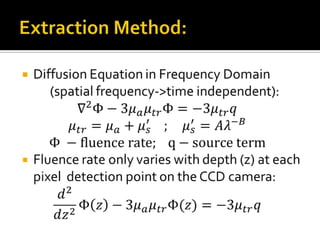
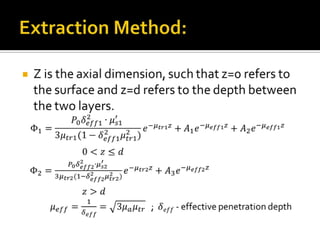
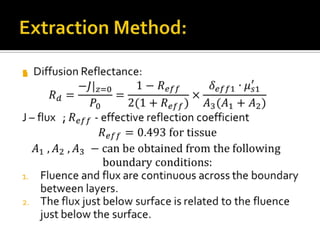
The document discusses the extraction of optical properties from biological tissues using structured light, which enables non-invasive imaging and diagnostic applications. It outlines the methods for calculating the absorption and reduced scattering coefficients of tissue, utilizing diffusion equations and reflectance measurements. Current research focuses on direct illumination of brain tissue, providing insights into its optical and spatial properties with a simple, cost-effective optical system.