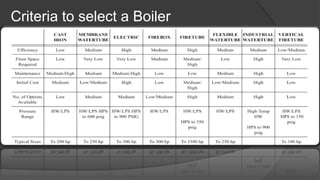
The document discusses the history and efficiency of steam-generating boilers, highlighting innovations by George Babcock and Steven Wilcox, as well as the principles of boiler efficiency and factors that affect it. It covers methods for maximizing efficiency, such as preheating feed water and using supplementary heat exchangers, along with the importance of safety devices in boiler operations. Waste heat recovery systems and various technologies for energy recovery are also outlined, emphasizing the significance of periodic maintenance and safety regulations.