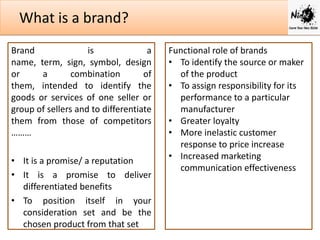
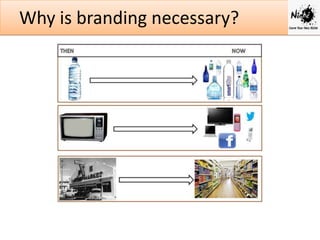
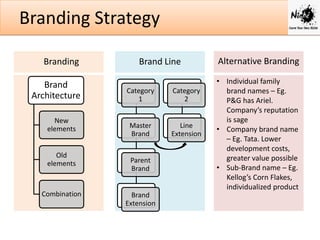
Branding is important for differentiating a company's products and services from competitors. A brand is a name, symbol or design that identifies a seller's goods and services. It creates value by building loyalty and trust with consumers.
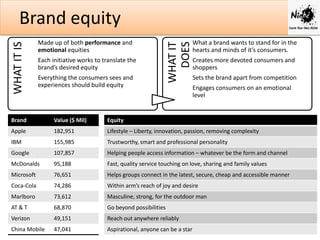
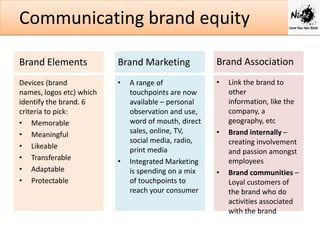
Brand equity refers to the additional value a brand name provides compared to an unbranded product. It is made up of performance and emotional benefits in the minds of consumers. Strong brands have high awareness, preference and financial metrics like market share and revenue.
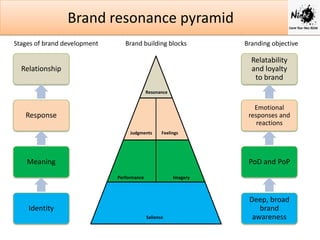
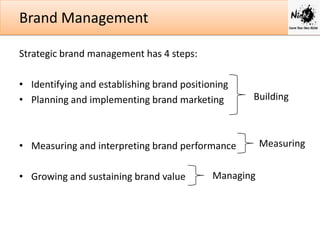
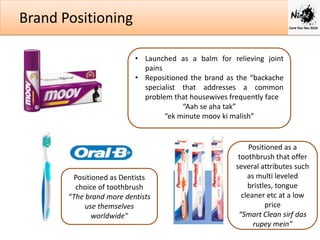
Effective brand management involves identifying brand positioning, implementing marketing strategies, measuring performance, and growing and sustaining brand value over time. Positioning communicates the core benefits and needs a brand satisfies. Marketing activities integrate different touchpoints to reach consumers