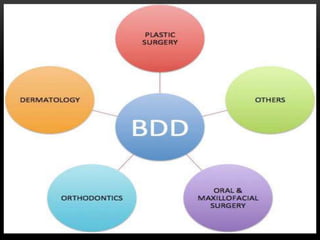
Body dysmorphic disorder is a mental health condition where one cannot stop thinking about a perceived flaw in their appearance that is not observable or only slightly noticeable to others. It causes significant distress and impairment and is often comorbid with depression, social anxiety, and obsessive compulsive disorder. Treatment involves cognitive behavioral therapy and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.