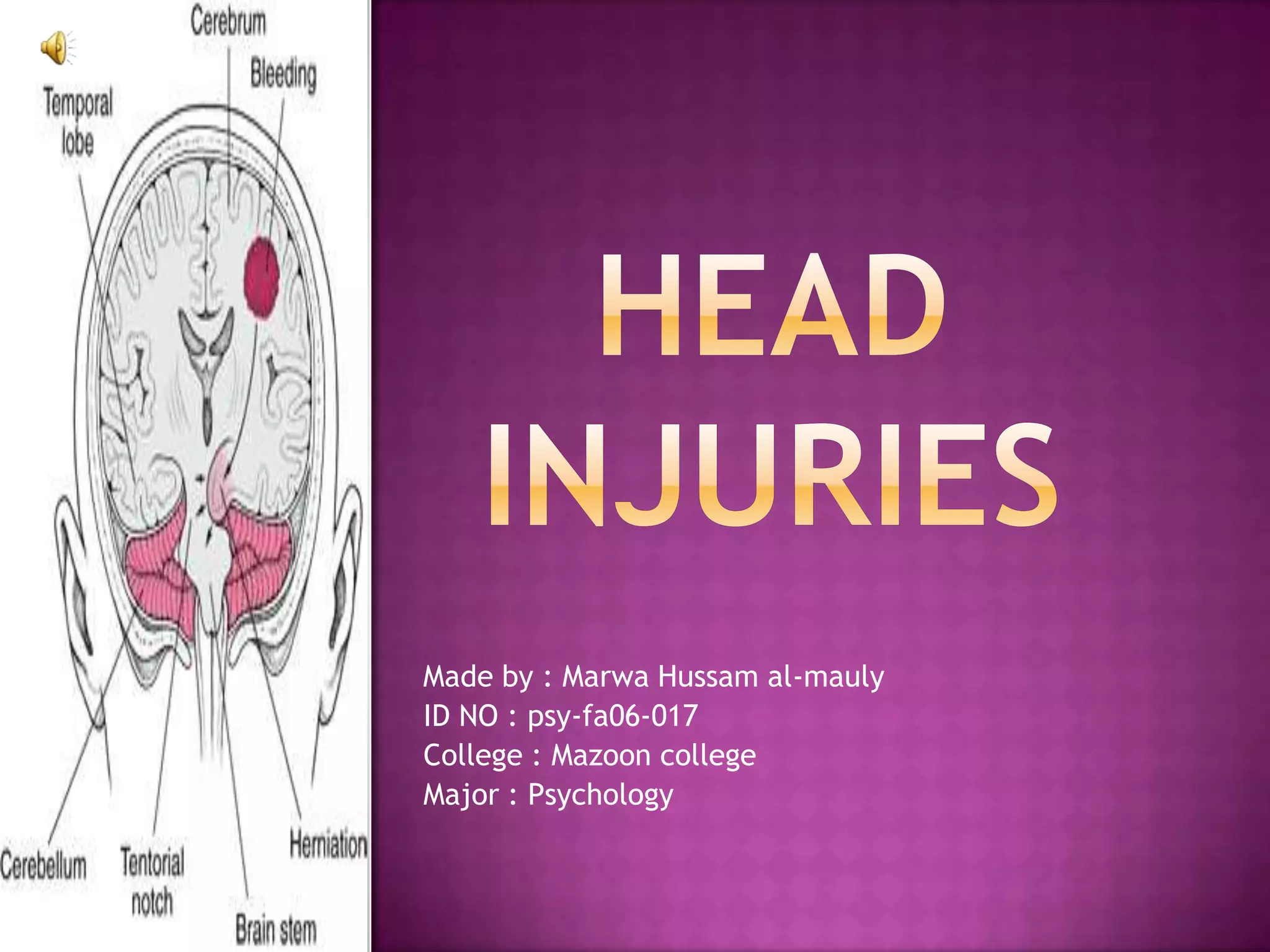
This document discusses different types of head injuries. It defines a head injury as trauma to the head that may or may not involve injury to the brain. The causes of head injuries include direct blows, rapid acceleration or deceleration of the head, and penetrating injuries from objects like bullets or knives. Symptoms can include loss of consciousness, vision issues, vomiting, and confusion. Head injuries are classified into types like concussions, contusions, diffuse axonal injuries, and coup-countercoup injuries. Shaken baby syndrome is also discussed as a form of traumatic brain injury caused by violently shaking an infant.