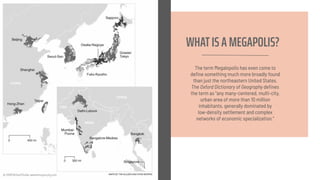
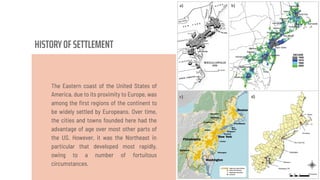
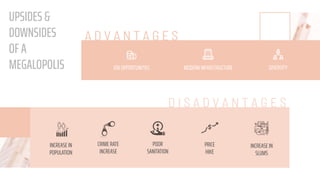
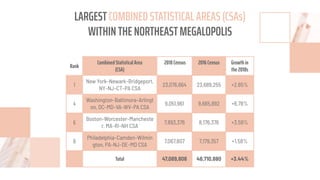
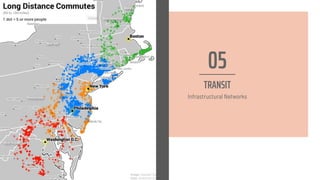
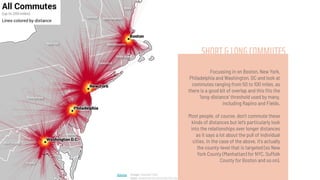
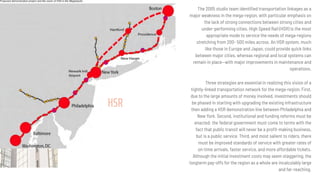
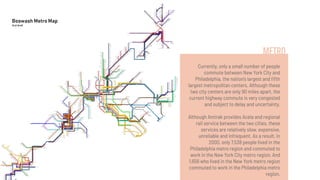
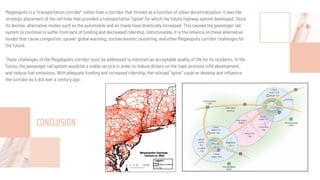
The document discusses the concept of a megalopolis, specifically focusing on the Northeast Megalopolis in the United States, which includes urban areas stretching from Washington, D.C. to Boston and has over 50 million residents. It highlights the historical development of the region, its dense population, and the role of transportation infrastructure, particularly rail systems, in shaping its urban landscape. The document also addresses the challenges faced by the region, including congestion, urban decentralization, and the decline of passenger rail services, suggesting that improved rail connectivity could enhance the quality of life and economic viability in the future.