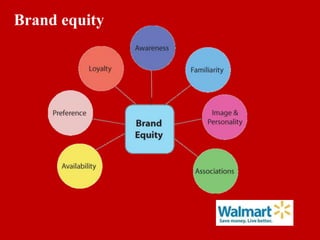
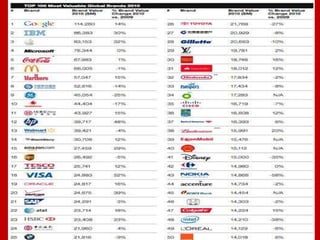
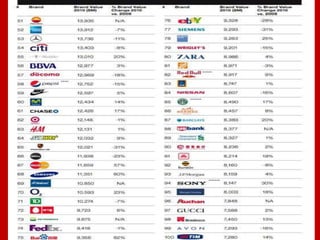
Brand equity is the added value provided to products and services due to the brand, which is reflected in consumer behavior and financial performance. It is an important intangible asset with psychological and financial value. There are various models that measure brand equity from different perspectives, including the customer perspective and financial value. Brand equity must be built and maintained through consistent marketing activities that reinforce the brand's meaning and position over time. It can also be improved through innovation, relevance, and brand revitalization strategies if necessary.