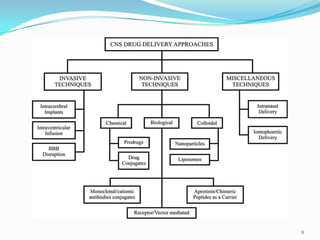
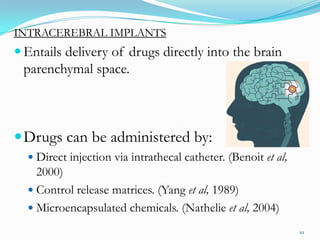
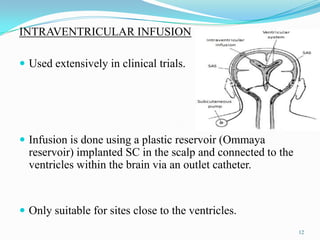
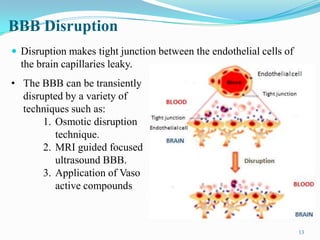
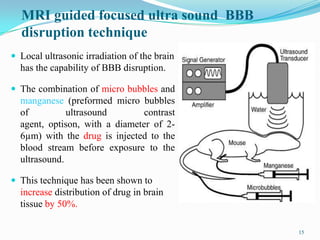
The document discusses various approaches to delivering drugs to the central nervous system (CNS). It begins by describing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) that limits drug entry into the brain. Invasive methods for direct CNS delivery include intracerebral implants and intraventricular infusion. Non-invasive methods aim to circumvent the BBB and include temporarily disrupting the BBB using osmotic pressure or ultrasound, as well as prodrug formulations and conjugating drugs to transporters like peptides. Nanoparticles, liposomes, monoclonal antibodies and intranasal delivery are also explored for non-invasive CNS drug delivery. Overall, the challenges of the BBB mean no single approach is suitable for all CNS disorders.