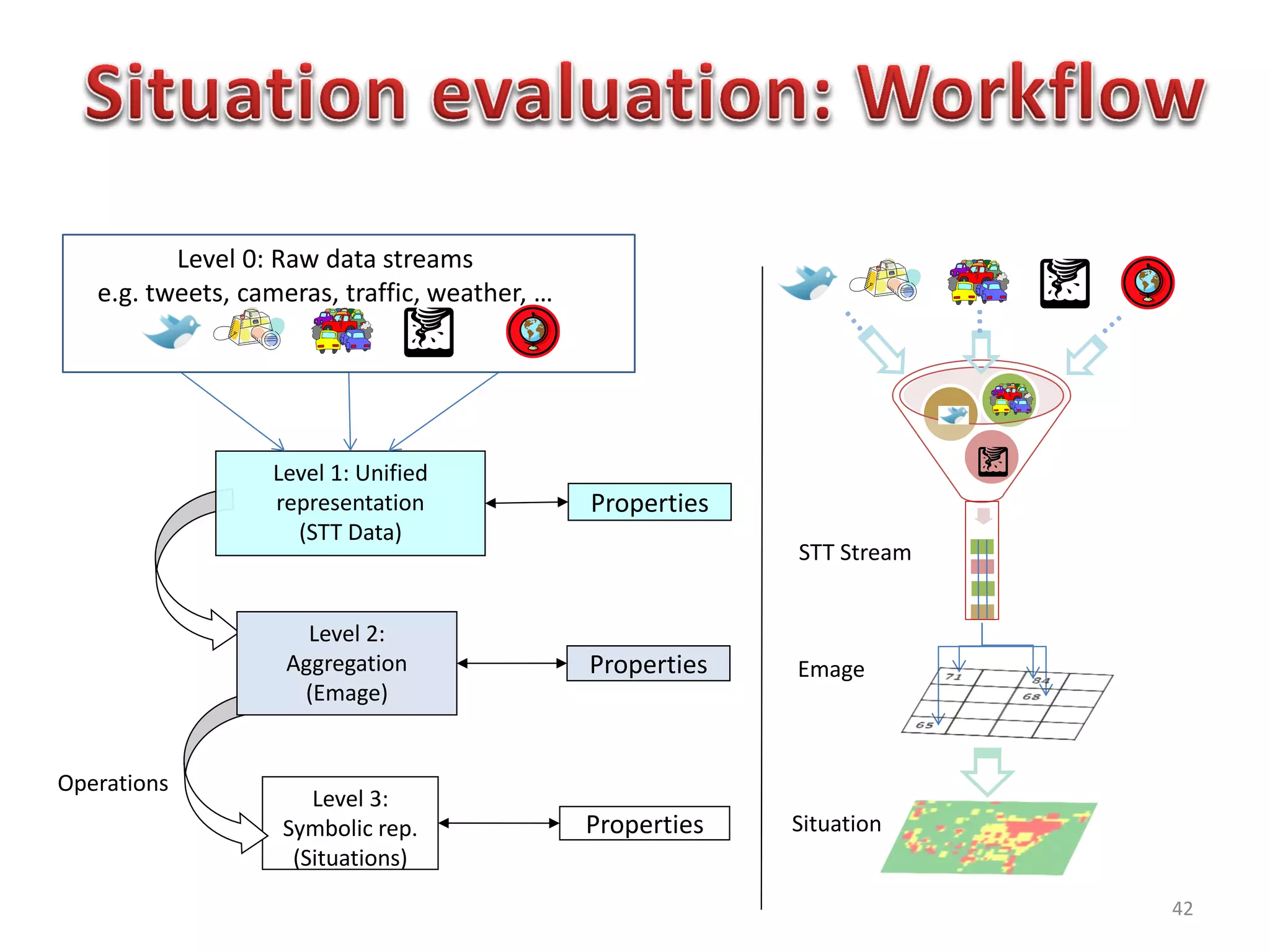
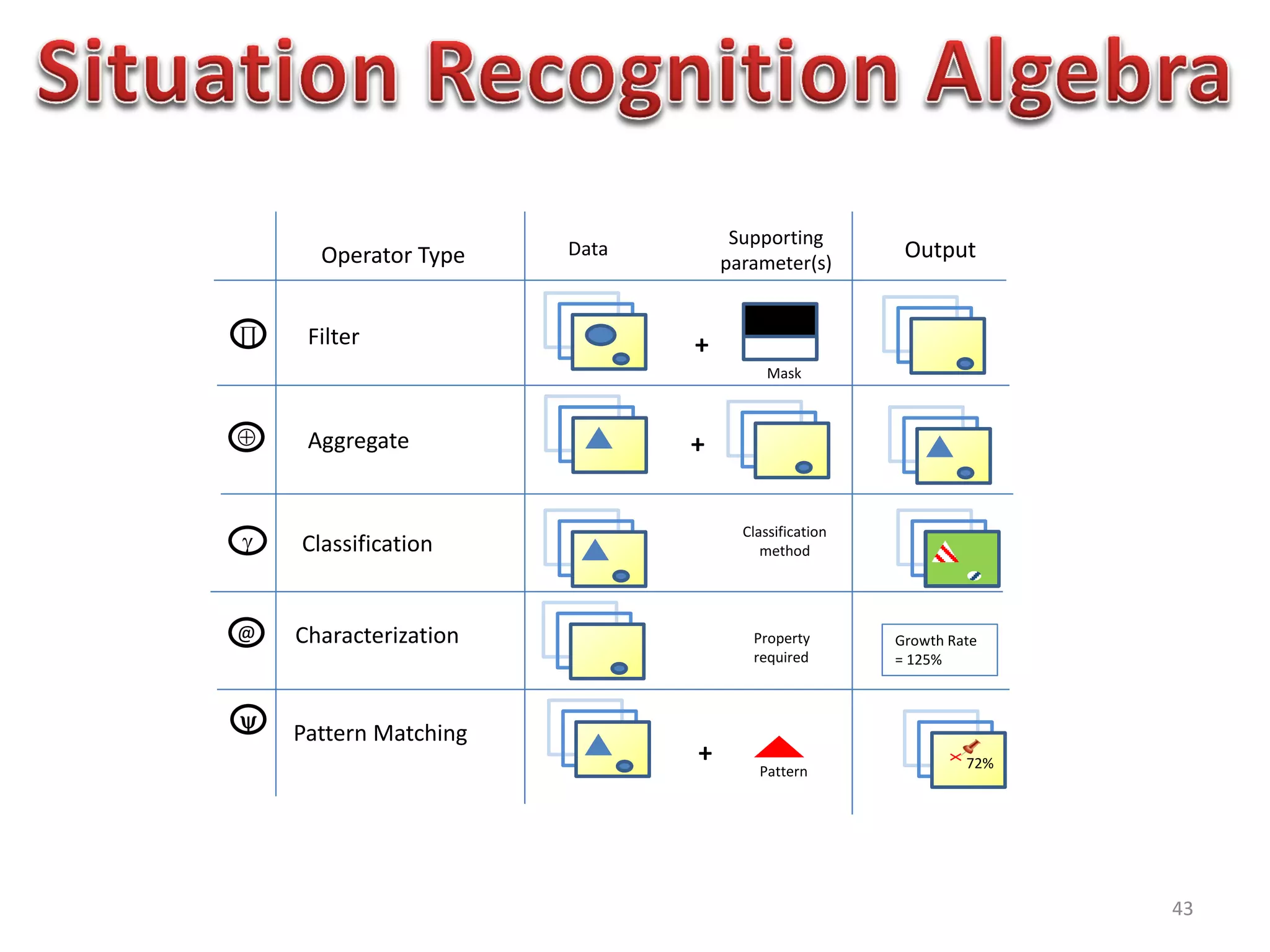
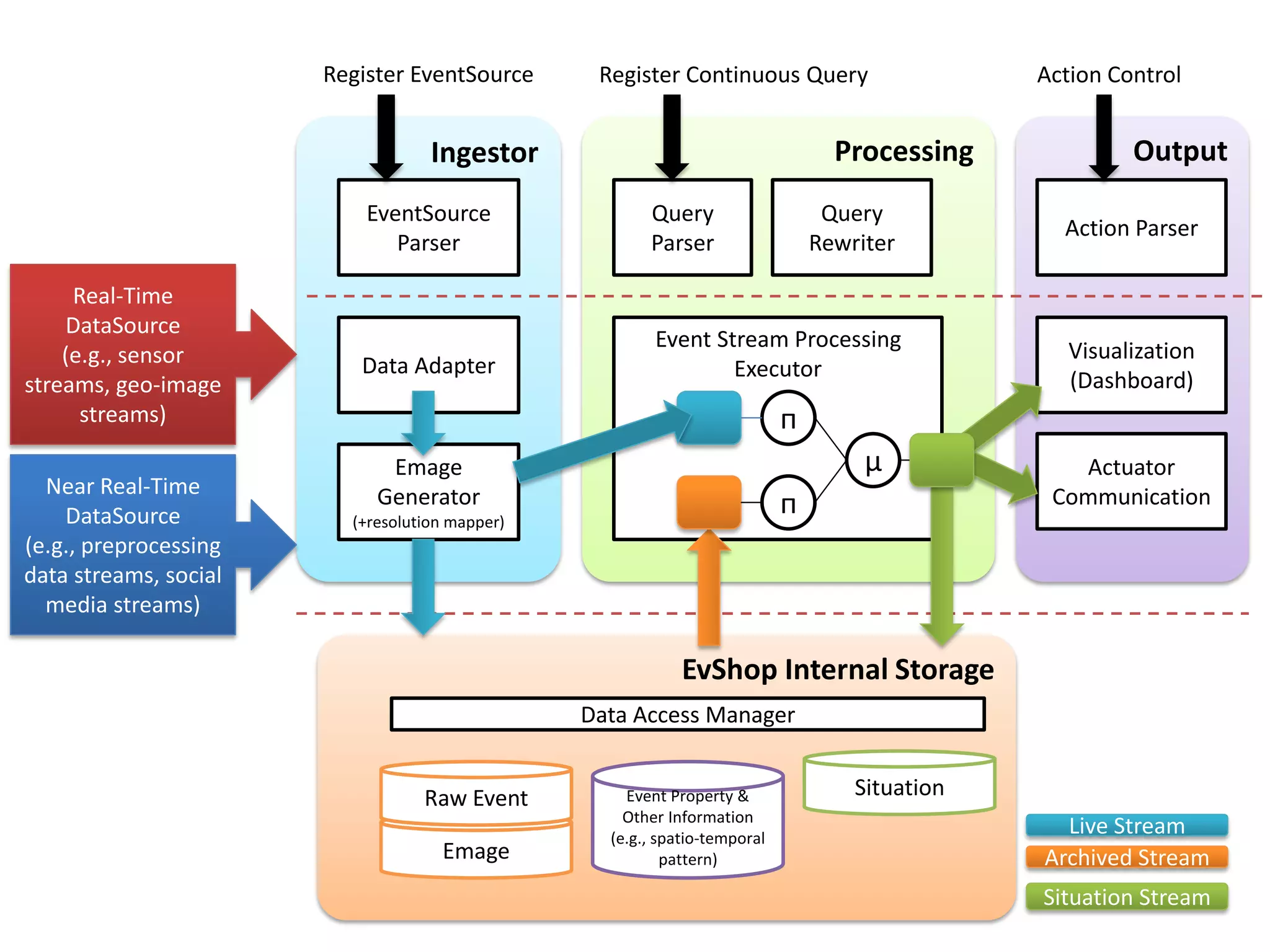
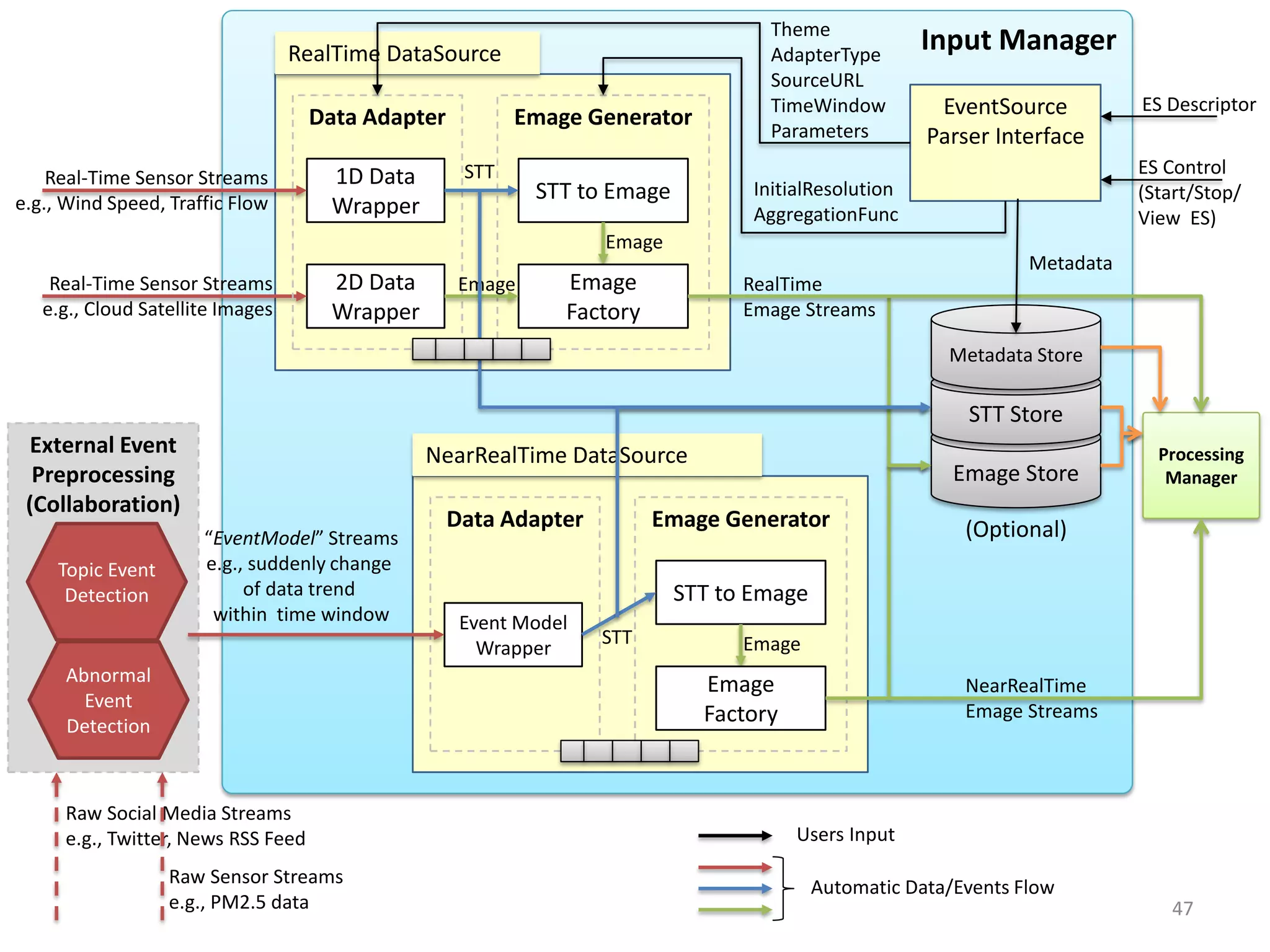
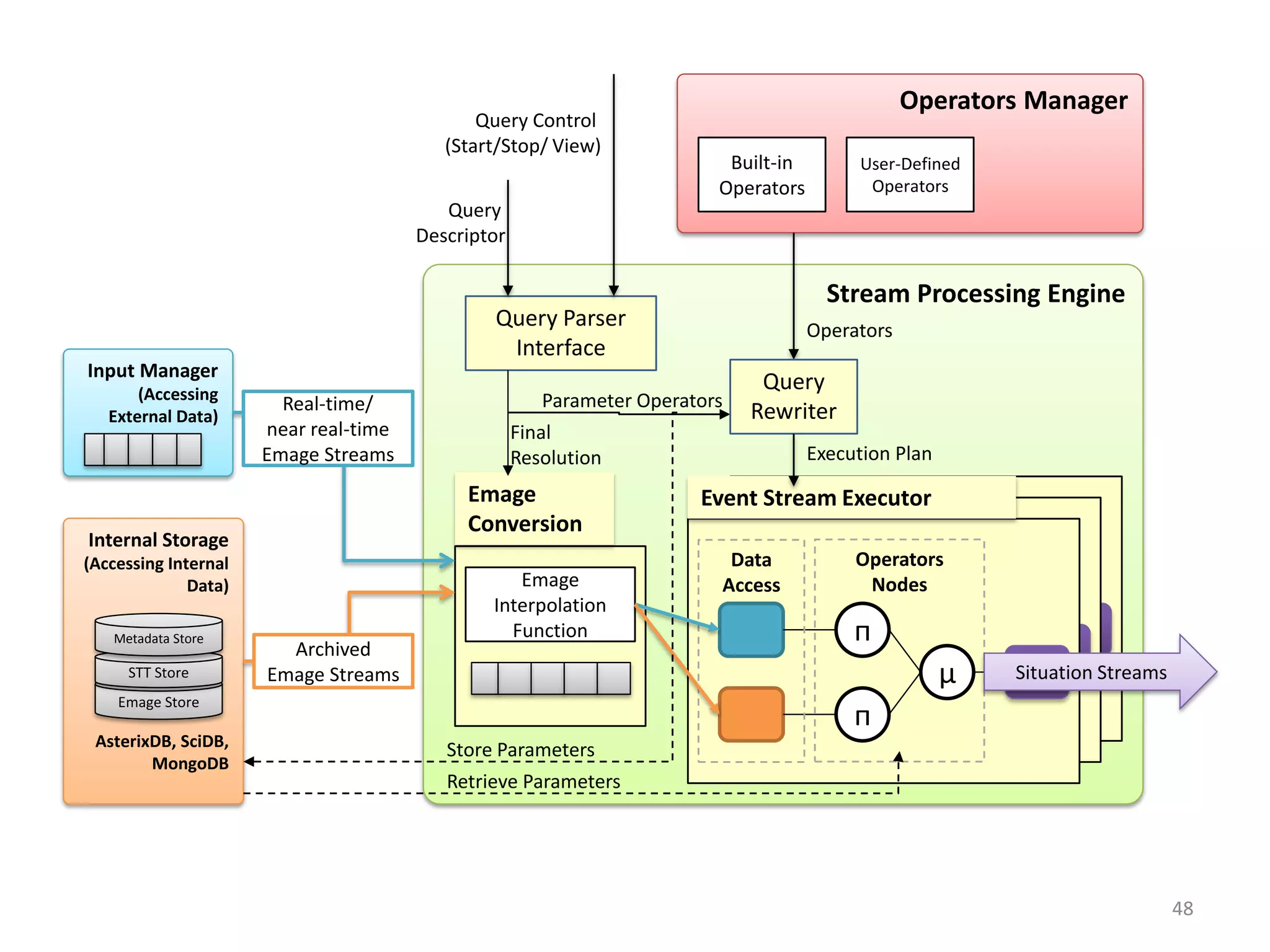
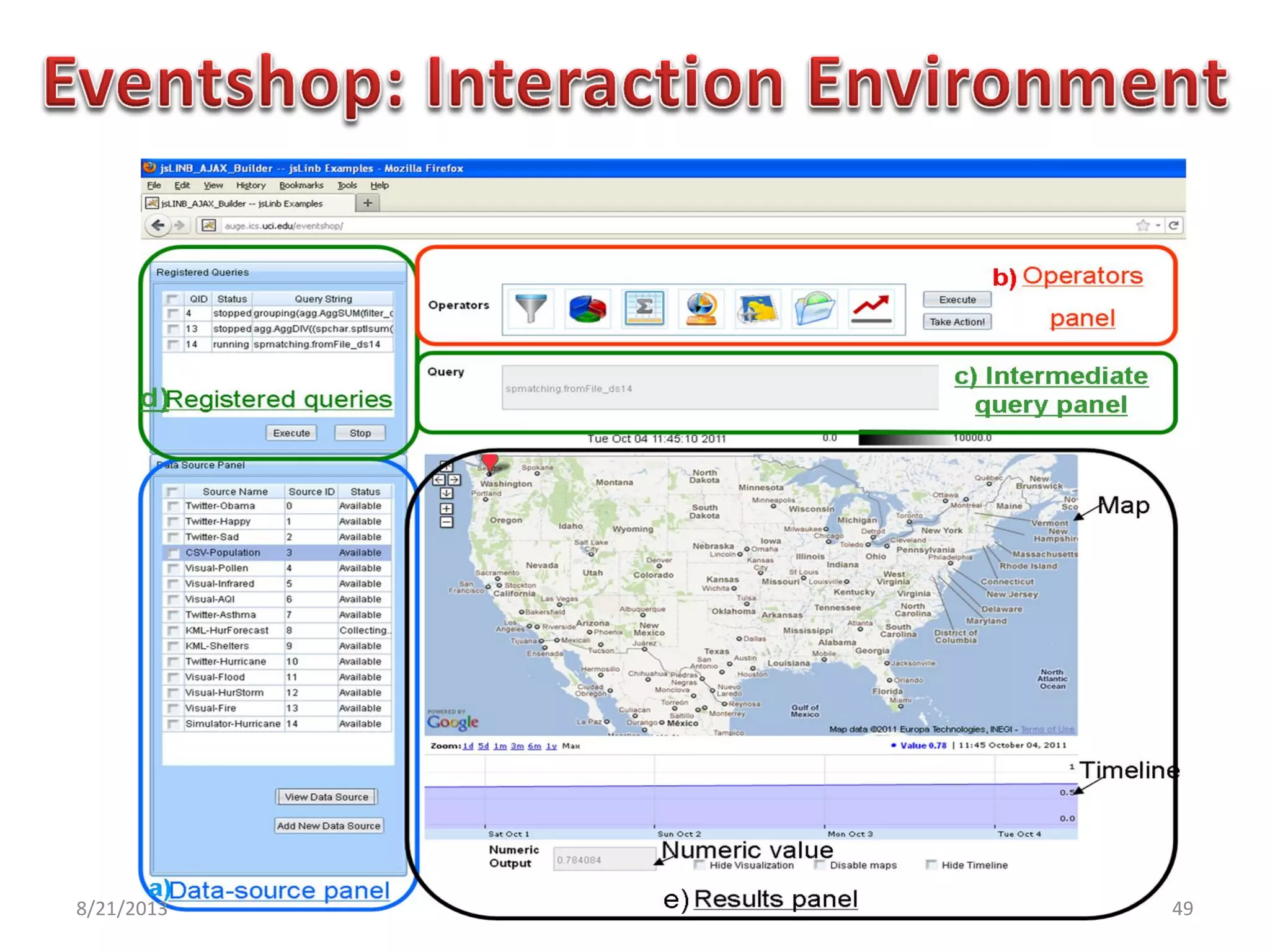
