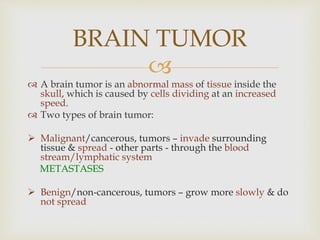
Brain damage can be caused by physical trauma, stroke, tumors, infections, toxins, genetic factors, or lack of oxygen. The main types of brain damage are traumatic brain injury from blows to the head, stroke from blocked or burst blood vessels in the brain, brain tumors which can be cancerous or non-cancerous, and infections from bacteria or viruses. Brain injuries can also result from chemical exposure, genetic disorders like Down syndrome, or cell death processes in the brain.