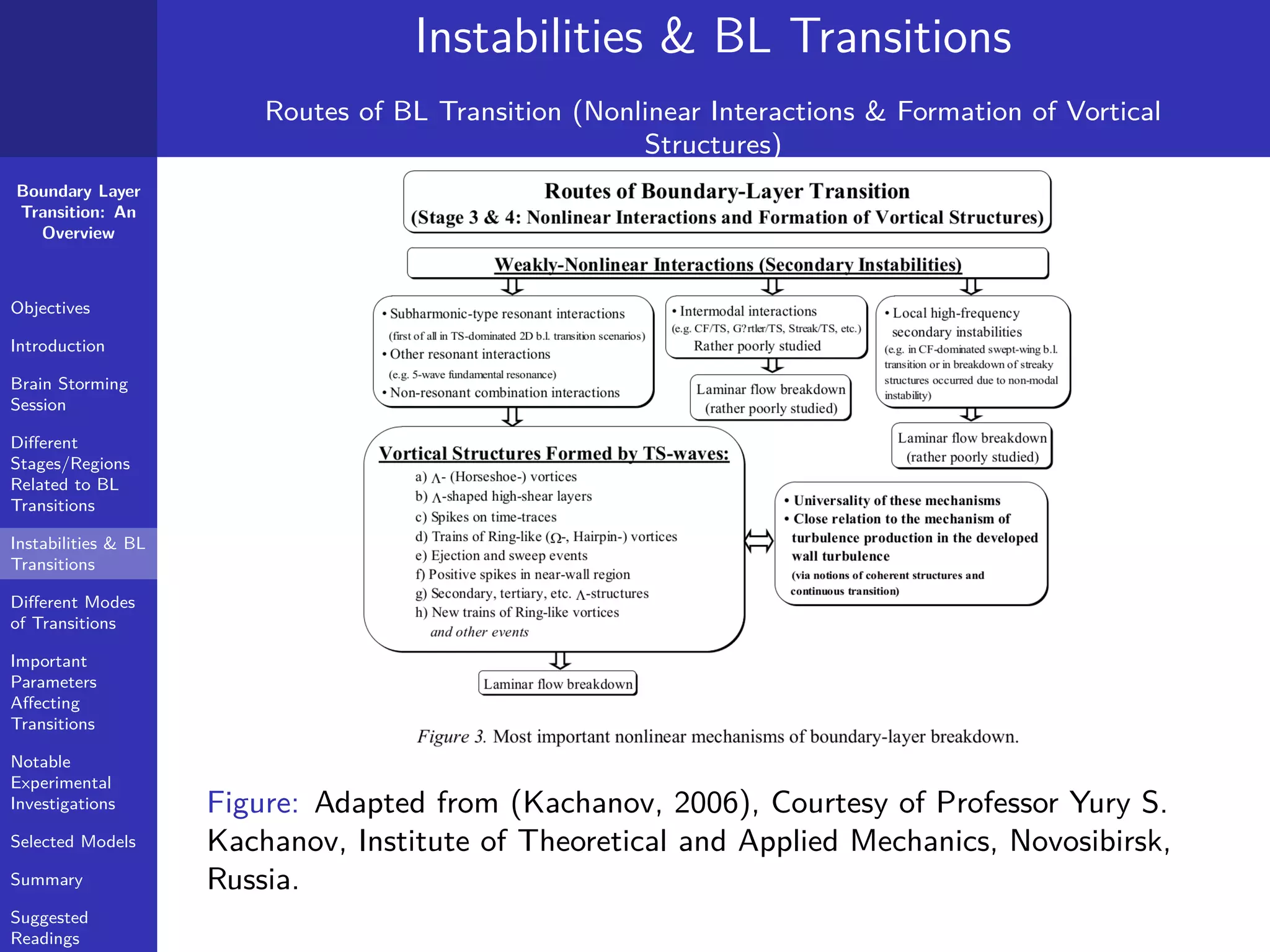
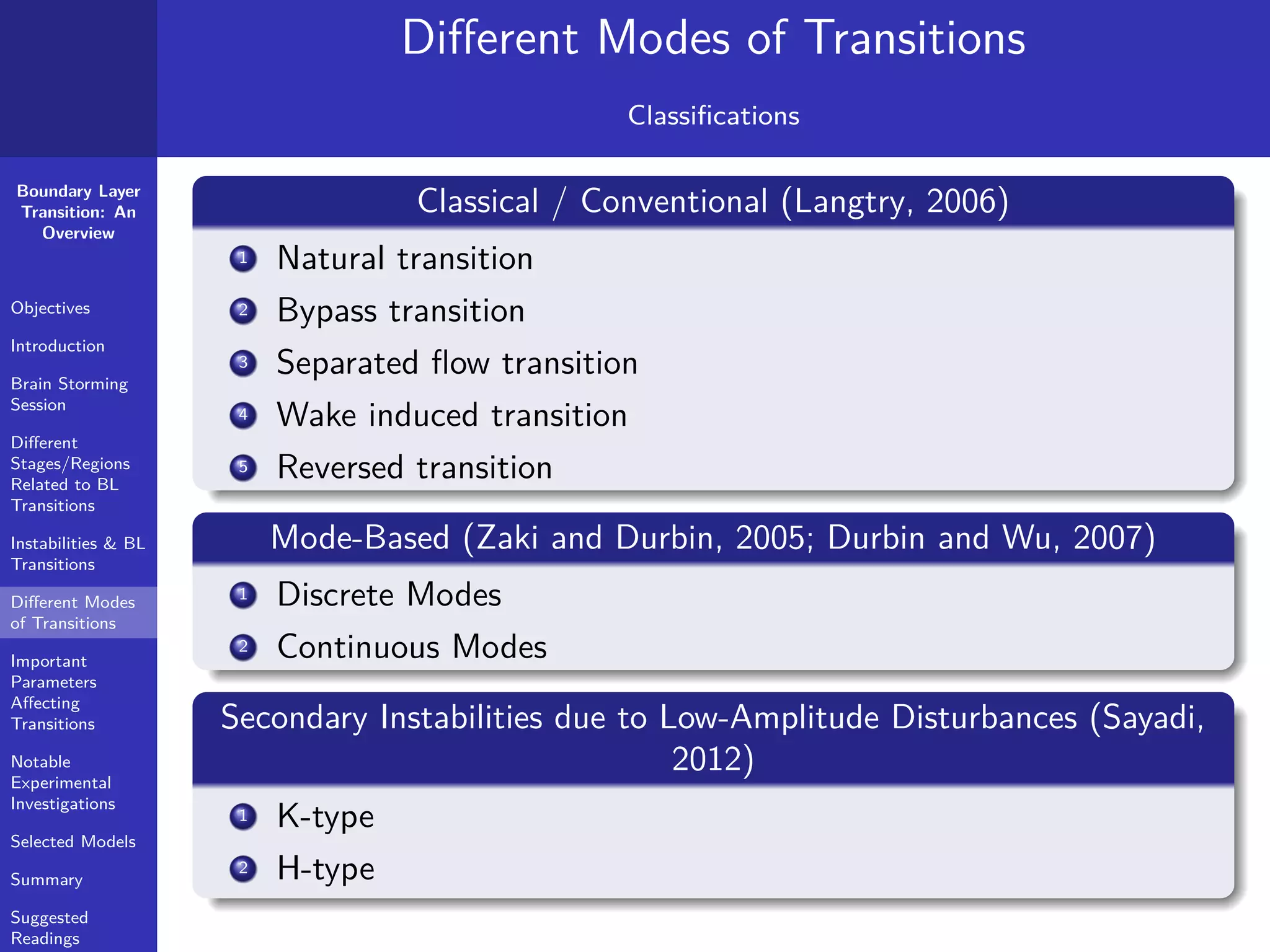
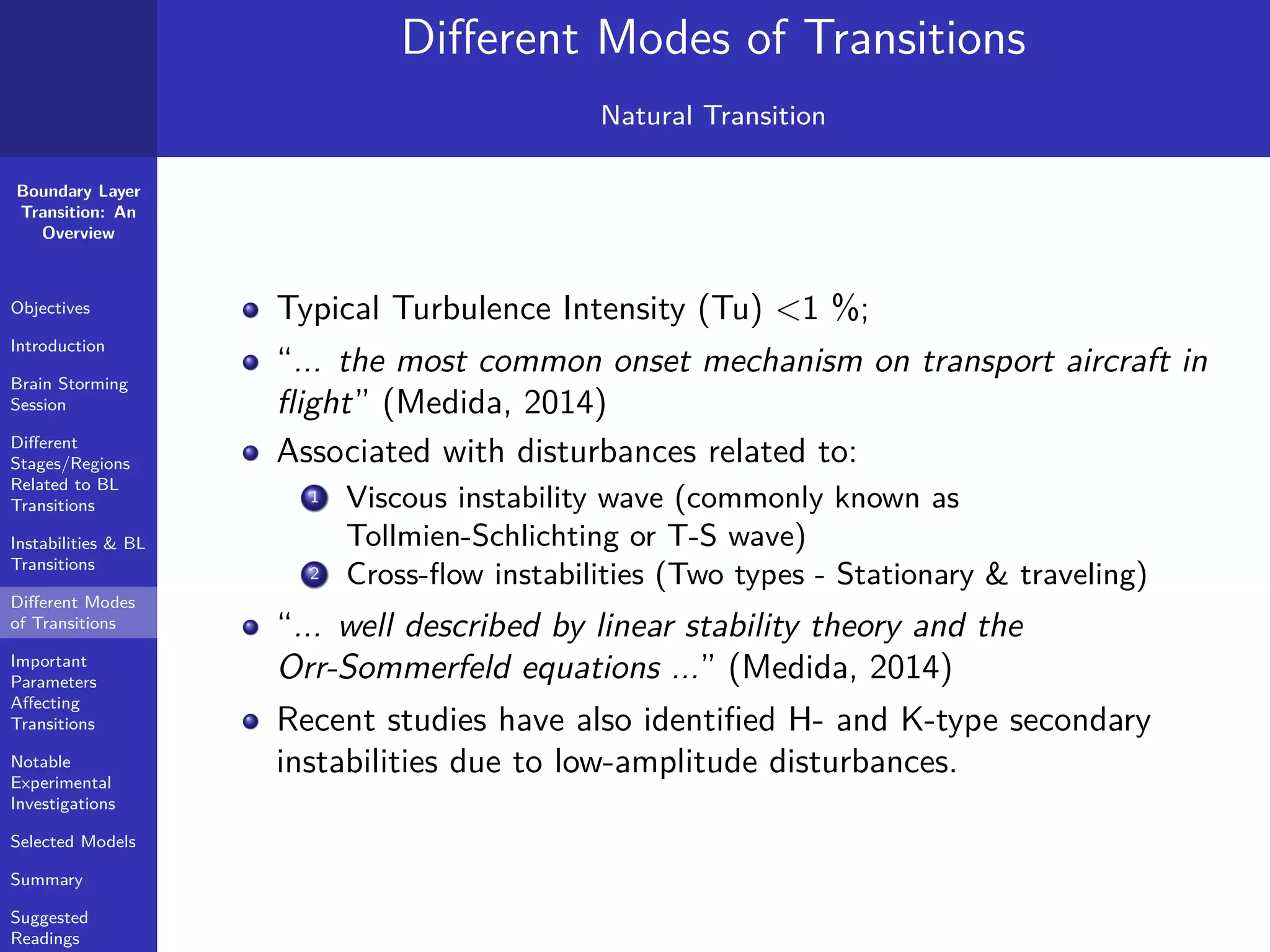
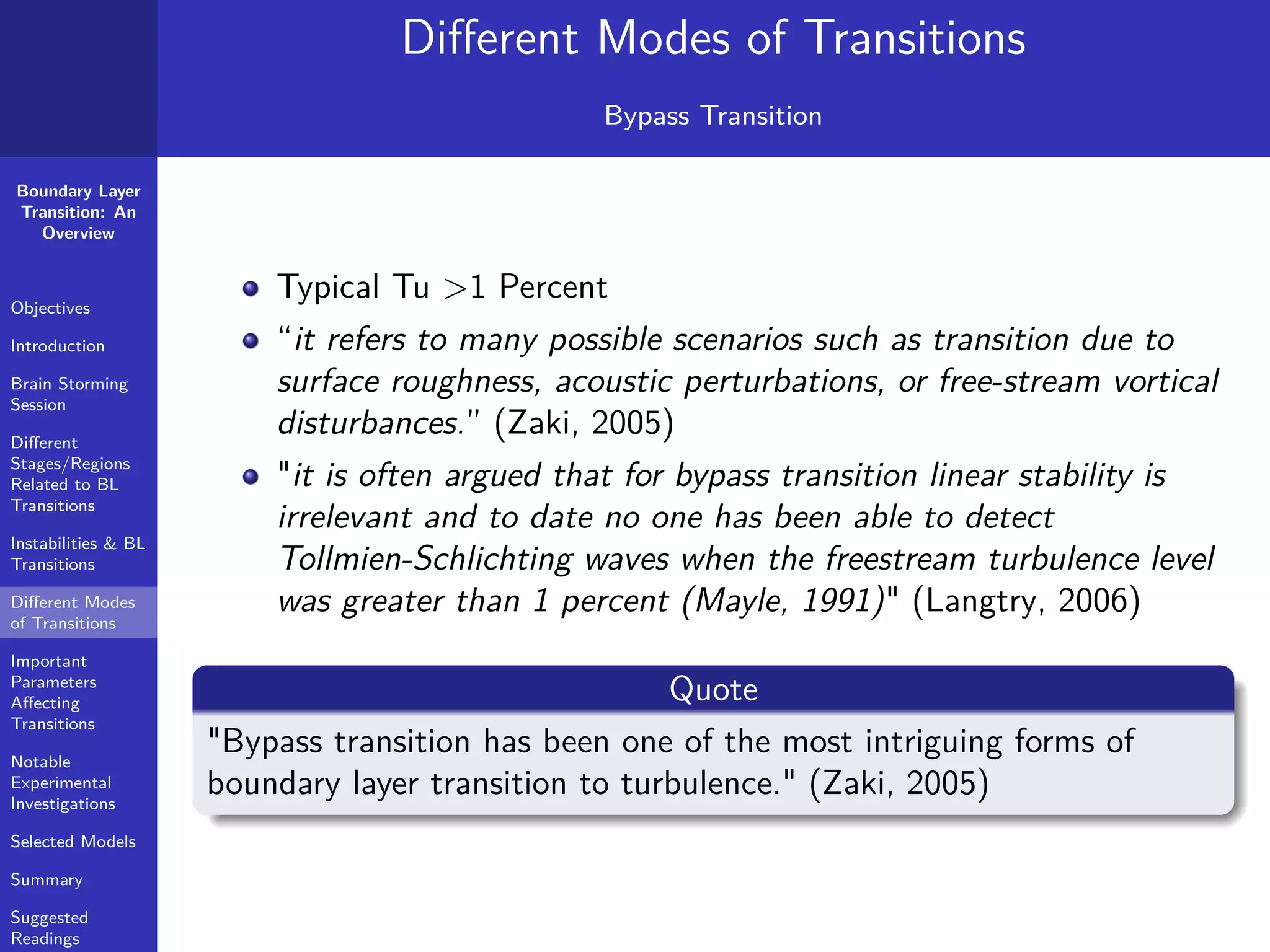
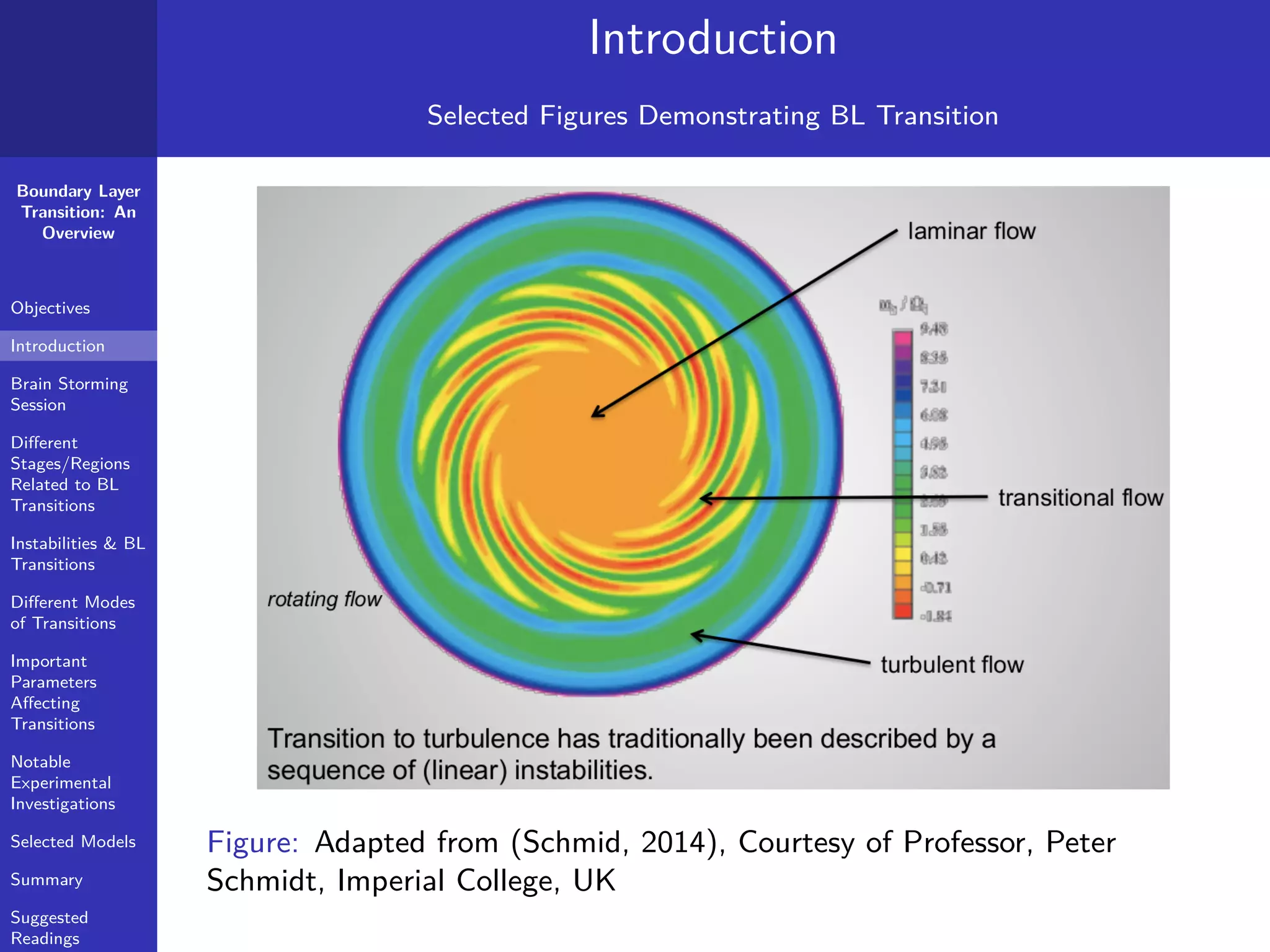
The document provides a comprehensive overview of boundary layer transition (BLT), detailing its objectives, stages, and different modes linked to instabilities. It emphasizes the importance of understanding BLT for accurately predicting aerodynamic drag and