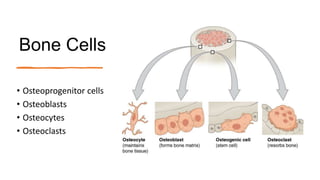
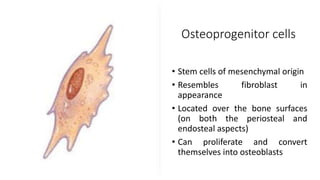
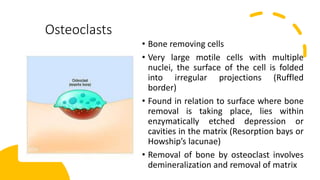
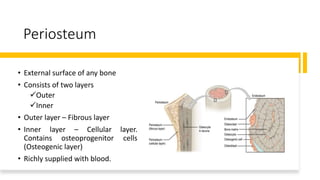
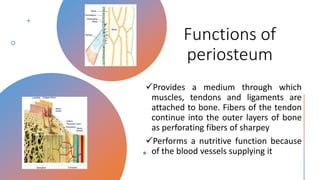
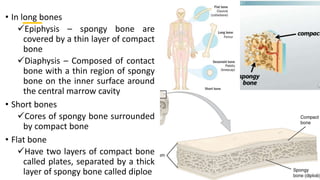
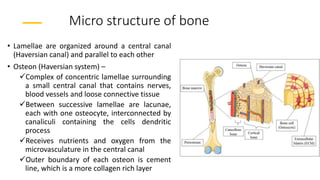
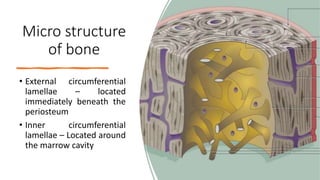
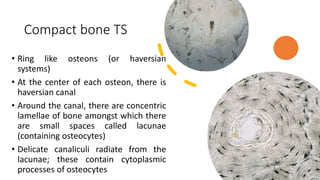
This document discusses the histology of bone. It describes bone as a specialized connective tissue composed of cells, an organic matrix, and inorganic minerals. The main cell types are osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Bone has two types of tissue - compact bone which is dense, and cancellous or spongy bone found deeper within bones. Microscopically, bone is made up of concentric rings called osteons surrounding central canals, with osteocytes housed in lacunae between lamellae. This detailed structure allows for nutrients and waste exchange to support the living cells.