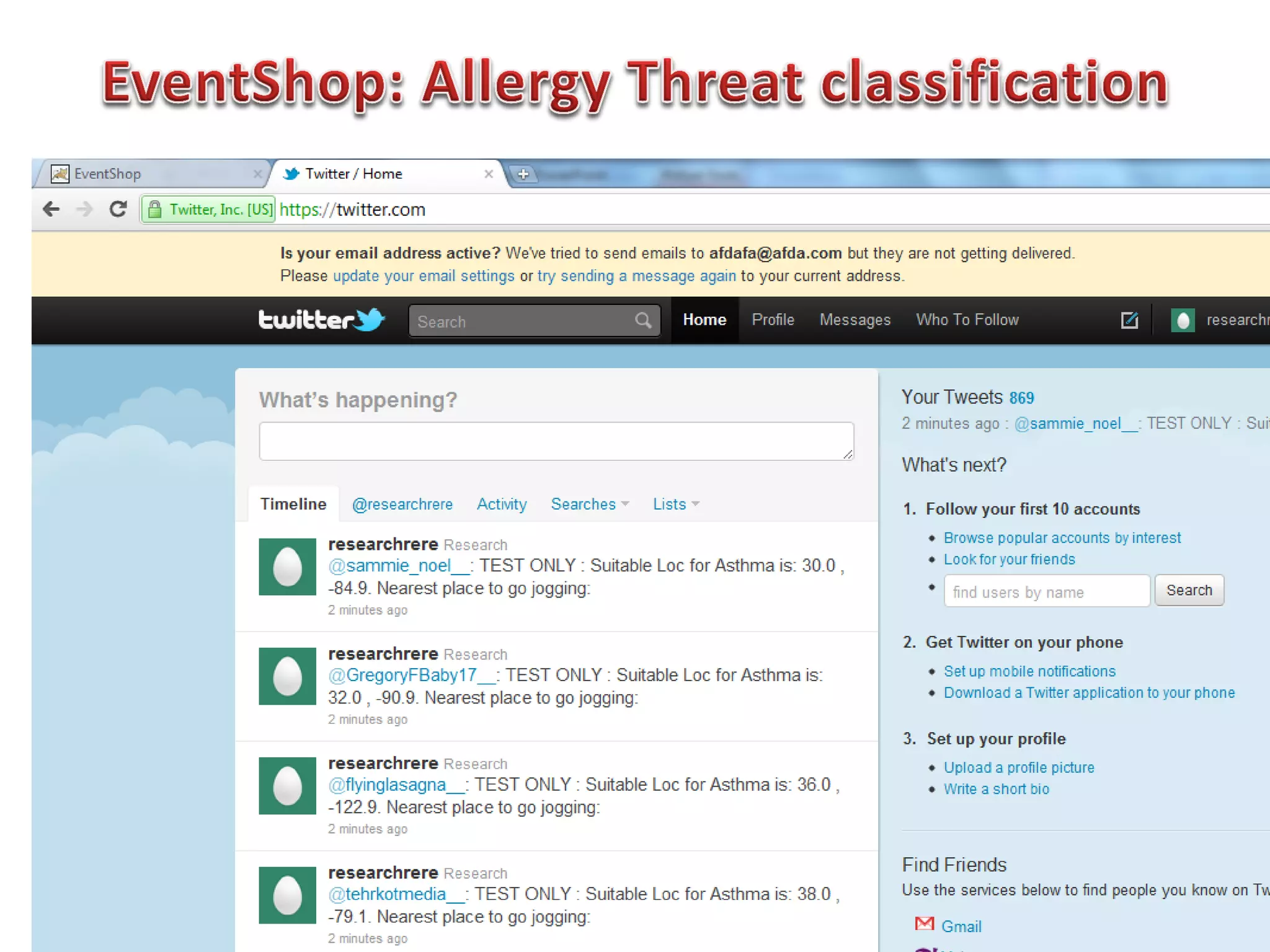
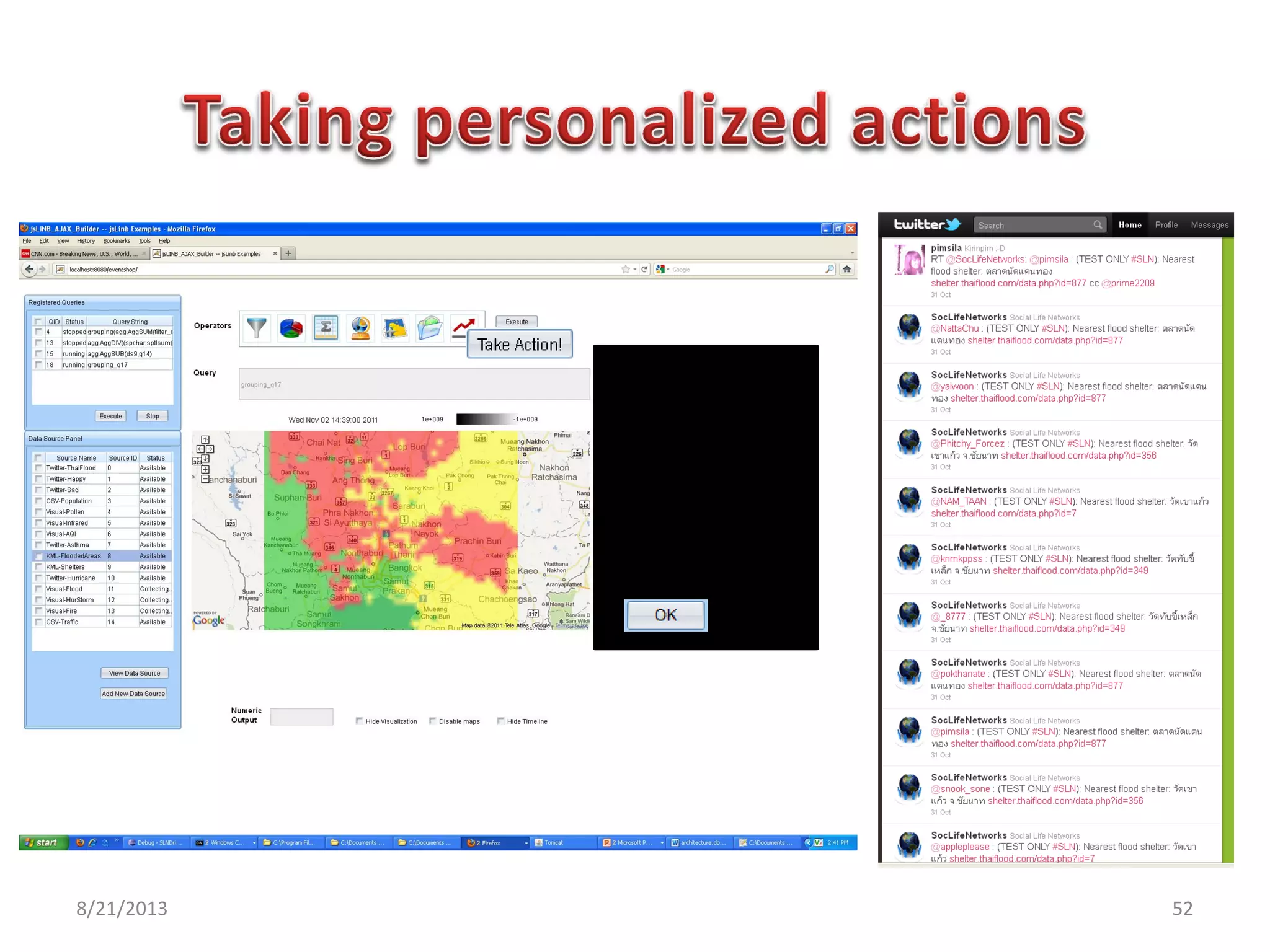
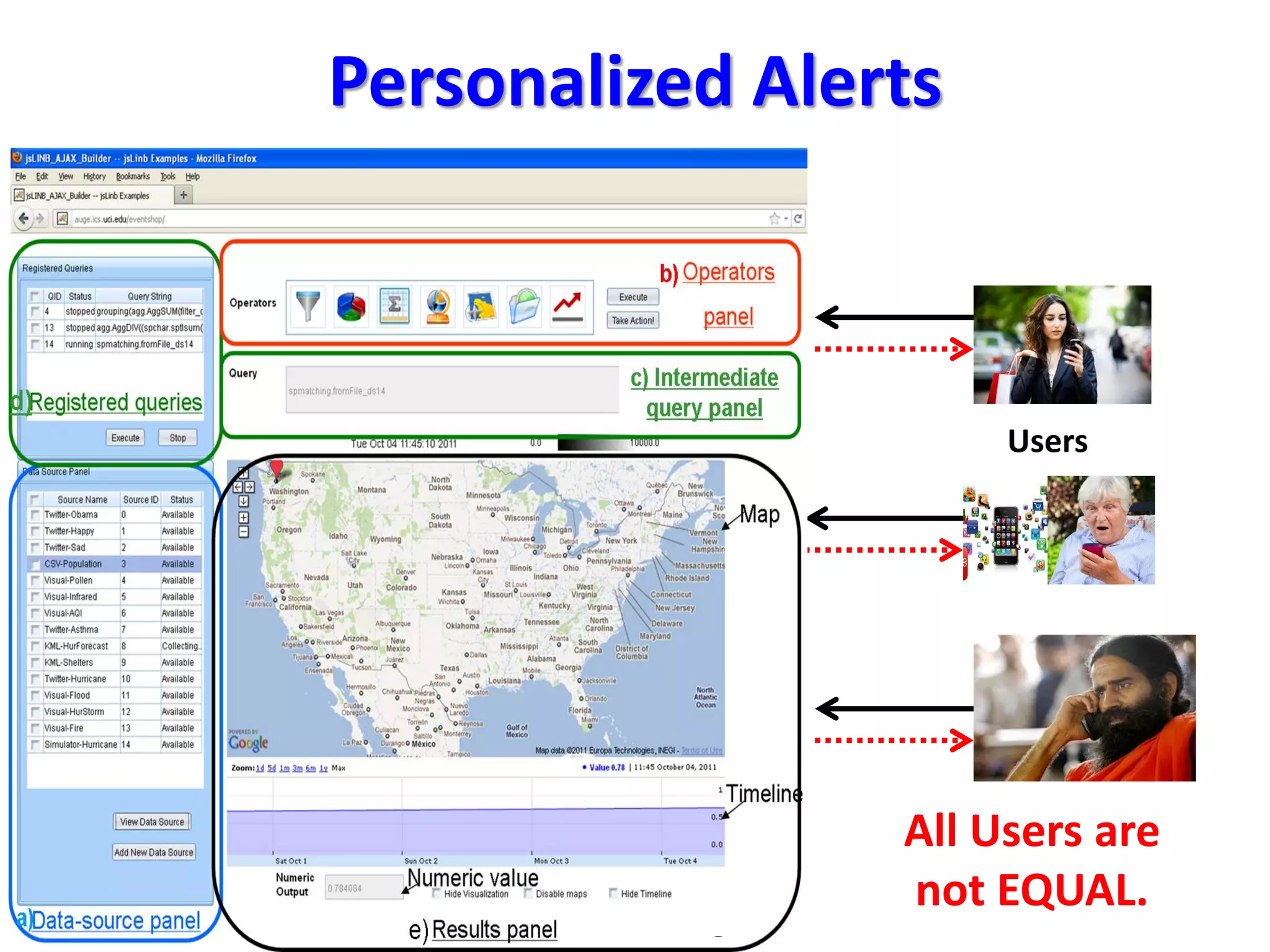
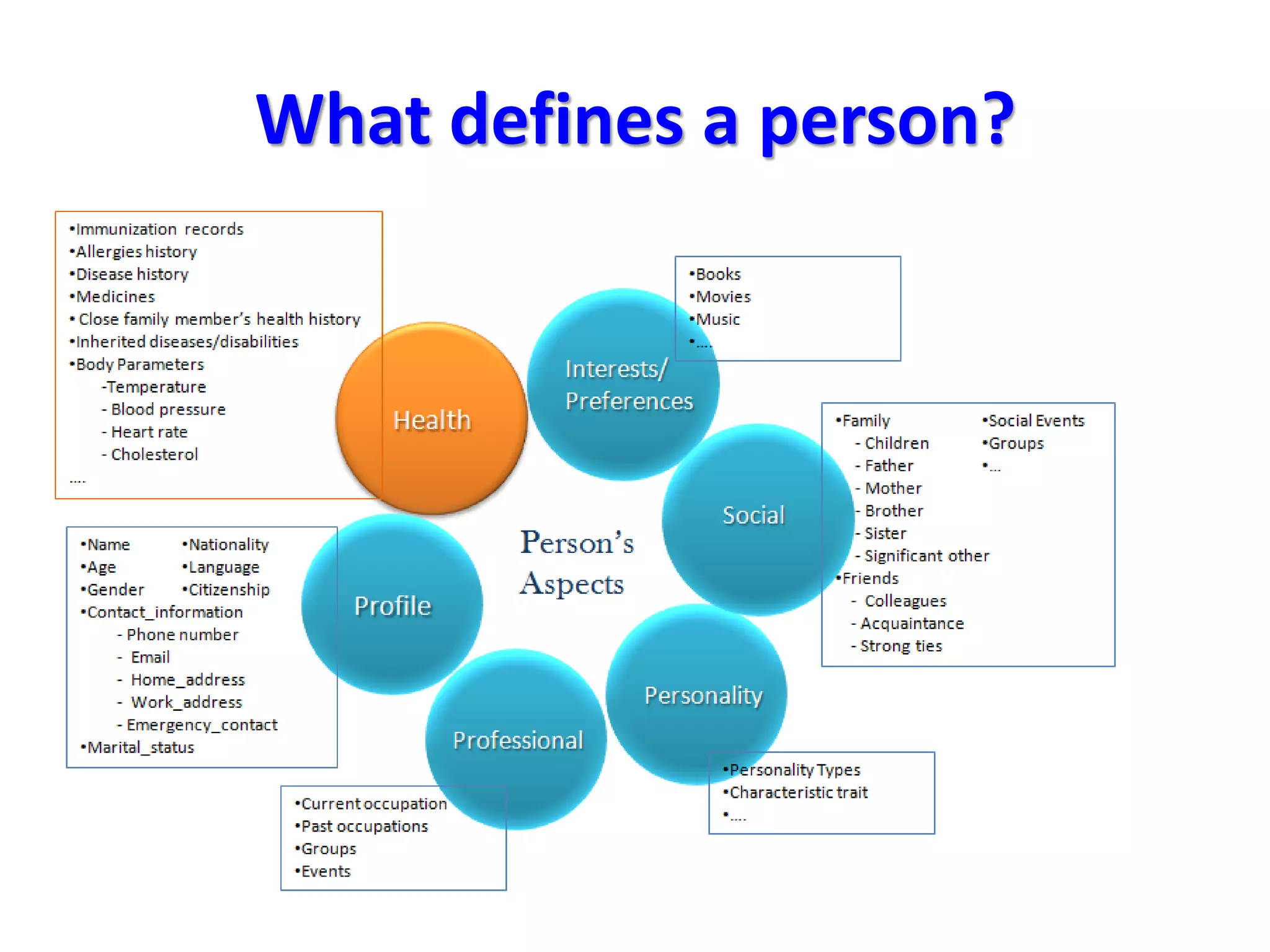
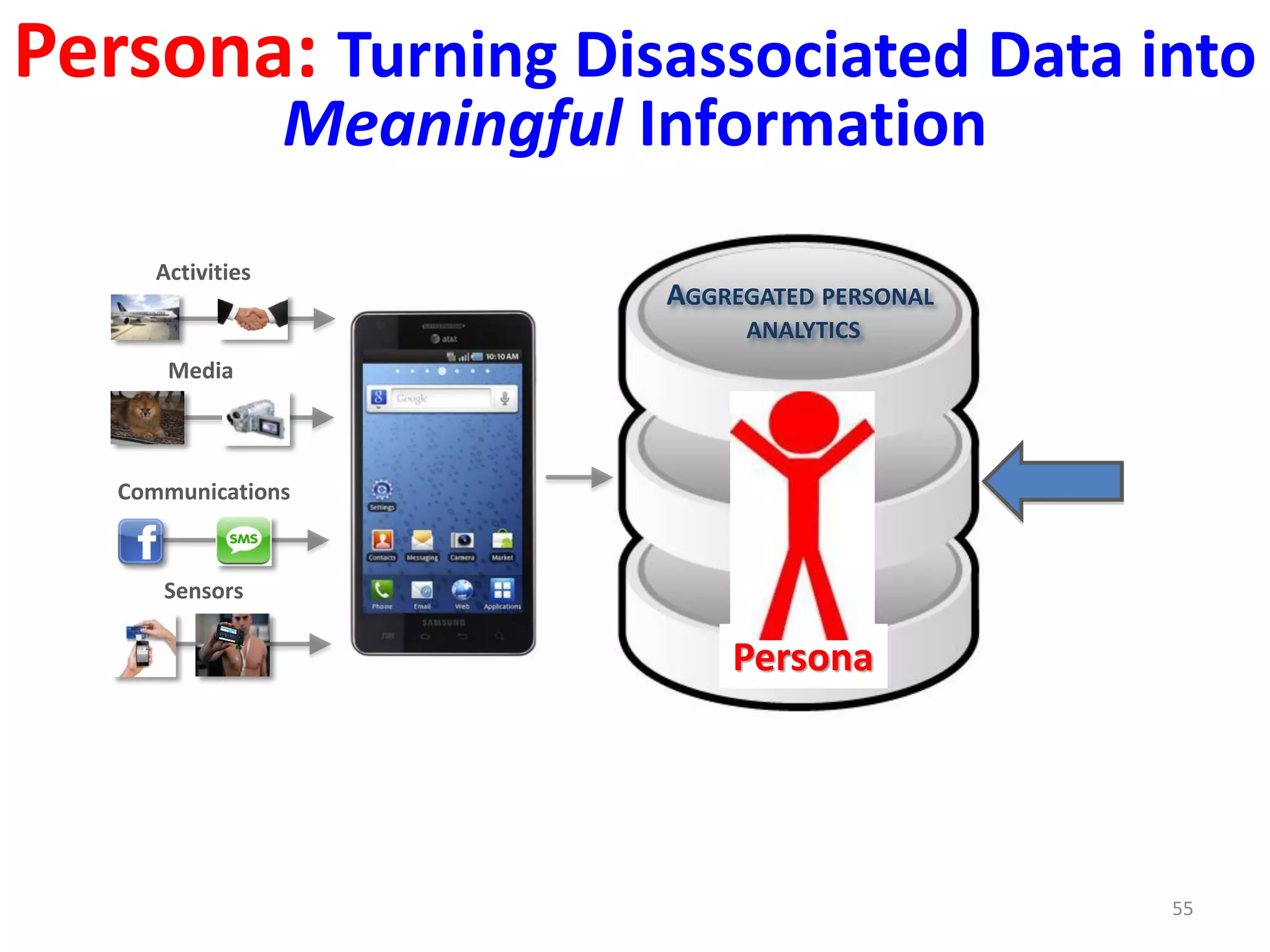
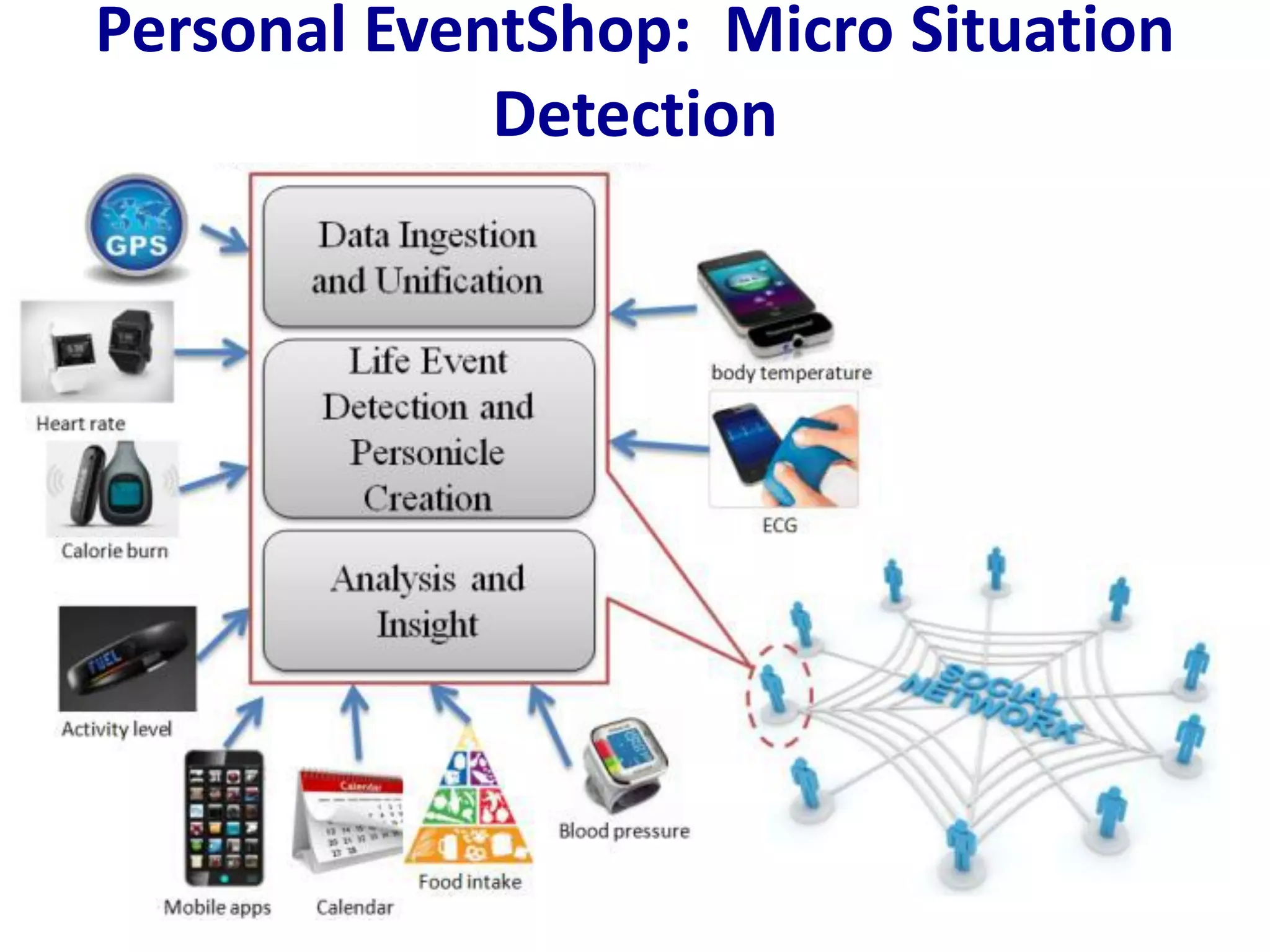