highlights various types of instabilities and experimental investigations. Key concepts such as critical Reynolds numbers, natural and bypass transitions, as well as secondary instabilities, are discussed extensively.











![Boundary Layer
Transition: An
Overview
Objectives
Introduction
Brain Storming
Session
Different
Stages/Regions
Related to BL
Transitions
Instabilities & BL
Transitions
Different Modes
of Transitions
Important
Parameters
Affecting
Transitions
Notable
Experimental
Investigations
Selected Models
Summary
Suggested
Readings
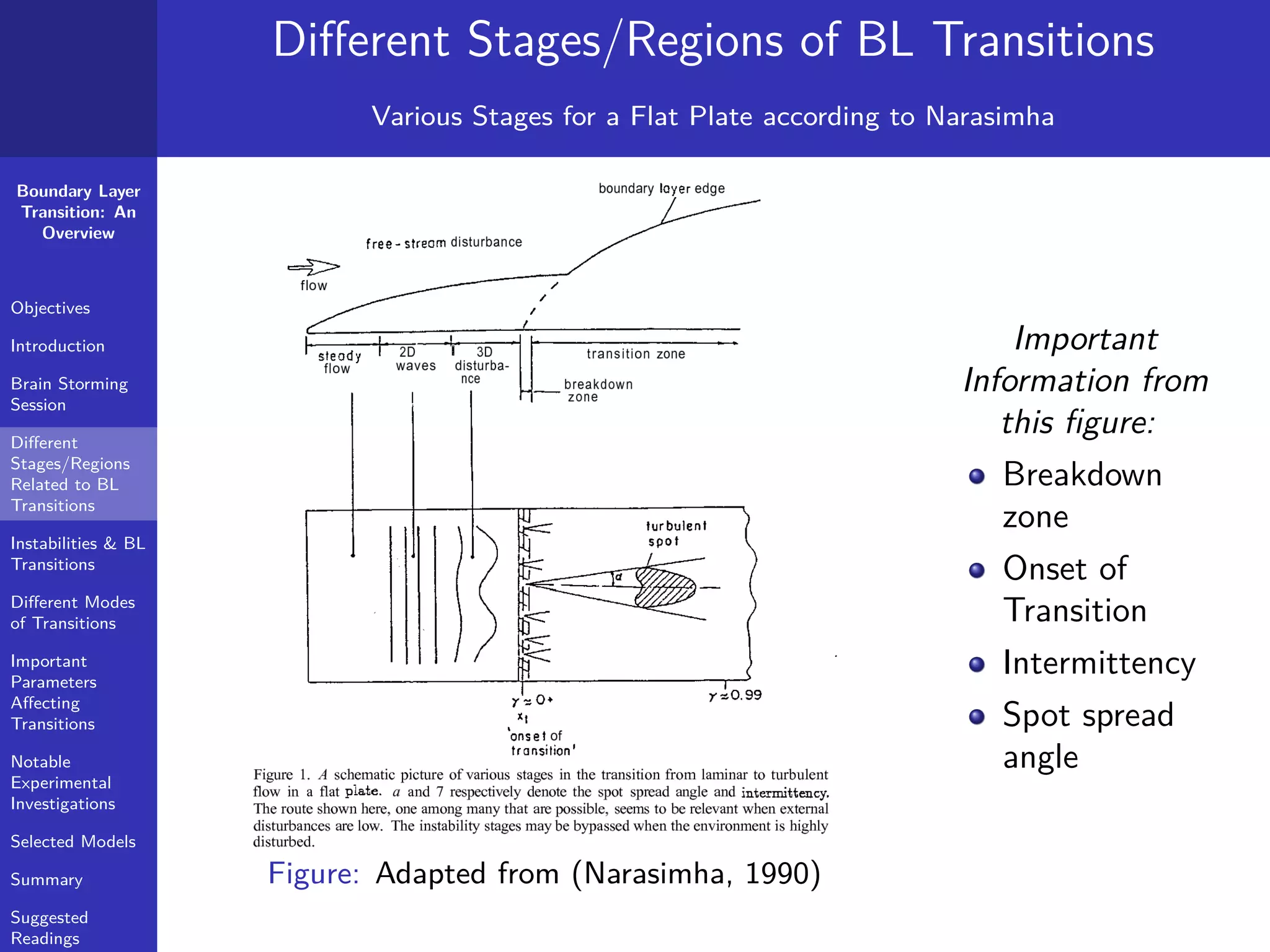
Different Stages/Regions of BL Transitions
"Onset of Transition", "Turbulent Spot" & "Intermittency"
Onset of Transition: "The point of minimum skin friction is
typically considered the start of transition" (Medida, 2014)
Turbulent Spot: "... a turbulent spot is initiated when the
maximum velocity fluctuation in the streamwise direction
