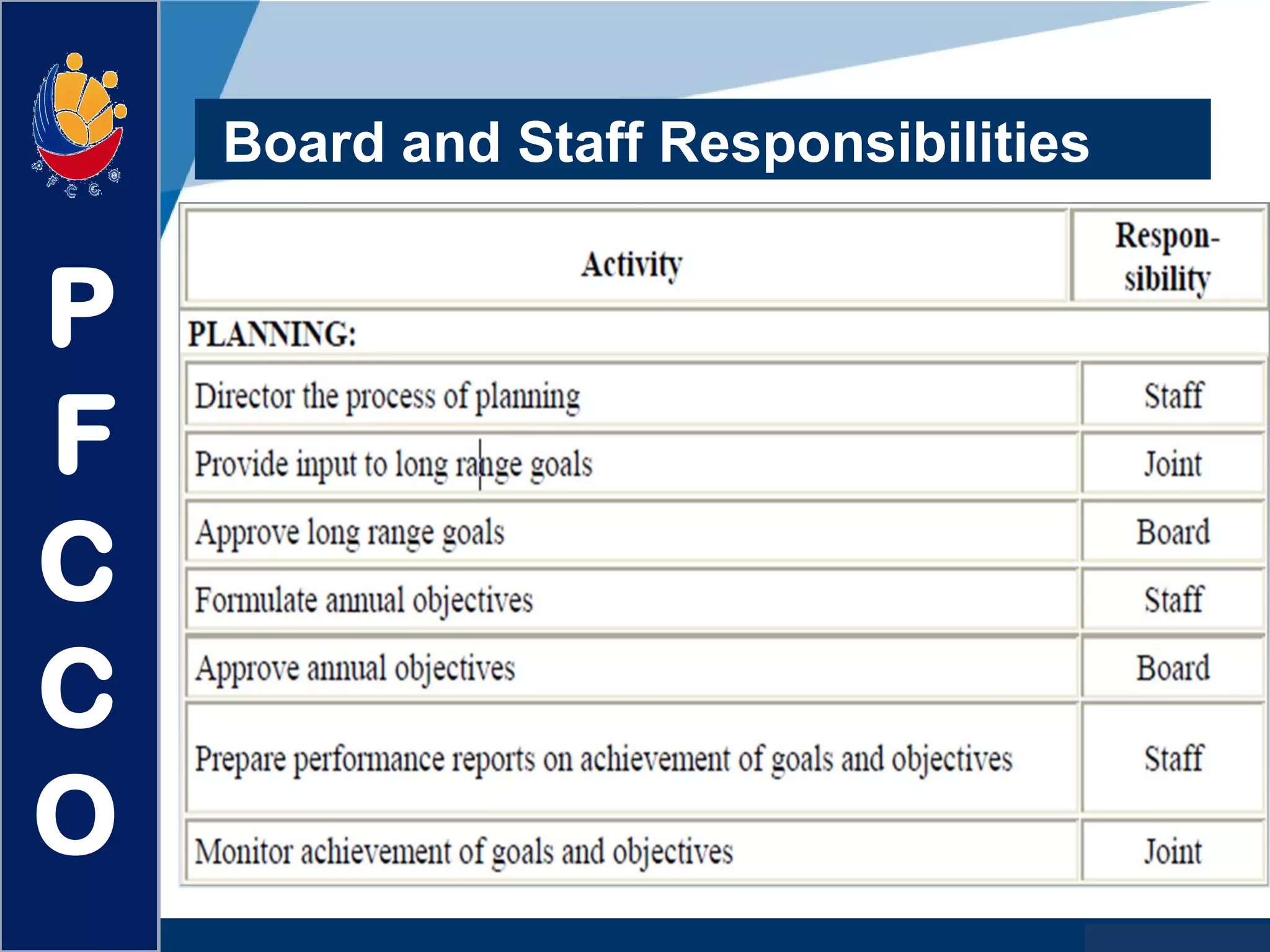