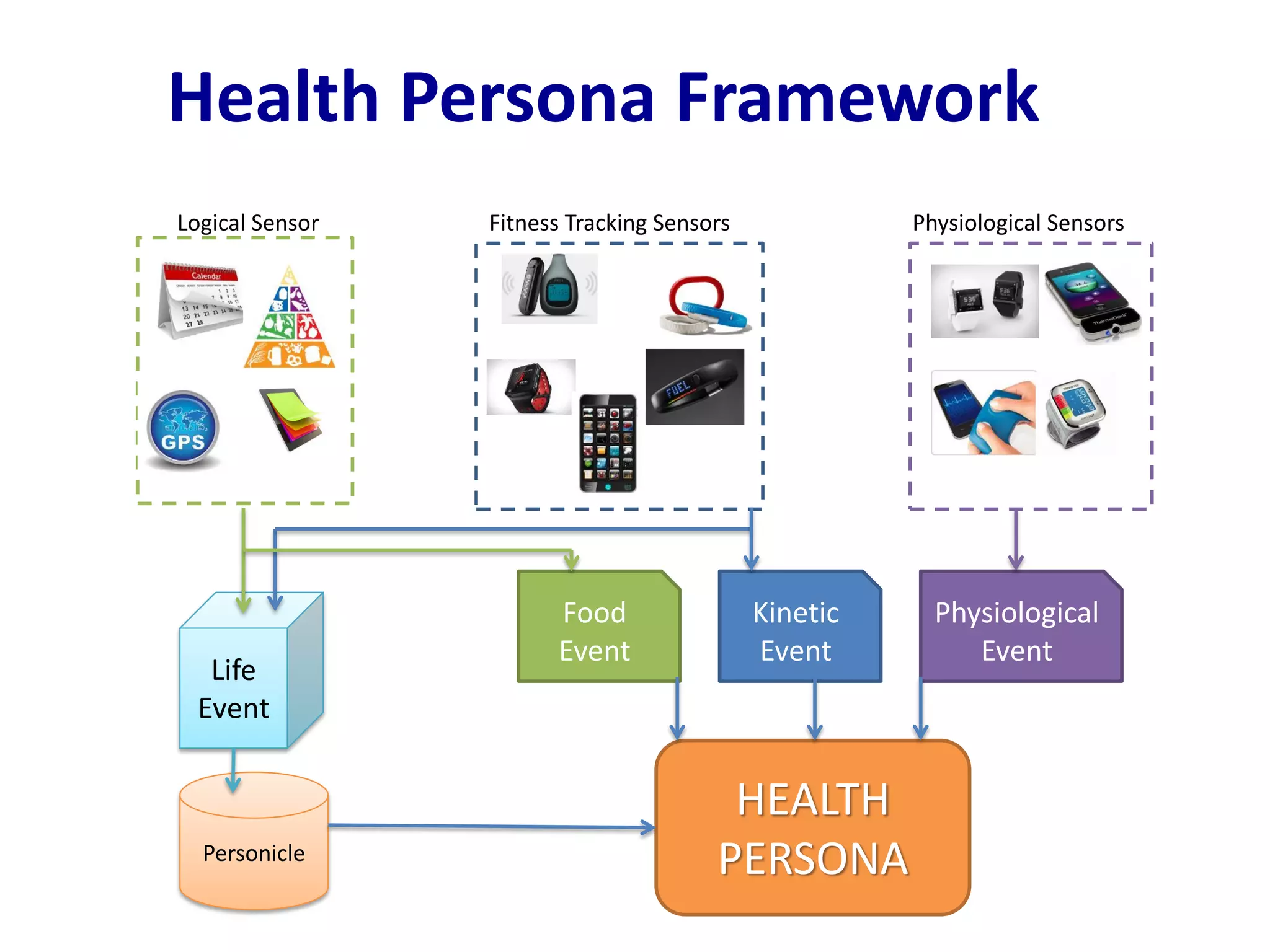
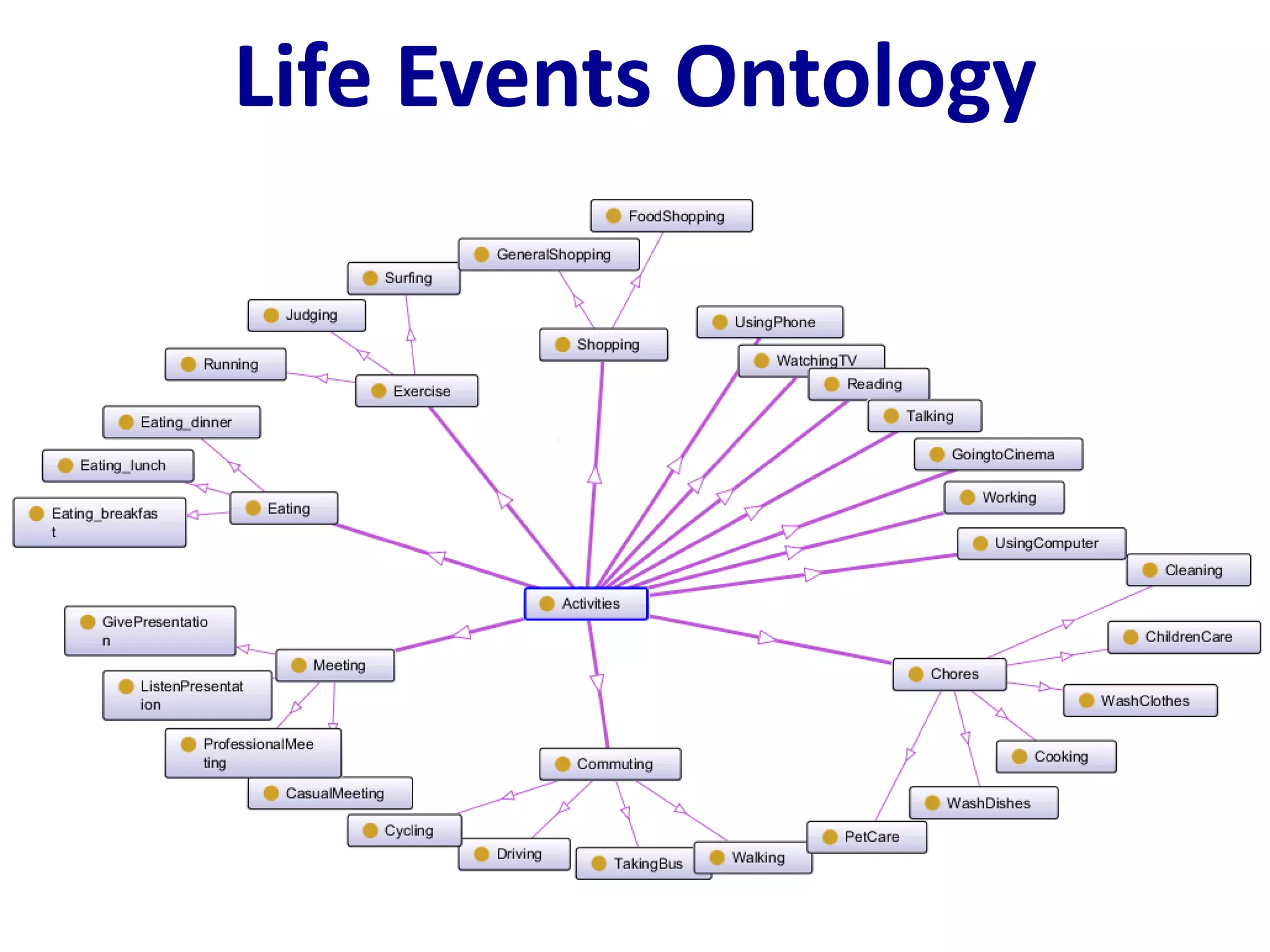
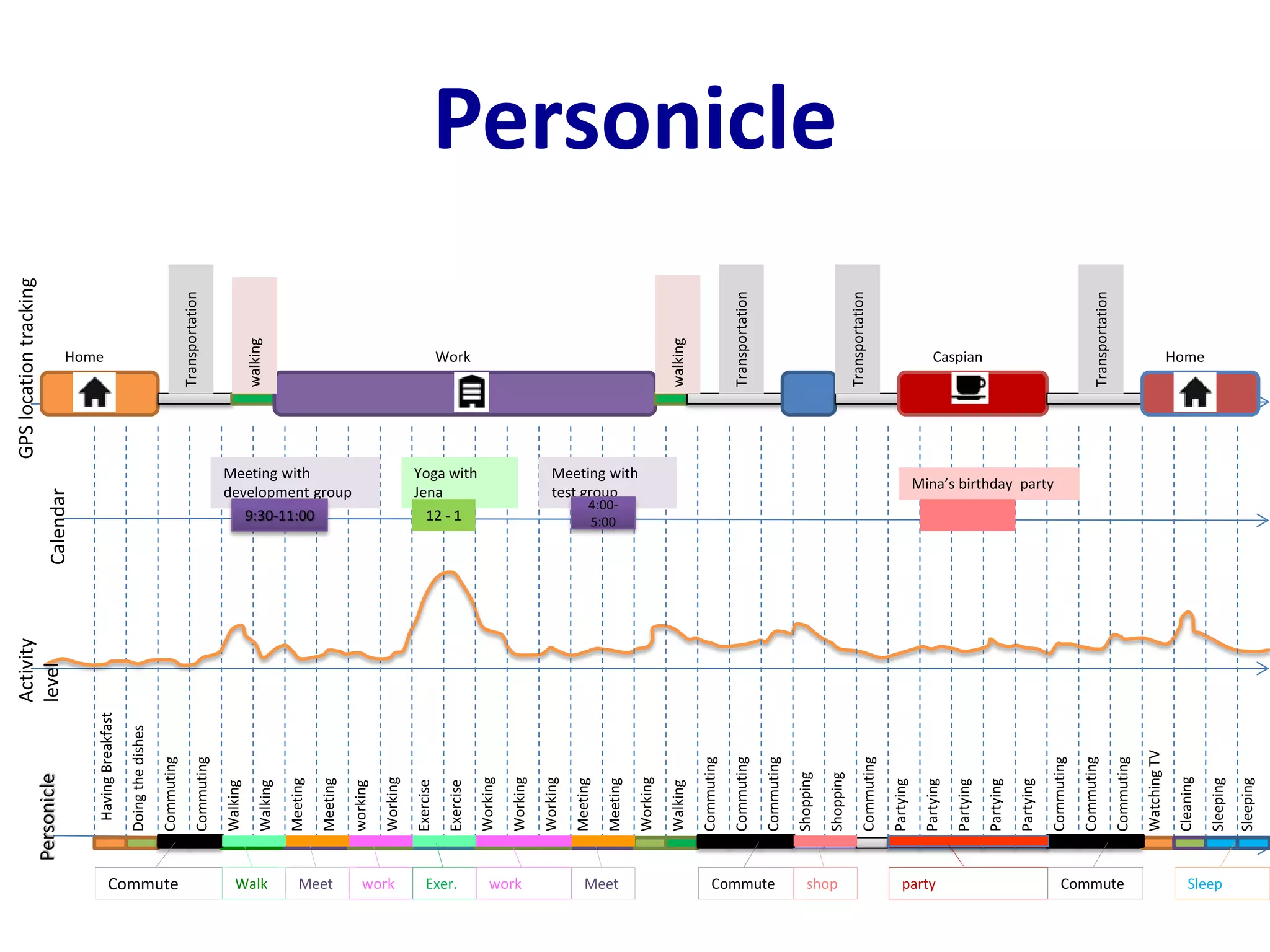
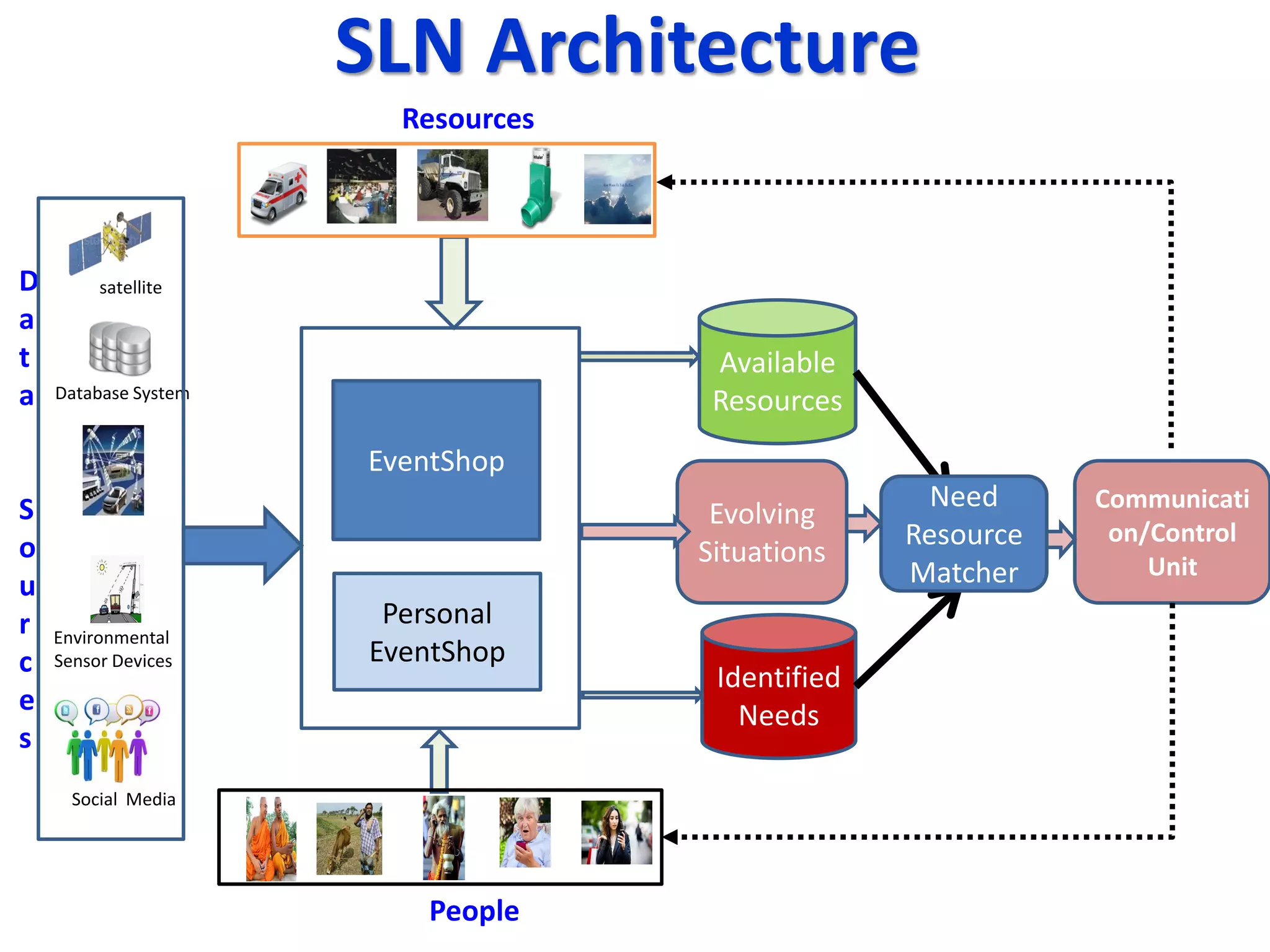
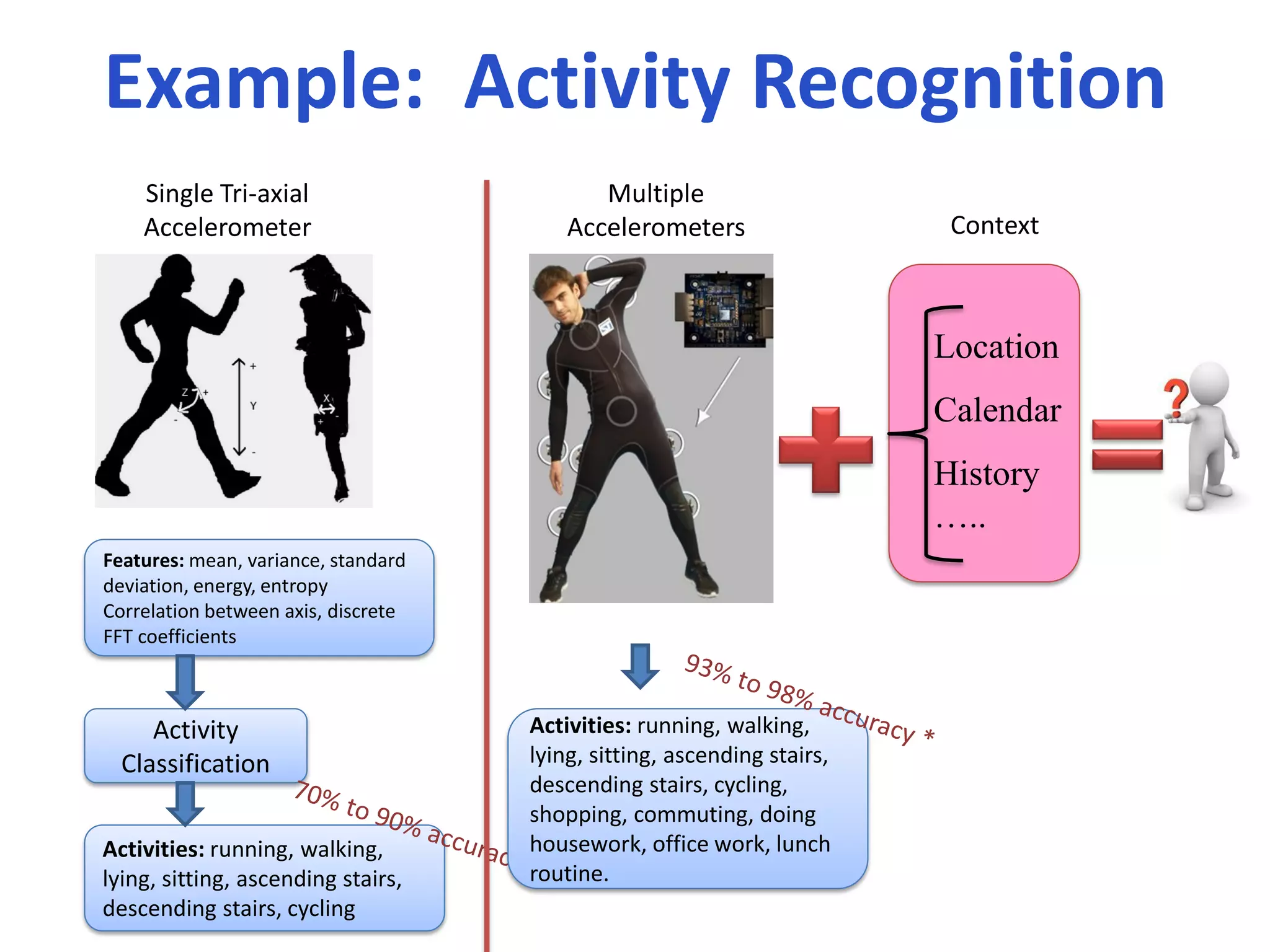
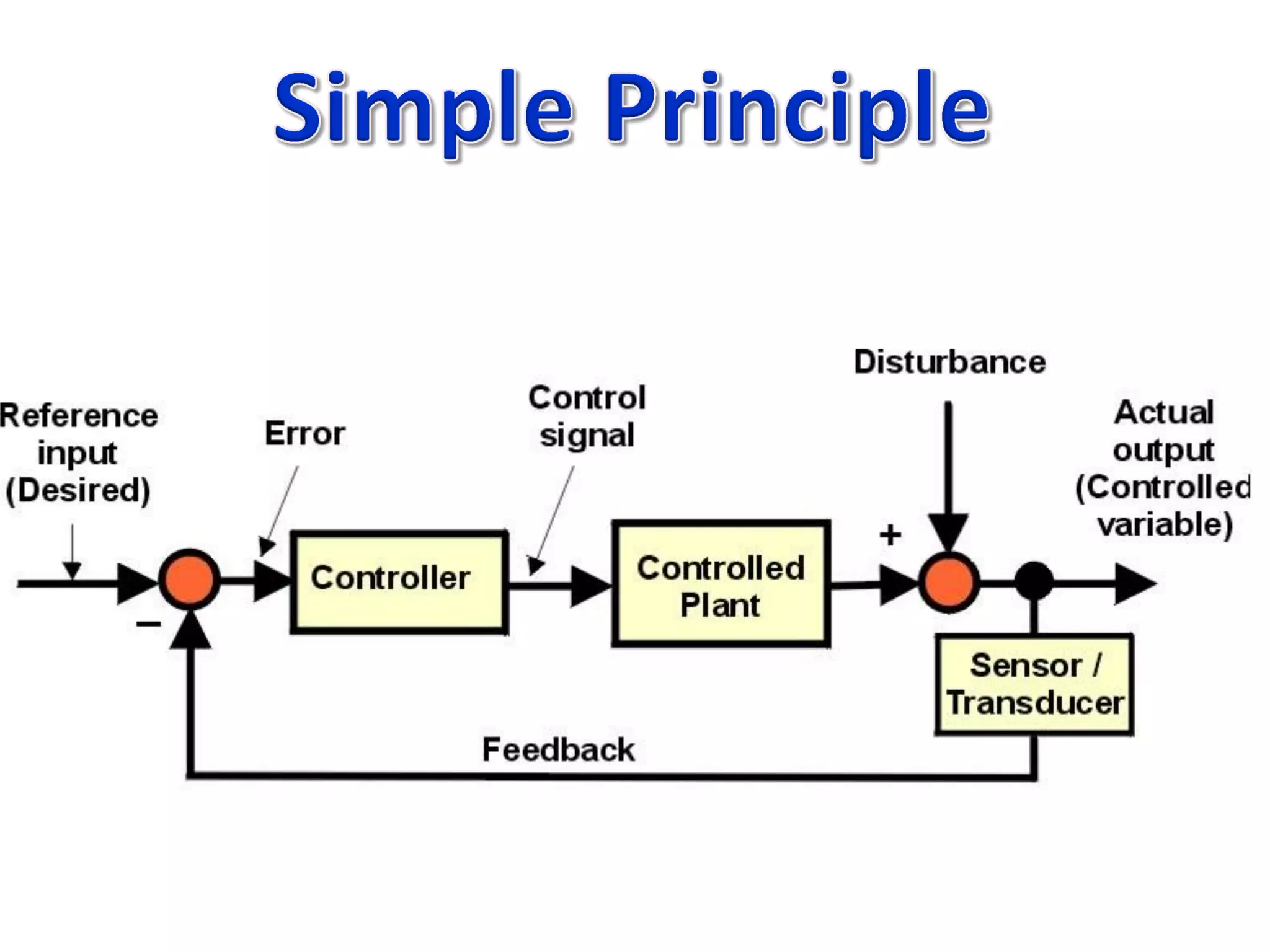
