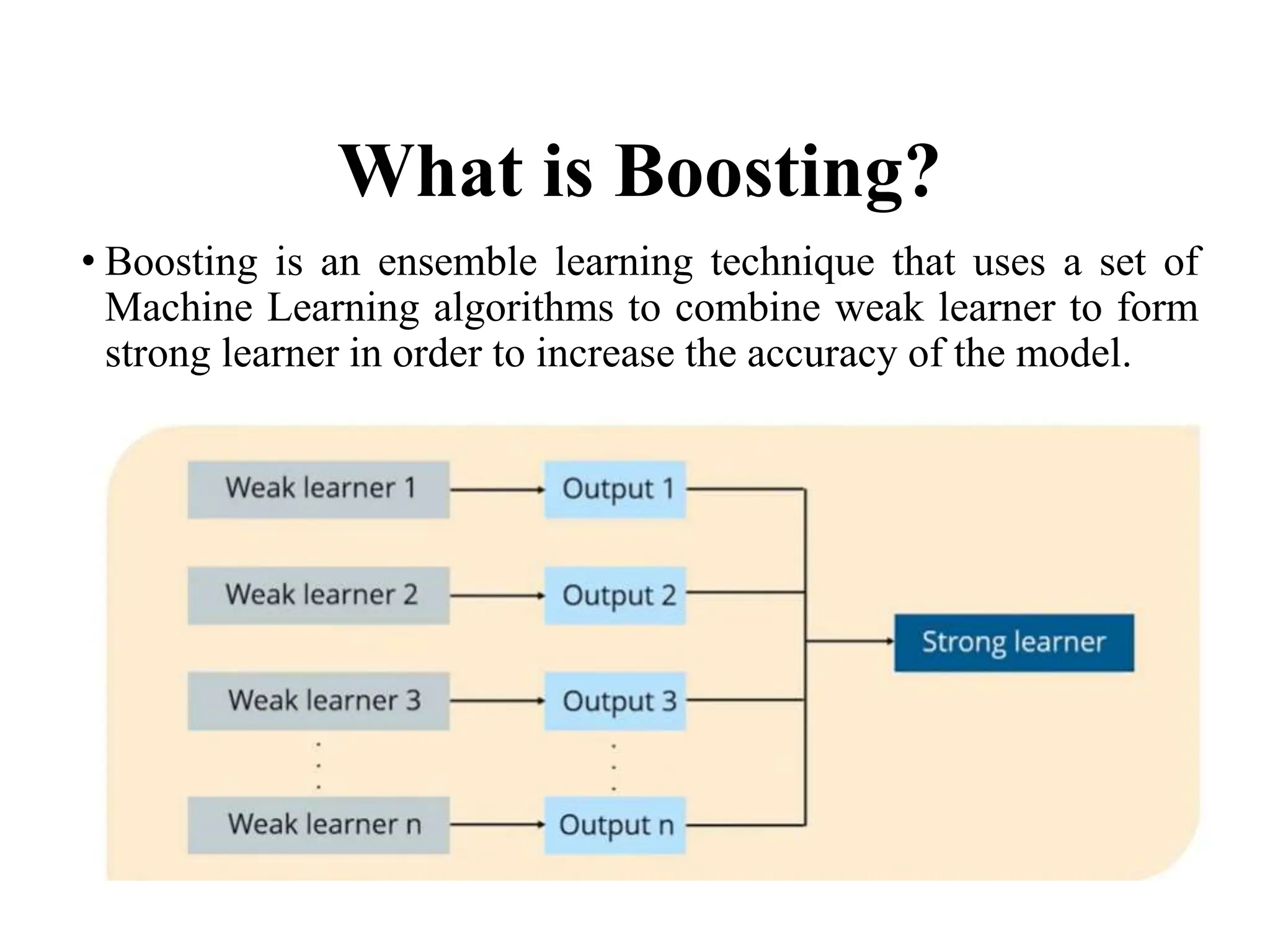
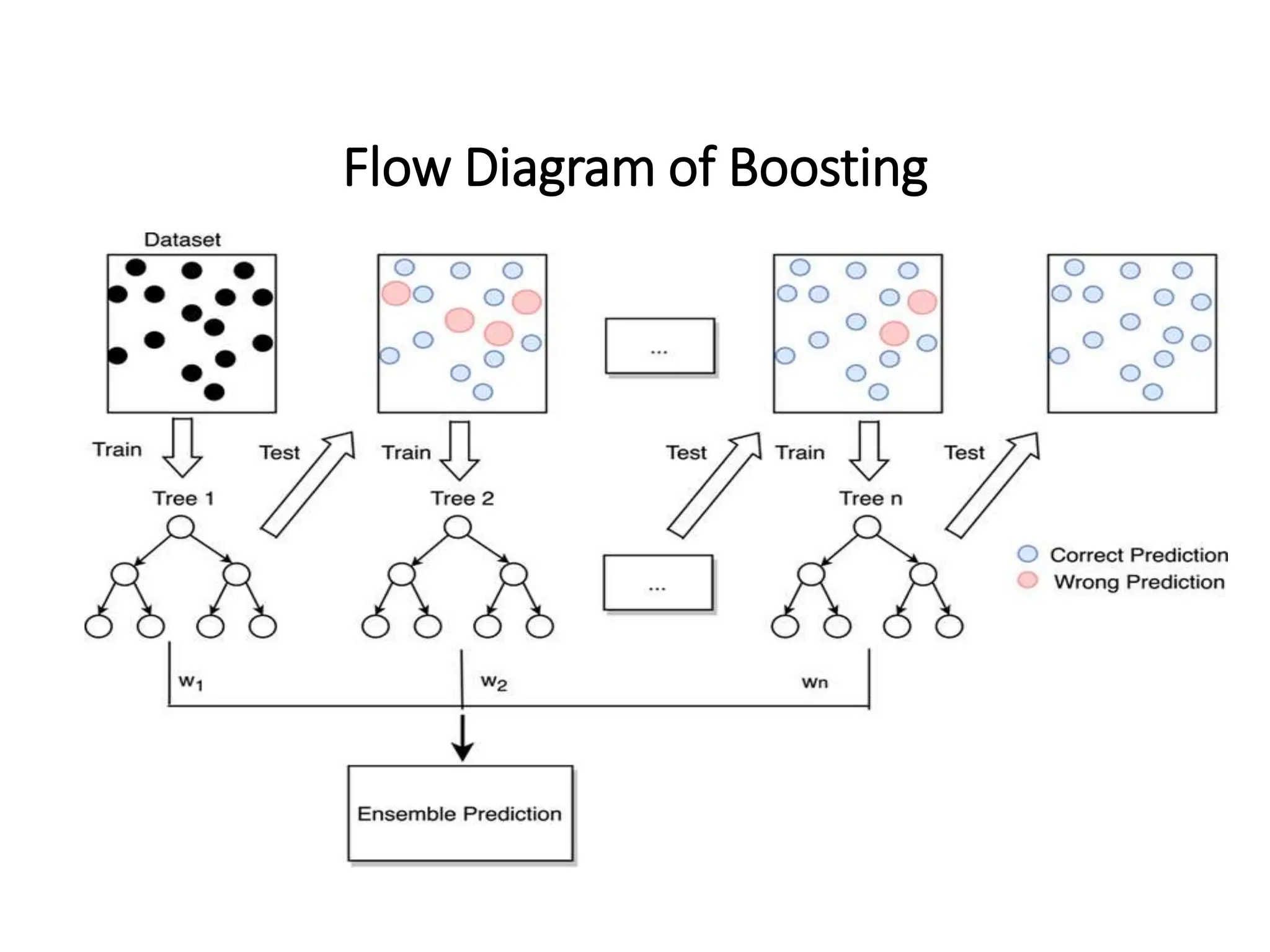
Boosting is an ensemble learning technique that combines multiple weak learners to create a strong learner, enhancing the model's accuracy when classifying data. It operates sequentially, adjusting the weights of misclassified samples to improve performance with each iteration. Various types of boosting methods include Adaboost, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost.