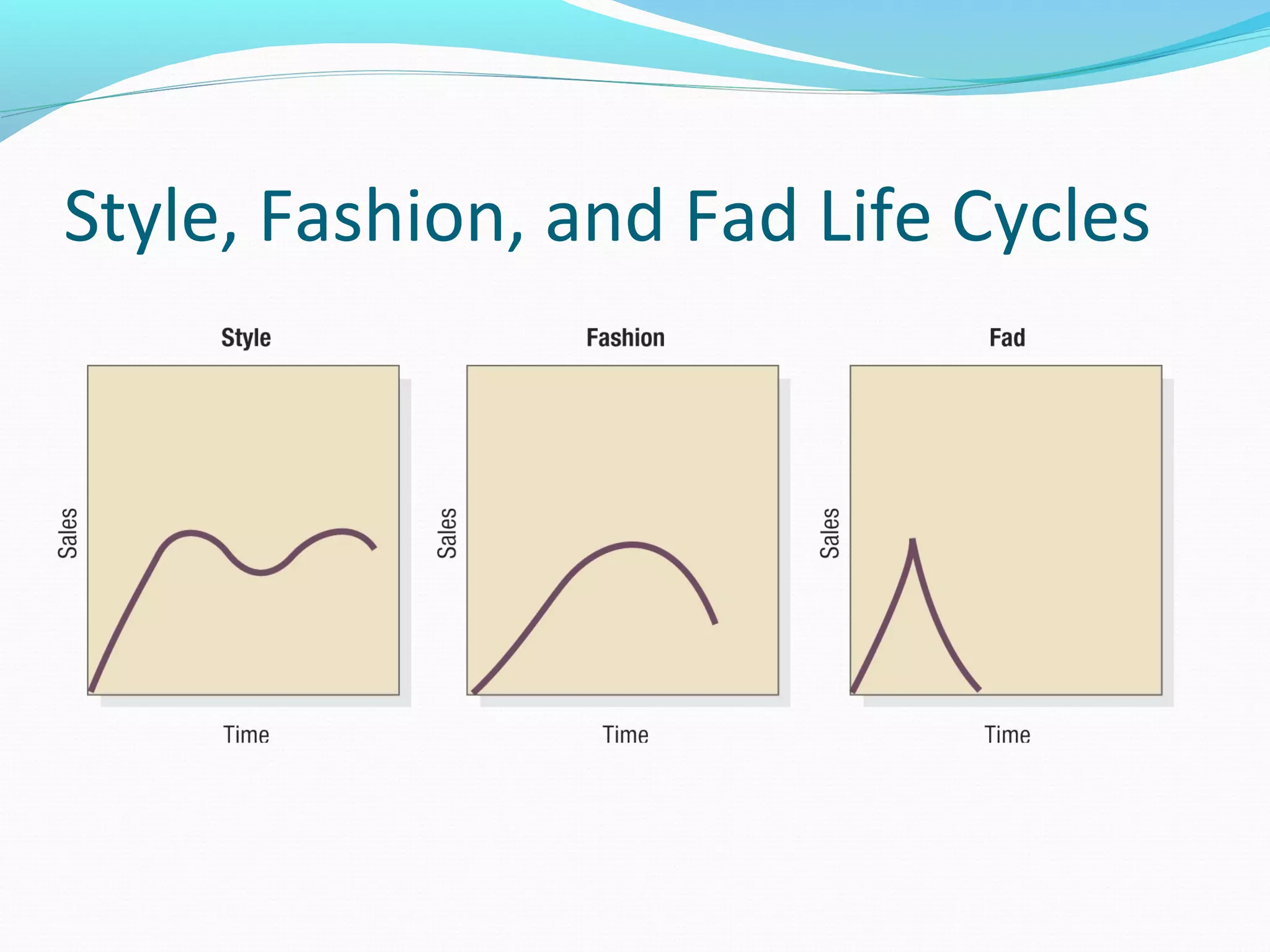
The document discusses key concepts related to branding, including defining brands, the functions of brands for consumers and marketers, brand loyalty, recognition and preference. It also covers selecting brand names, packaging considerations and functions, and strategies for sustaining growth over the product lifecycle, including modifying marketing programs.