The document is a webinar overview on BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) hosted by Razvan Radulian, detailing its significance in addressing communication and precision issues in business process management. It discusses the fundamentals of BPMN, its advantages and challenges, as well as comparisons to alternative modeling techniques. Additionally, it highlights the importance of following best practices in creating BPMN models to ensure effective communication and process execution.







![Try this…
Try to explain the “Pull a cat by the tail” process and why
it’s not such a good idea:
• to a 2-year old child:
– Mostly Semantics
– Simple or no [standard] Symbols and/or Syntax
• to a Business Partner/Executive:
– Should be standard/precise Symbols, Syntax, and Semantics…
…BUT, often times, it’s a mix of inconsistent Symbols, confusing
“Syntax”, and imprecise & implied Semantics
As you can guess, talking with Business Partners/Execs is
(should be) a “bit” more complex…
… does our communication meet that requirement?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpmnprimerrradulianaspe-140912173332-phpapp02/85/BPMN-Primer-Razvan-Radulian-ASPE-Webinar-2013-9-320.jpg)

![Critics to BPMN
“Too complex for business people”
“Not expressive enough”
“There are a lot of bad BPMN models”
…so “BPMN is [must be] bad for Business People!”
But, does that make any sense?!?
Compare that with…
– Is English bad for communication only because many
college applicants submit bad essays (i.e. misspelled
words, wrong syntax, unclear message, messy, etc.)?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpmnprimerrradulianaspe-140912173332-phpapp02/85/BPMN-Primer-Razvan-Radulian-ASPE-Webinar-2013-11-320.jpg)

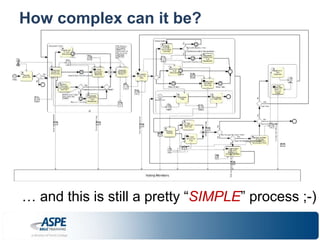
![IMPOSSIBLE to cover BPMN in 1-hour*…
Fundamentals (Descriptive level):
– Flow elements: Activities, Gateways, Events
– Connectors: Sequence & Message Flow, Associations
– Pools & Lanes
– Data & Artifacts
Some [of the many] unique features:
– Orchestration (internal) AND collaboration between
Participants/Processes
– Integrating Human Tasks/Workflow AND Automated Services
– “Happy path” AND Alternate/Exceptions paths
– Escalations & Compensations
– Fit for communication (business & IT) AND process execution
* A full BPMN class will be offered starting spring of 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpmnprimerrradulianaspe-140912173332-phpapp02/85/BPMN-Primer-Razvan-Radulian-ASPE-Webinar-2013-13-320.jpg)
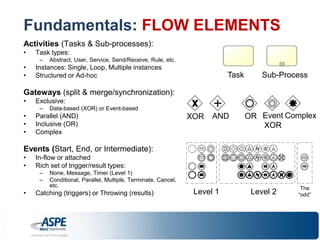
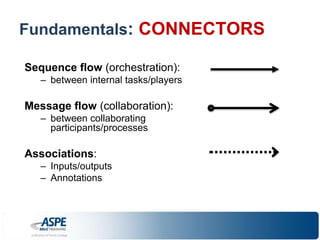
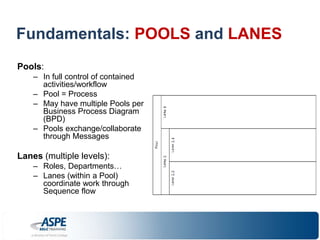
![Fundamentals: DATA & ARTIFACTS
Data:
– Data Objects
• Input & Output
• Have state (e.g.
Request[Approved])
• Process-data
– Data Store:
• Permanent storage (e.g.
database, repository, etc.) of the
process data
Artifacts:
– Annotations
– Group](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpmnprimerrradulianaspe-140912173332-phpapp02/85/BPMN-Primer-Razvan-Radulian-ASPE-Webinar-2013-18-320.jpg)

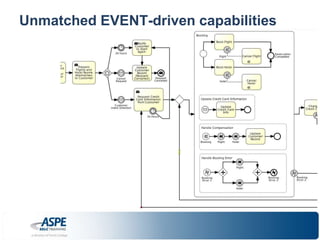
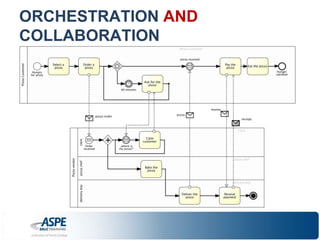
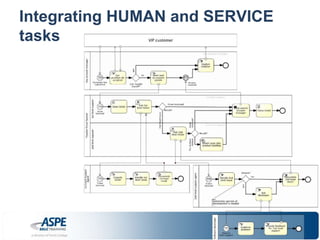
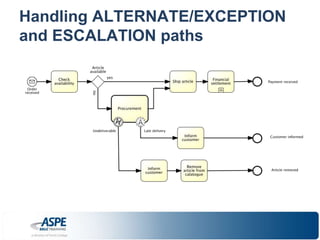
![Some of [the many] UNIQUE features!
• Rich/unmatched event-driven capabilities
• Explicit definition/description of BOTH…
– Orchestration of internal activities/tasks AND
– Collaboration between Participants/Processes
• Integration of BOTH…
– Human Tasks/Workflow AND
– Automated Services (heard of SOA?)
• Going beyond the “Happy path”, in a clear and
concise way:
– Alternate/Exceptions paths:
• attached events: Interrupting and Non-interrupting (BPMN 2.0)
– Escalations & compensations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpmnprimerrradulianaspe-140912173332-phpapp02/85/BPMN-Primer-Razvan-Radulian-ASPE-Webinar-2013-20-320.jpg)