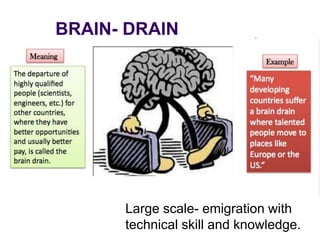
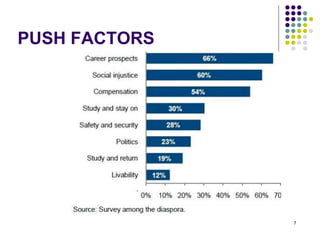
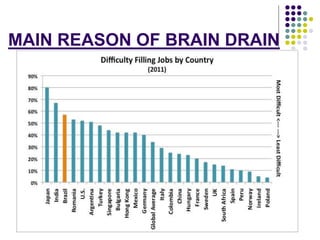
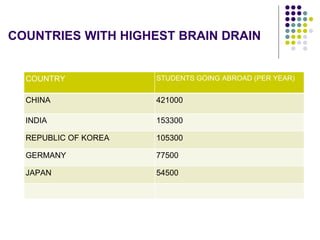
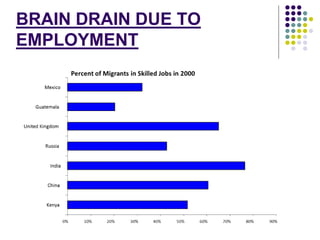
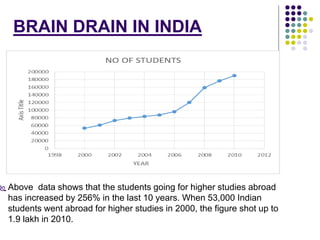
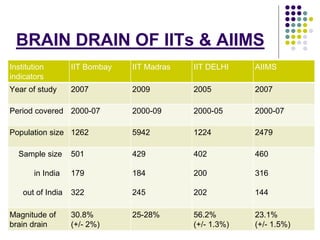
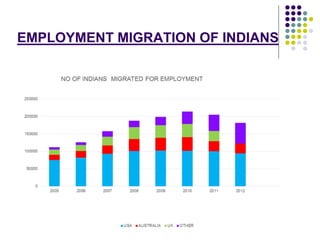
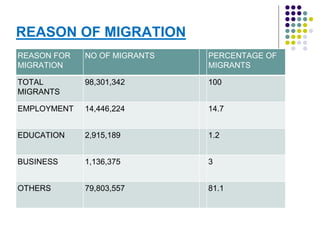
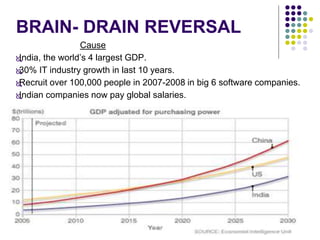
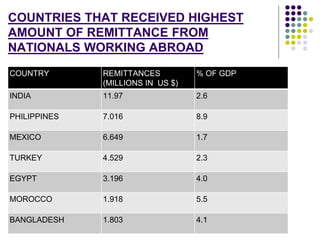
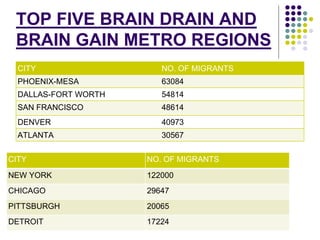
This document discusses brain drain, which refers to the emigration of trained professionals and skilled individuals from their home country to other nations. It provides background on the history and characteristics of brain drain, as well as the push and pull factors that contribute to it. Specific examples of brain drain are examined, such as the emigration of skilled workers and students from India. The concepts of brain gain and reverse brain drain, where skilled individuals return to their home country, are also introduced. Overall causes and impacts of brain drain are assessed.