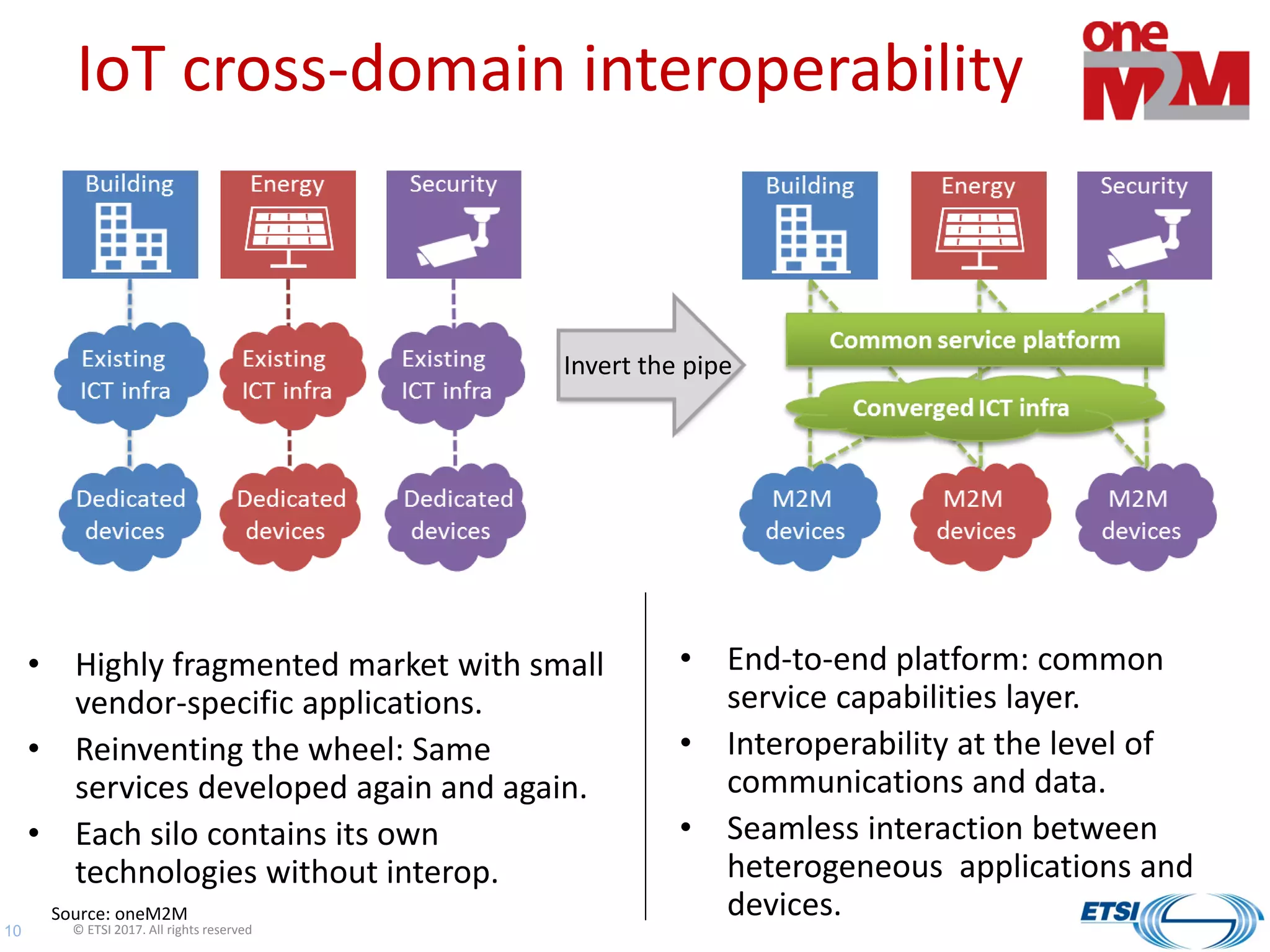
ETSI is working on several standards related to smart cities through various groups. These groups are developing standards for technologies like wireless connectivity, security, energy efficiency, and data management that are applicable to smart city initiatives. ETSI is also collaborating with external groups to further standardization efforts and help cities understand and apply relevant standards. The presentation provided an overview of ETSI's smart city-related groups and standards work.





![Open
Data
User
Apps
IoT
Smart City related Groups in ETSI
7
ISG CIM (Context Information Management)
© ETSI 2017. All rights reserved
Information
Systems
Context
Information
Management
Data
Publication
PlatformsCIM-API
[JSON-LD]
Context
Information
Models
Mca
Applications
EXAMPLE:
Citizen
Complaints
Photo-App
Application
Applications CIM-API
[JSON-LD]
System
Integrators
Linked Data
experts
Smart City
organisations
OpenSource
developers
Stakeholders
Public Authorities
Citizens!
Goal = interoperable exchange of data & metadata between systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boswarthickdavid-180523081150/75/Boswarthick-david-7-2048.jpg)