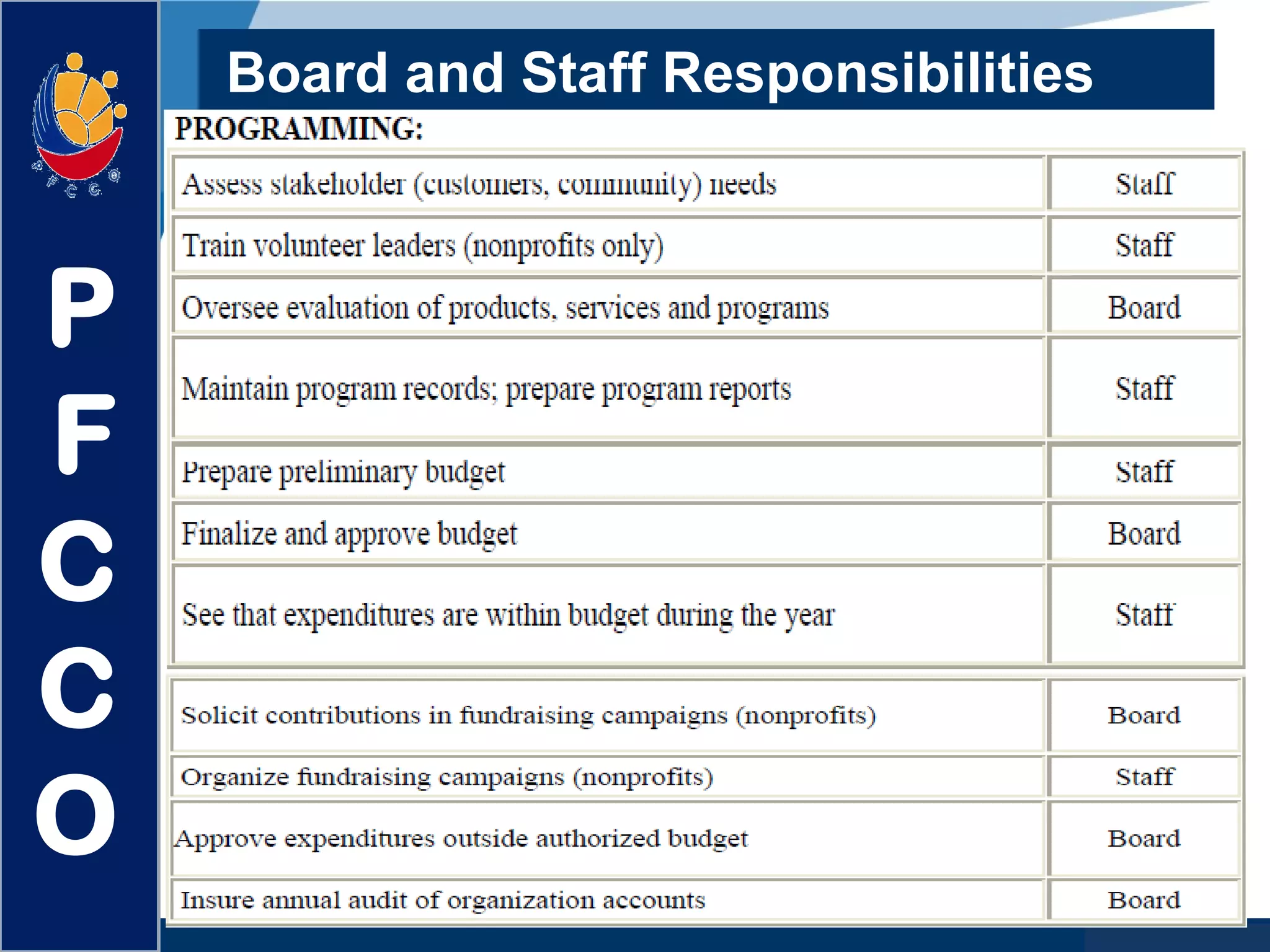
