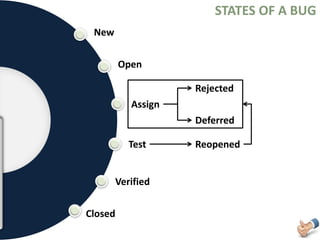
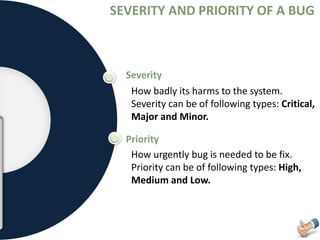
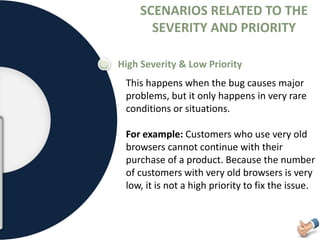
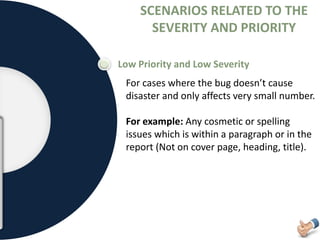
The document is a presentation on software testing that explains the concept of a bug and its life cycle, detailing various states such as new, open, assign, test, verified, and closed. It also clarifies the differences between errors, bugs, and defects, alongside the severity and priority classifications of bugs with examples. Additionally, the author disclaims any liability and emphasizes that the content is for educational purposes only.













![ERROR BUG DEFECT
A mistake done by a
programmer in
coding is called Error.
Error which found
during the testing
process is called Bug.
If testers find any
deviation between
expected and actual
results will say it as
Defect.
For example to say,
instead of A+b,
he/she has mention
A-B
For example to say,
clicking on link is not
directing to page.
For example to say,
customer raises 21
issues, tester raises
267 Issues but there
were 17 invalid
defects (because of
wrong tests? mistake
by tester)
Then your Defect
Leakage Ratio would
be:
[21/(267-17)] x 100 =
8.4%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/darshitppt-150425232736-conversion-gate02/85/Knowledge-sharing-18-320.jpg)