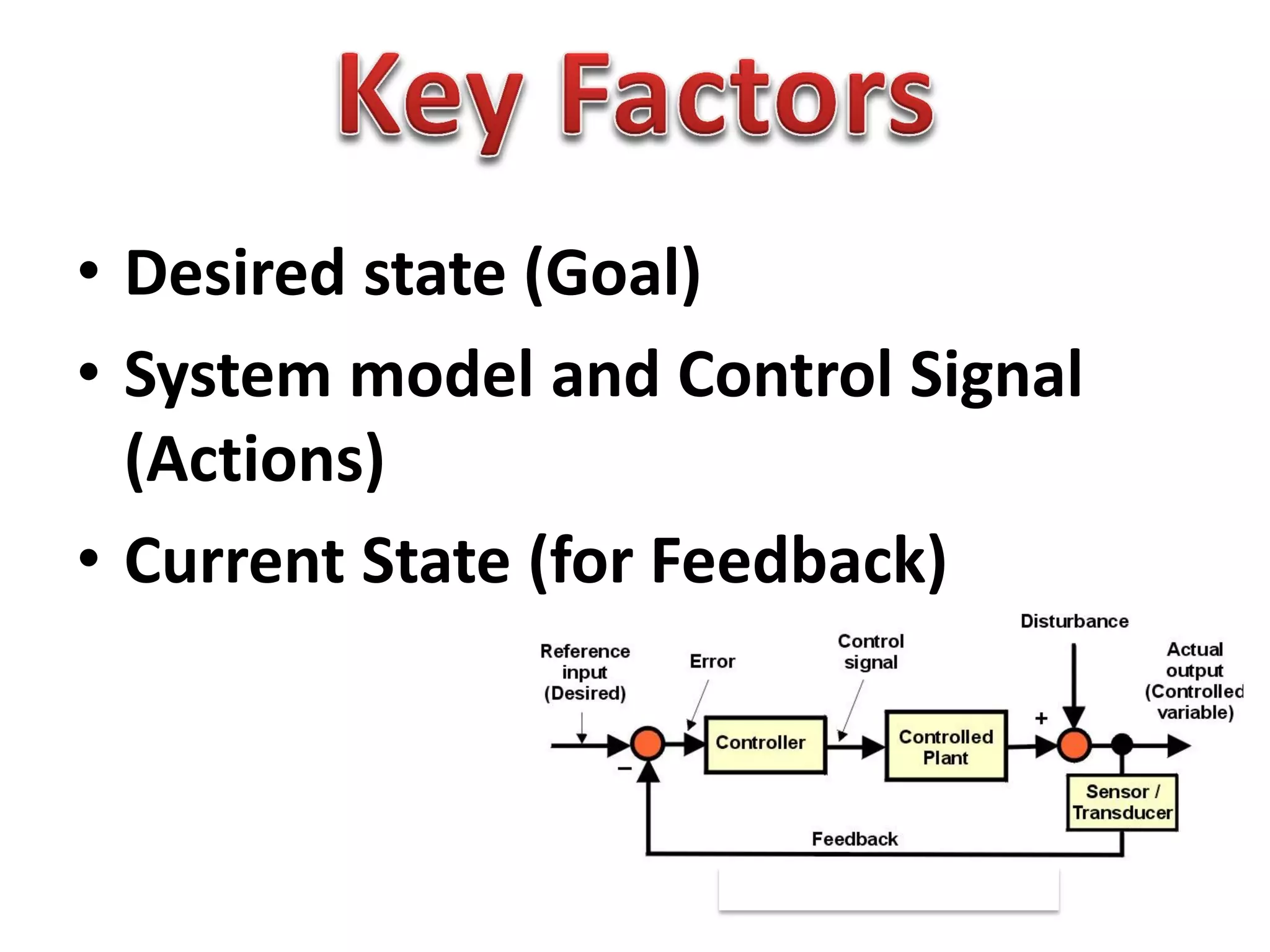
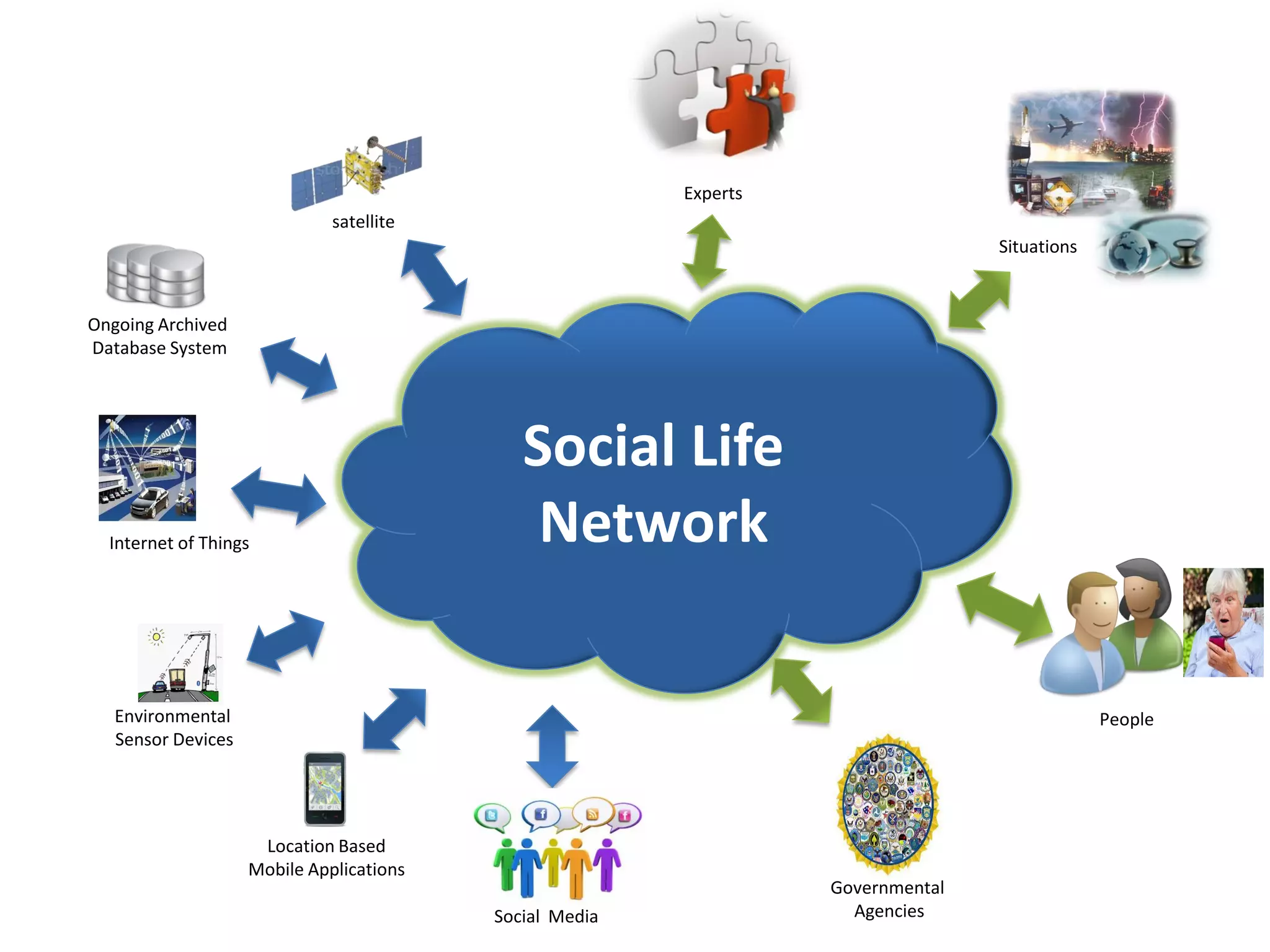
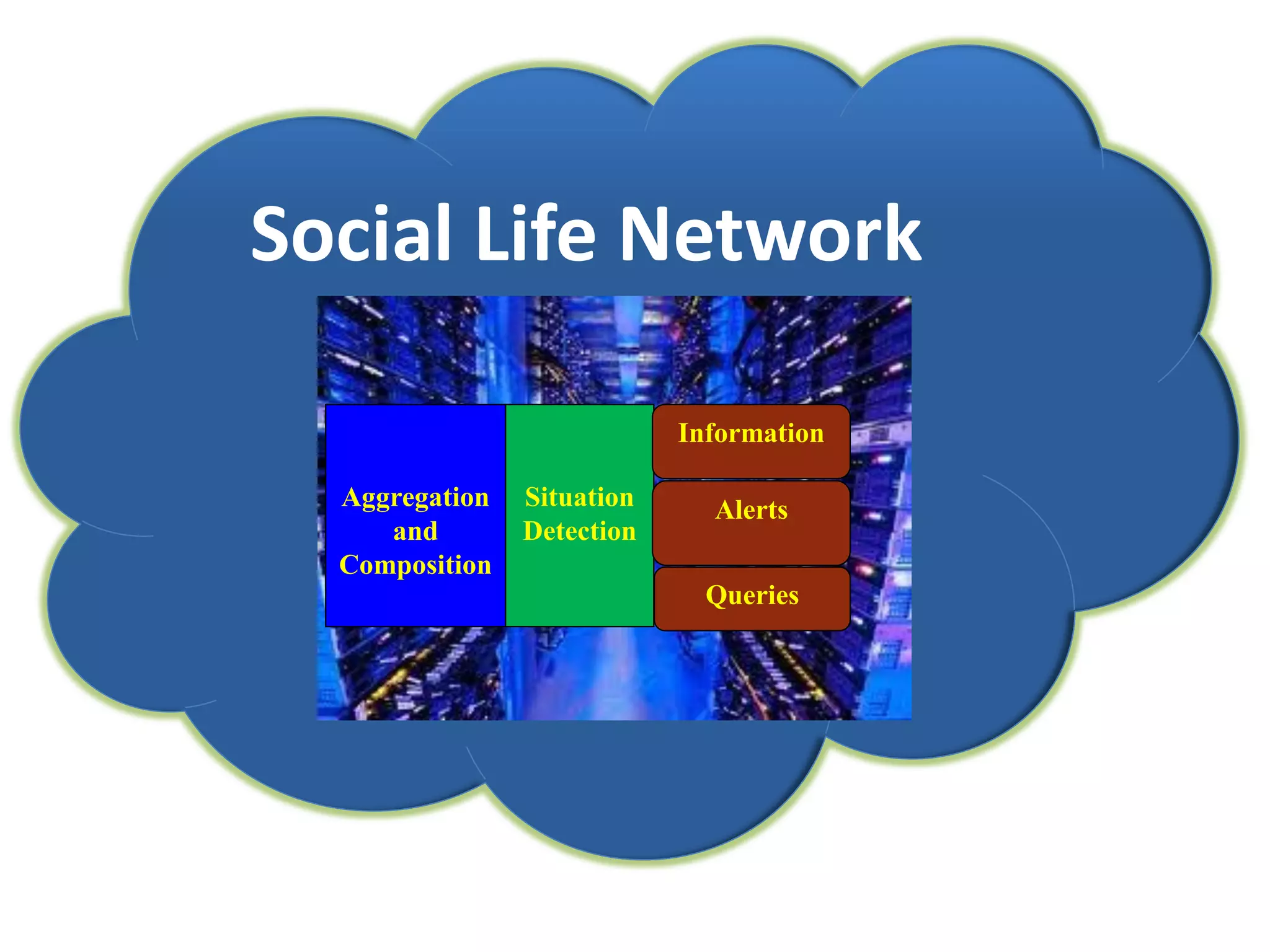
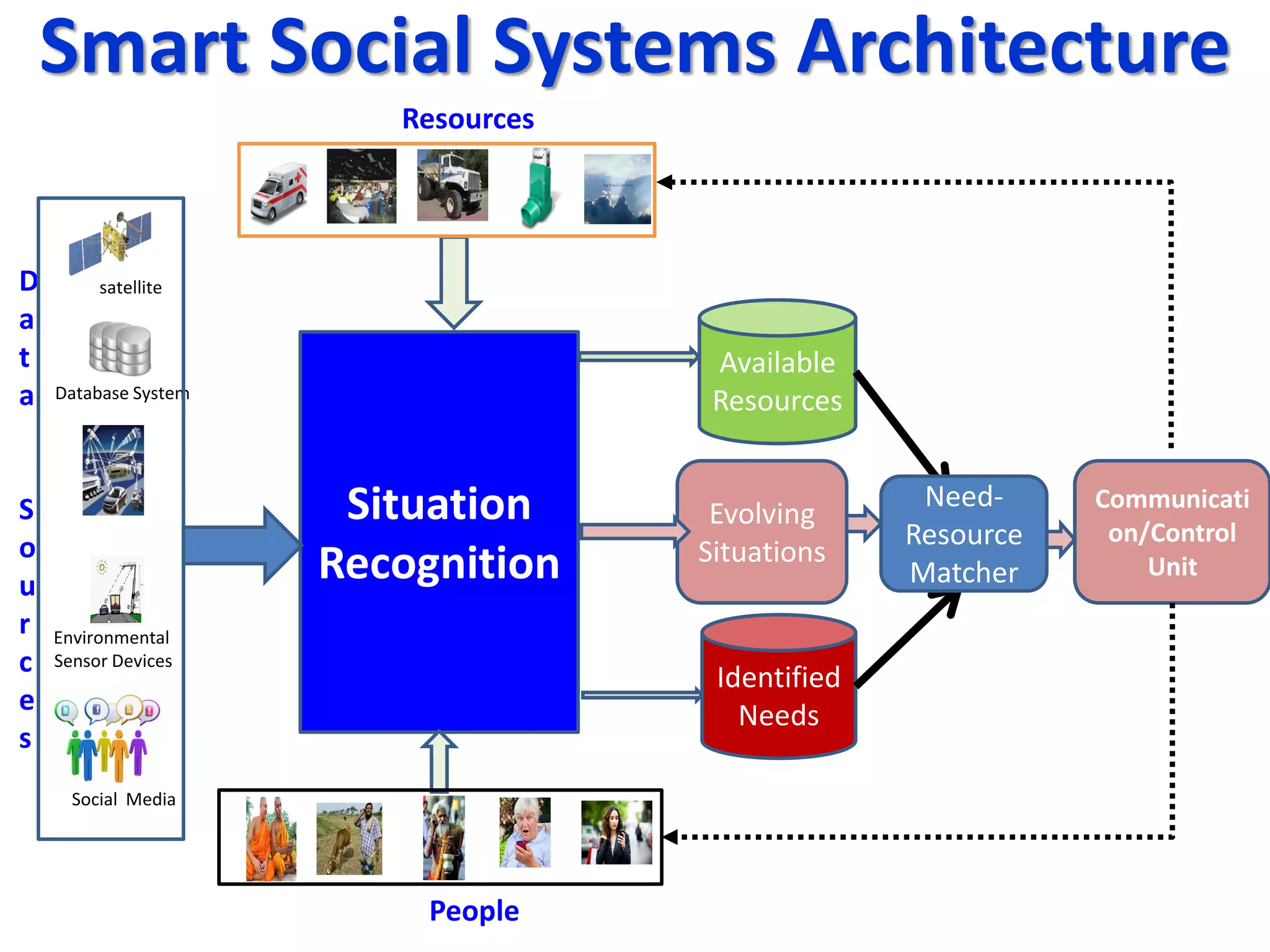
The document discusses challenges in connecting people to essential