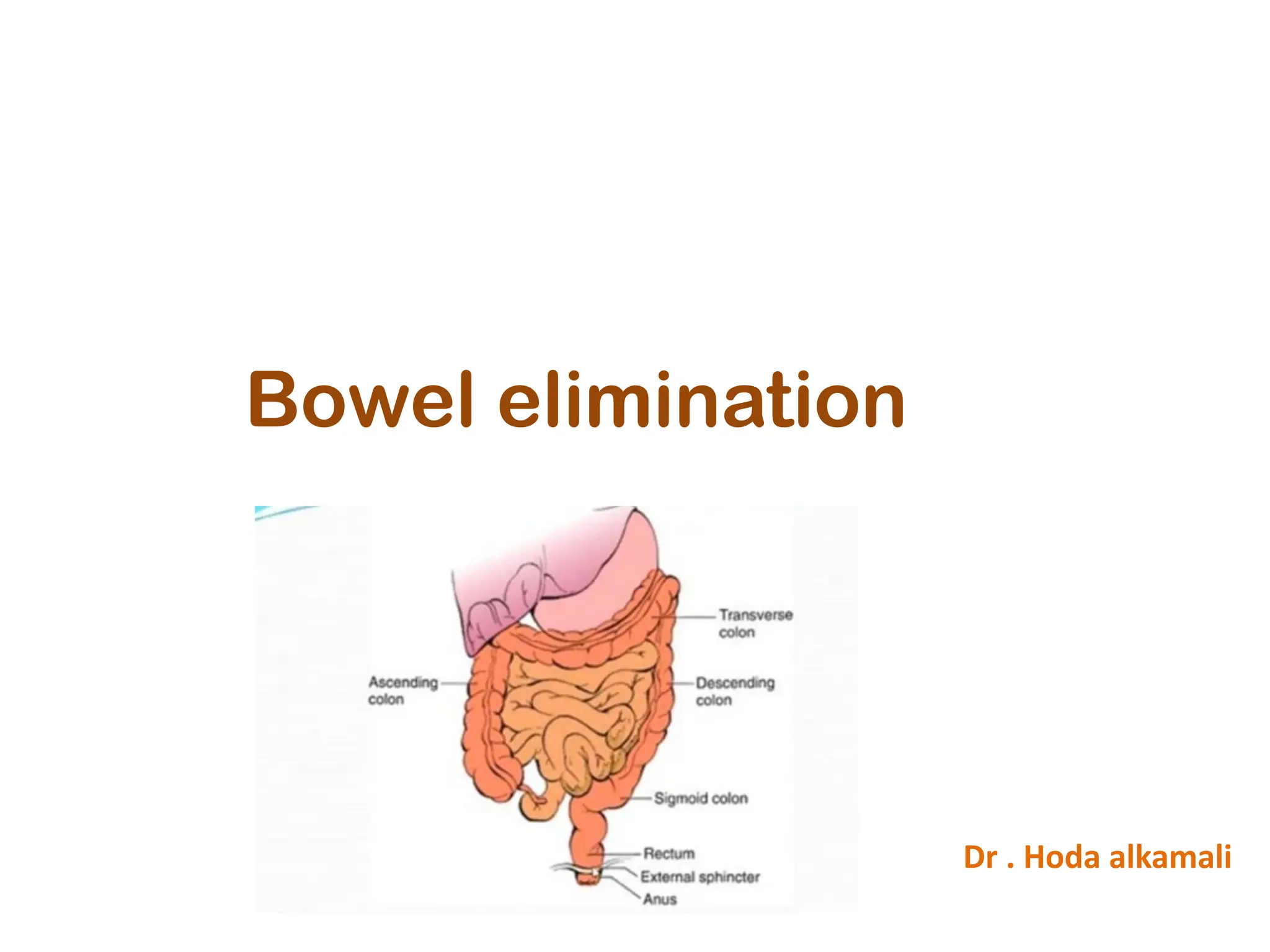
This document outlines the process and assessments involved in bowel elimination, describing the mechanisms of defecation, and common alterations such as constipation, fecal impaction, diarrhea, and fecal incontinence. It also provides guidelines for nursing management, health education on bowel health, and procedures for bowel irrigation and gas relief. Key points include recognizing symptoms, identifying types of constipation, and the importance of regular assessments, especially for older adults.