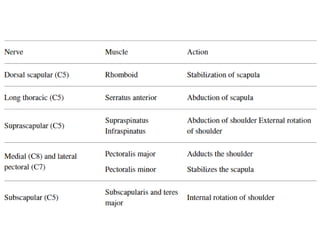
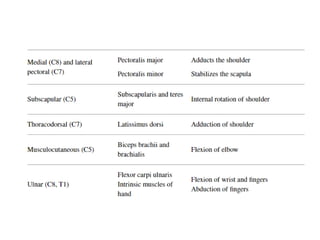
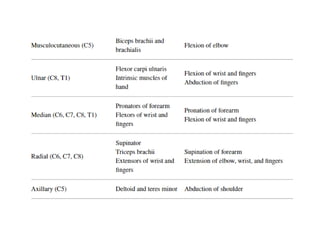
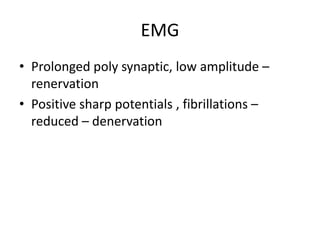
The document discusses the anatomy and clinical examination of the peripheral nervous system. It describes various nerves including the radial nerve, median nerve, ulnar nerve, and brachial plexus. It discusses the muscles each nerve innervates and how to test muscle strength. It also covers common nerve injuries, clinical presentations, and diagnostic techniques.