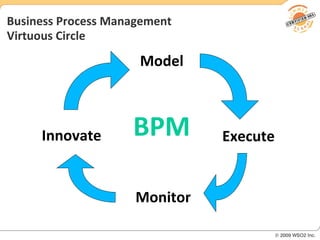
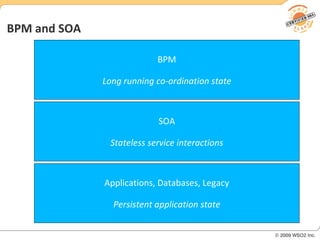
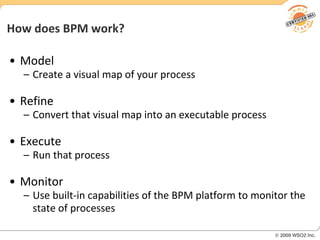
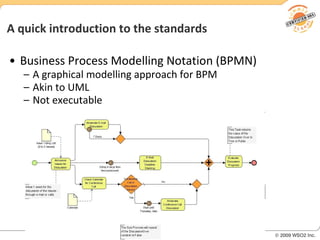
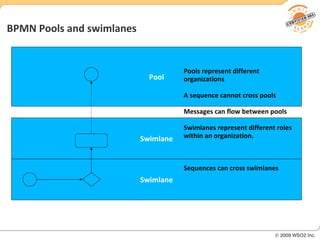
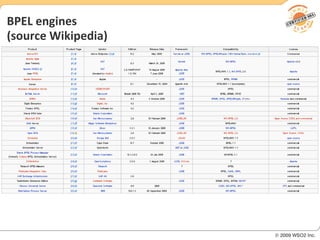
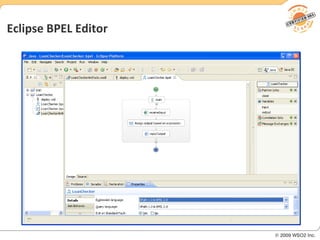
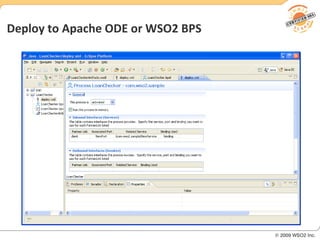
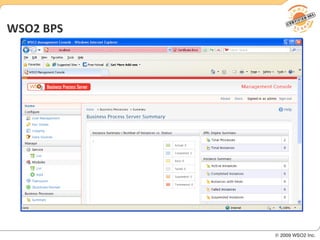
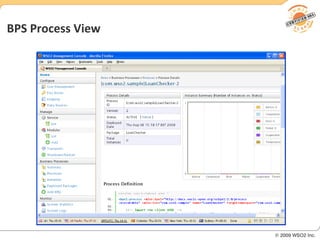
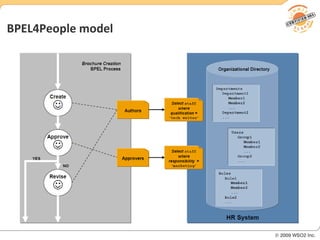
BPM involves defining, executing, and monitoring business processes to improve operations. BPM works with SOA by connecting processes to distributed services. BPMN models processes visually while BPEL allows executable orchestration of services within a process. Monitoring processes is a key benefit of BPM.
![BPM and SOA Paul Fremantle [email_address] CTO and Co-Founder, WSO2 VP, Apache Synapse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssbpm-090809225354-phpapp02/75/Ssbpm-1-2048.jpg)