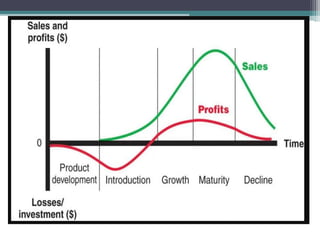
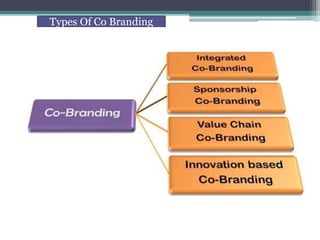
The document discusses brand management strategies, focusing on brand rejuvenation, re-launch, and co-branding, emphasizing their importance in keeping a brand relevant and profitable. Brand rejuvenation involves enhancing product features to revive consumer interest, while brand re-launch refers to repositioning a brand to improve sales and market share. Additionally, co-branding is highlighted as a strategy for collaboration between brands to leverage their strengths and expand market reach.