exceeds about one-fifth of the freestream velocity, almost
independently of the Reynolds number [16]. " (Medida, 2014)
Intermittency: "The intermittency factor was introduced [17] to
quantify the rate of turbulent spot production and a relation
between the transition Reynolds number and the intermittency
factor was deduced. Once initiated, these intermittent turbulent
spots grow in size and they travel downstream, until they merge
into a fully turbulent boundary layer, thus completing the
transition process." (Medida, 2014)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1bltransitionoverviewhandout20march2015-190624032149/75/Boundary-Layer-Transition-An-Overview-17-2048.jpg)
![Boundary Layer
Transition: An
Overview
Objectives
Introduction
Brain Storming
Session
Different
Stages/Regions
Related to BL
Transitions
Instabilities & BL
Transitions
Different Modes
of Transitions
Important
Parameters
Affecting
Transitions
Notable
Experimental
Investigations
Selected Models
Summary
Suggested
Readings
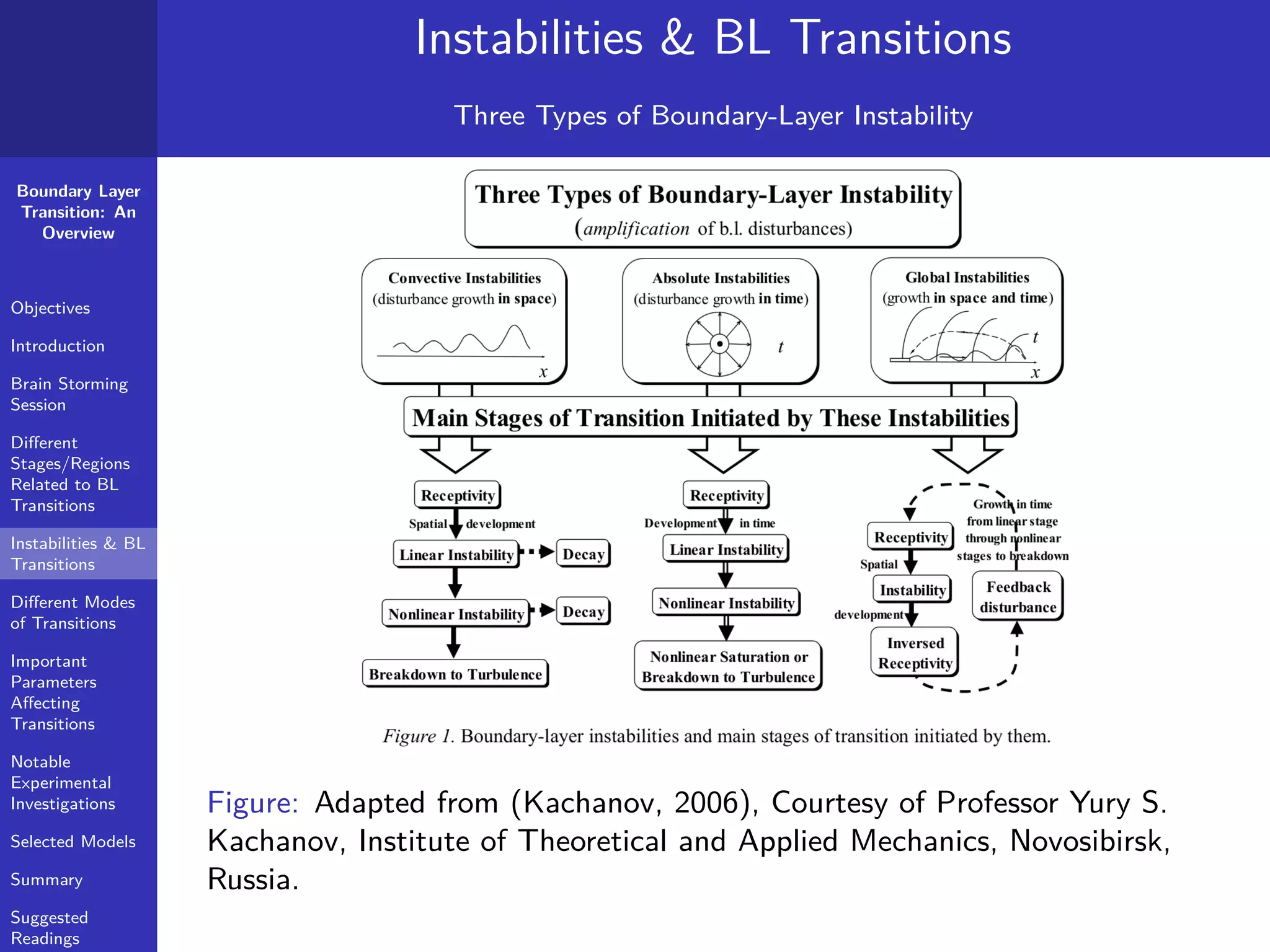
Instabilities & BL Transitions
What is Receptivity?
According to Kachanov (2006) -
"The term ’boundary-layer receptivity’ stands for various
mechanisms of transformation of external (with respect to the
boundary layer) perturbations into boundary-layer
perturbations."
"The receptivity process represents an initial stage of the
transition process(see Fig. 2 and reviews in [3-5]), which starts,
in fact, from the very leading edge, where the free stream just
touches with a body."
"Consequently, almost any laminar boundary layer can be
regarded as a transitional boundary layer, at least when the
Reynolds numbers are not too low."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1bltransitionoverviewhandout20march2015-190624032149/75/Boundary-Layer-Transition-An-Overview-20-2048.jpg)