resources through modern data processing, particularly in areas like computer vision, machine learning, and social networks. It emphasizes the need for effective resource management and the development of smart social systems capable of recognizing situations and needs. Additionally, it outlines the importance of handling large-scale data streams and personal contexts in creating responsive applications.













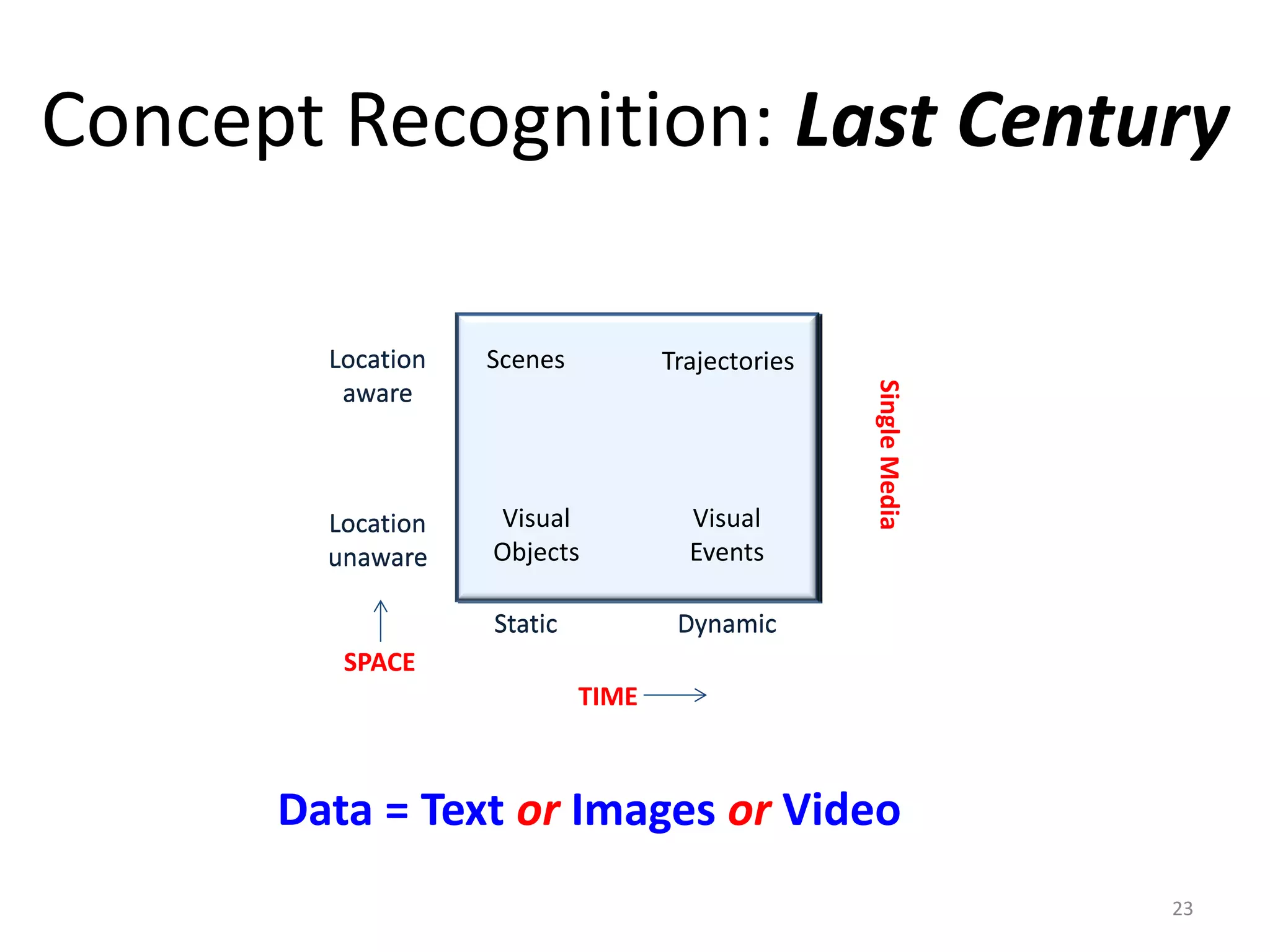
![Visual Concept Recognition: Quick History
• 1963: Object Recognition [Lawrence + Roberts]
• 1967: Scene Analysis [Guzman]
• 1984: Trajectory detection [Ed Chang+ Kurz]
• 1986: Event Recognition [Haynes + Jain]
• 1988: Situation Recognition [Dickmanns]
1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Object Scene Trajectory Event Situation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/building-20sln-20-20130814-130821125115-phpapp01/75/Building-Social-Life-Networks-130818-24-2048.jpg)