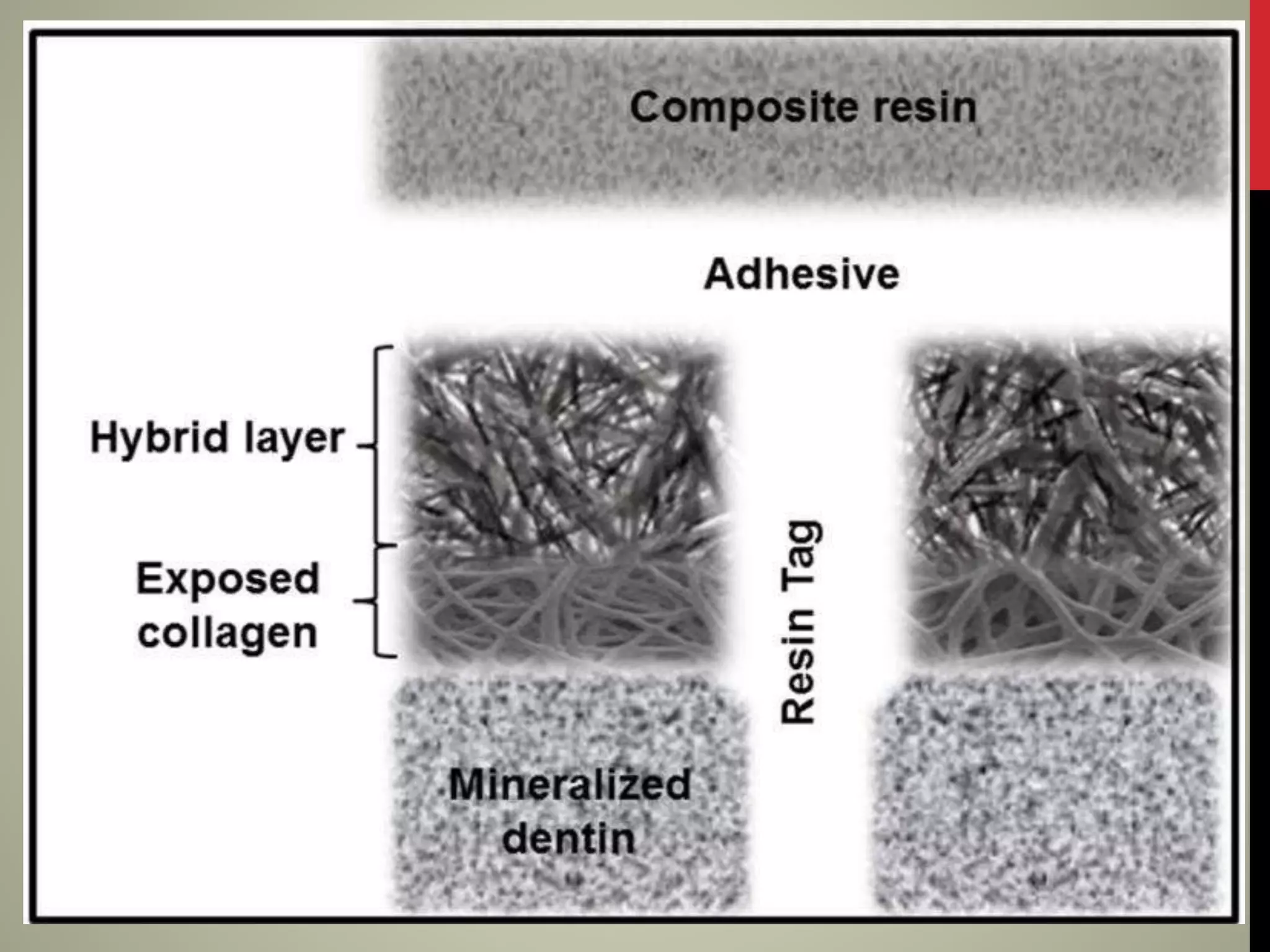
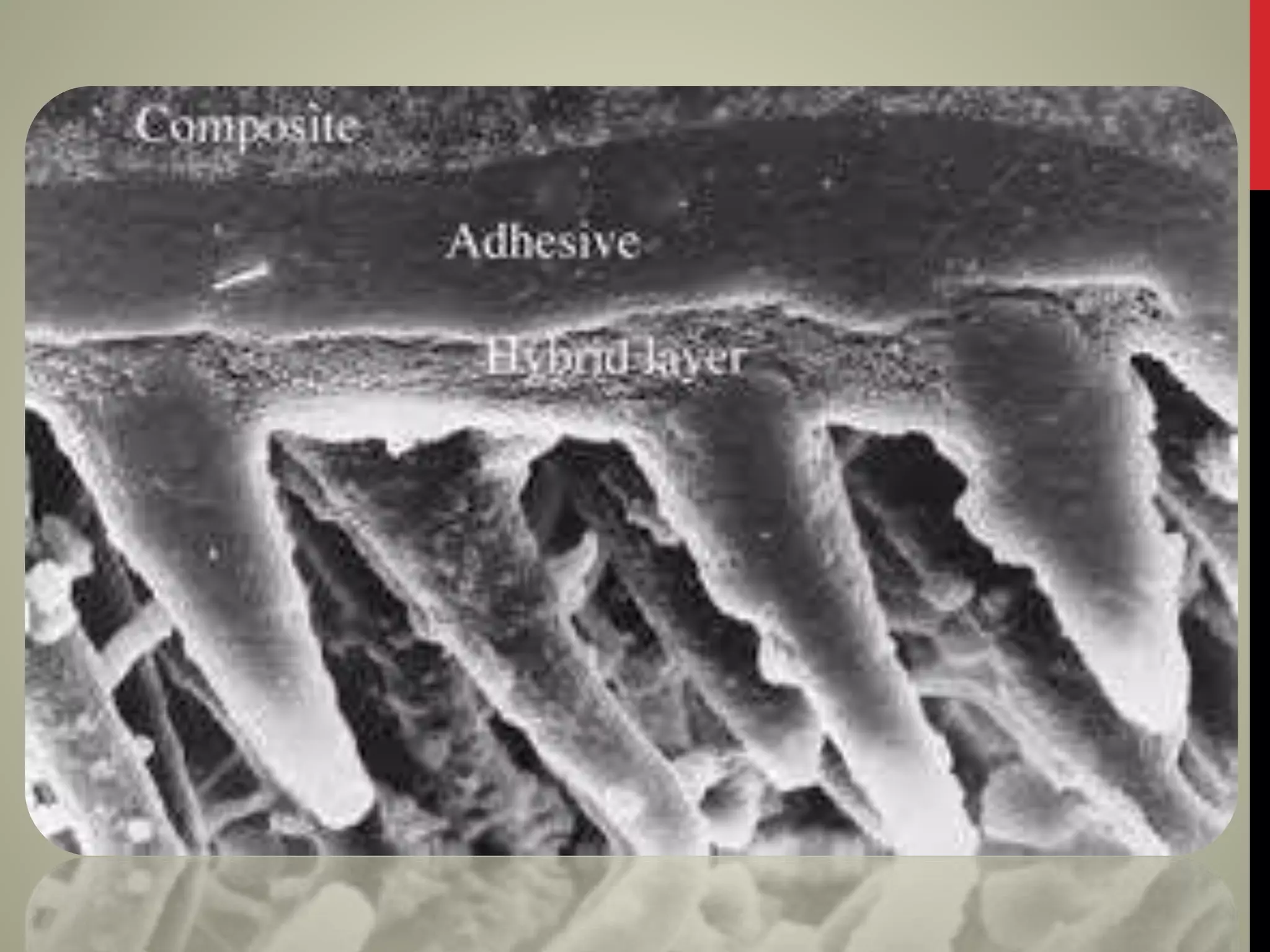
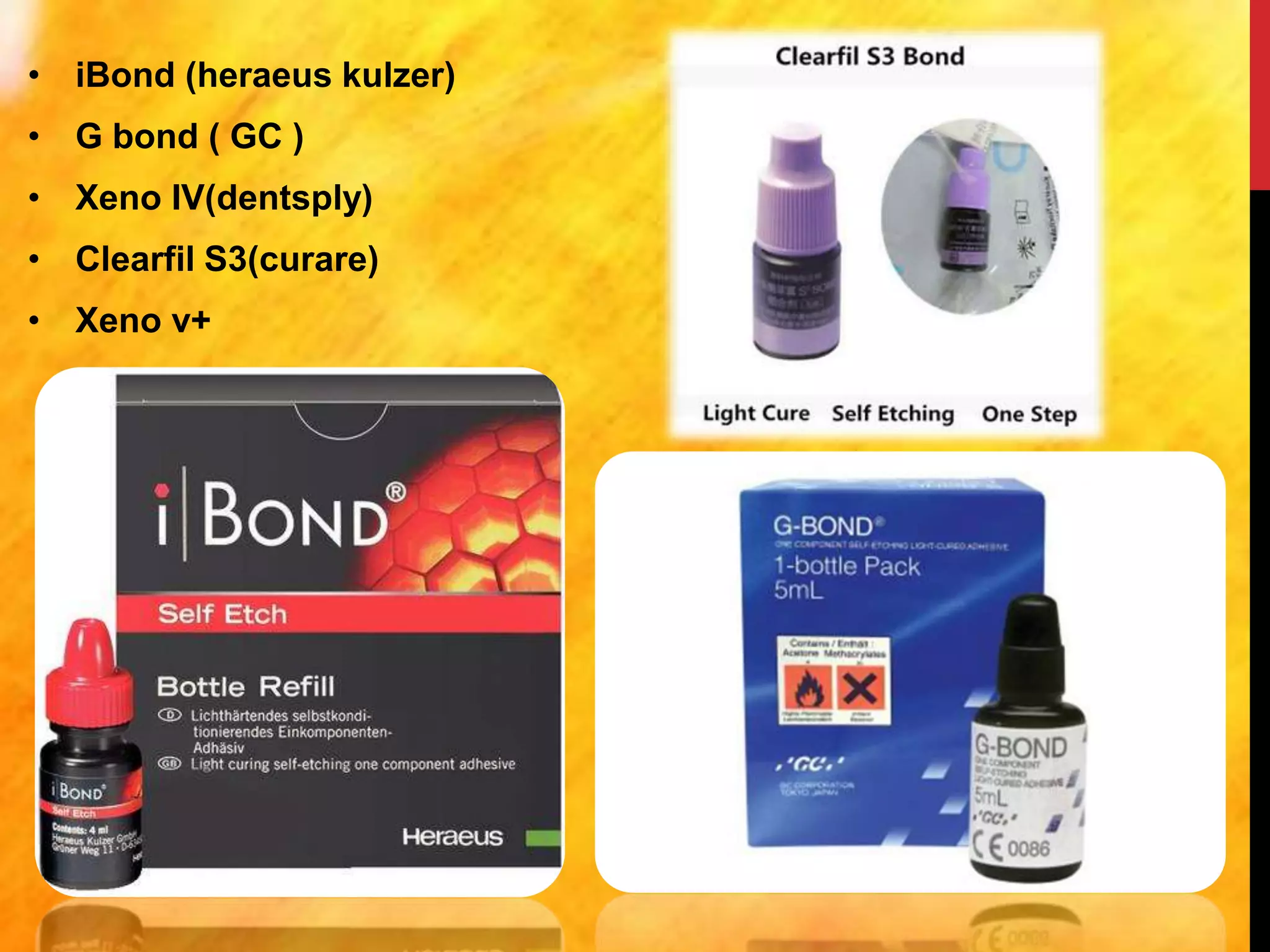
Universal adhesives were introduced as the seventh generation of dental adhesives. They can be used with self-etch, selective-etch, and total-etch techniques without needing separate activators. They contain MDP monomers that enable effective bonding to calcium, dentin, enamel, zirconia and metal alloys. Universal adhesives simplify the application process and are more resistant to contamination compared to previous adhesive generations. They form both a hybrid layer and chemical bonds through MDP monomers, making the bond more durable over time.