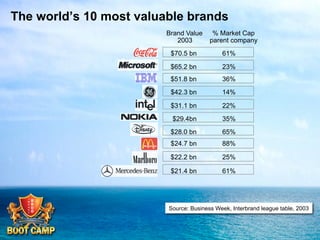
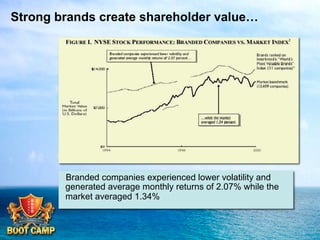
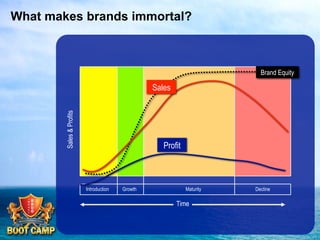
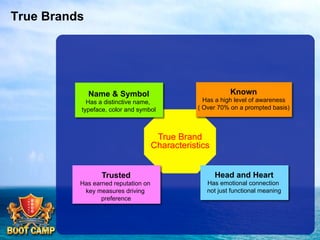
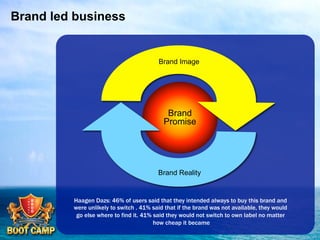
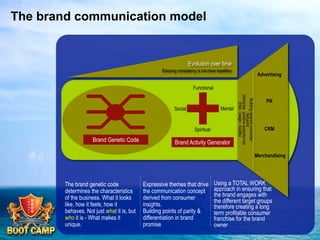
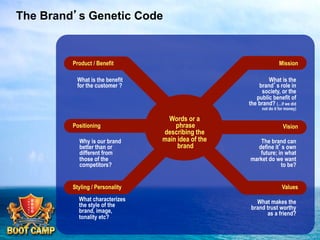
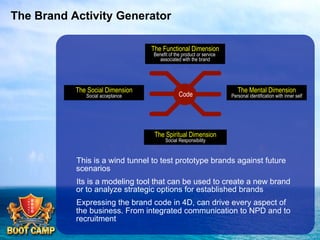
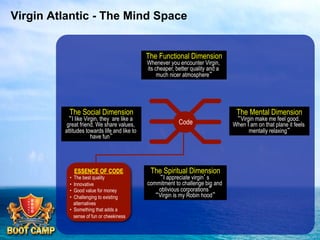
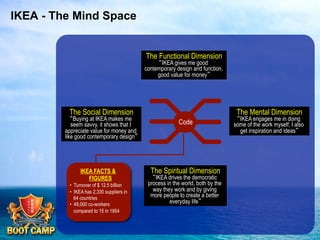
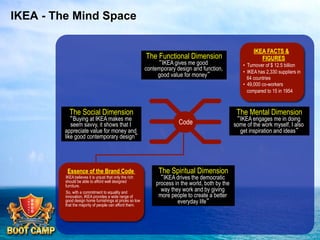
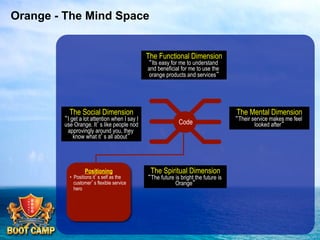
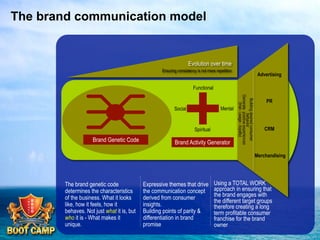
A brand is defined as a set of promises that link a product to customers and assure them of consistent quality and superior value. The document examines various aspects of strong brands including the world's most valuable brands, how brands create shareholder value, and what makes brands immortal. It discusses brand genetics and how successful brands adapt to changes while maintaining their core identity, like natural species. Key aspects of a brand's genetic code are identified such as benefits, positioning, personality, mission, vision, and values. The brand communication model is presented which is driven by the brand's genetic code.