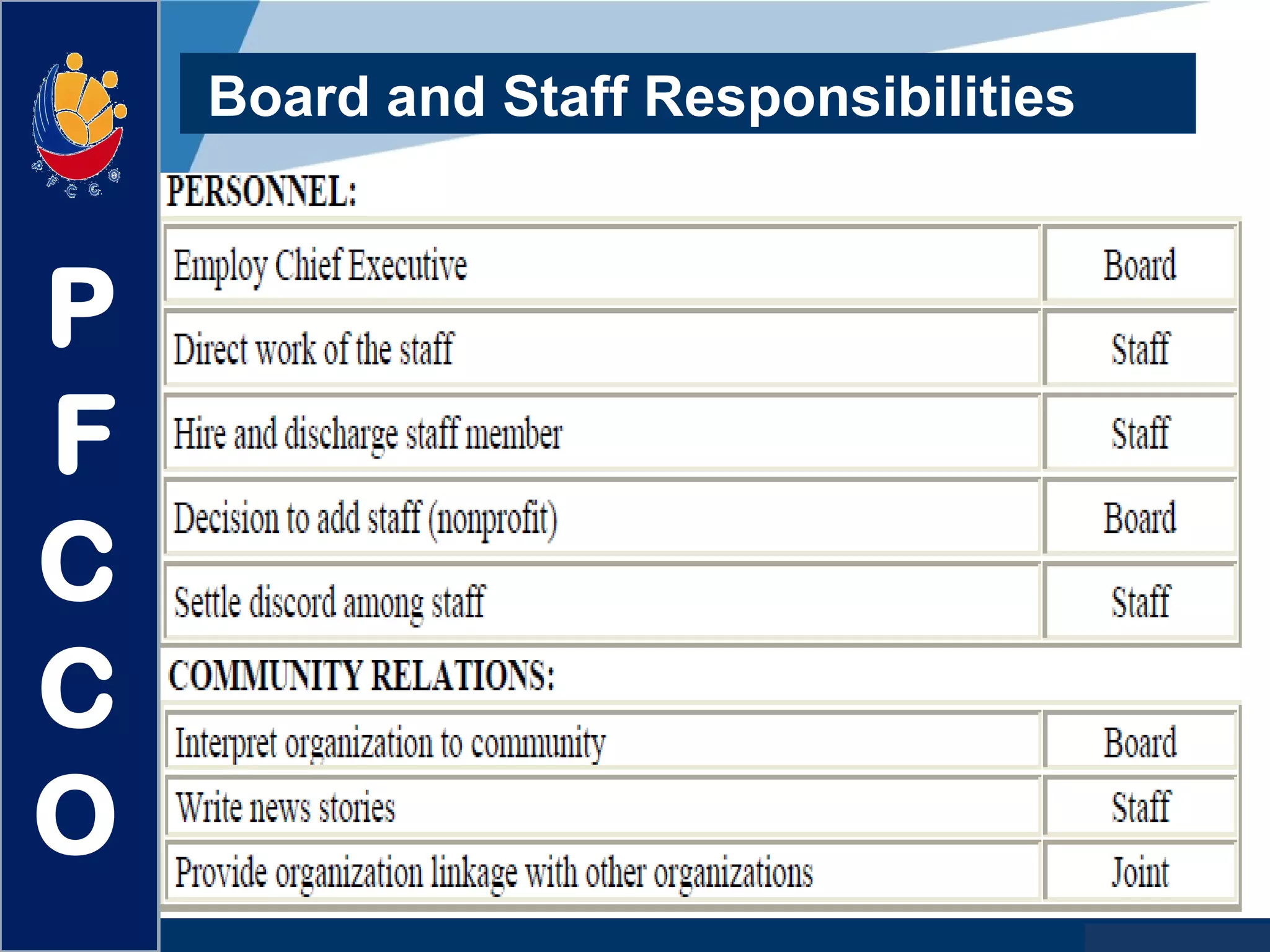
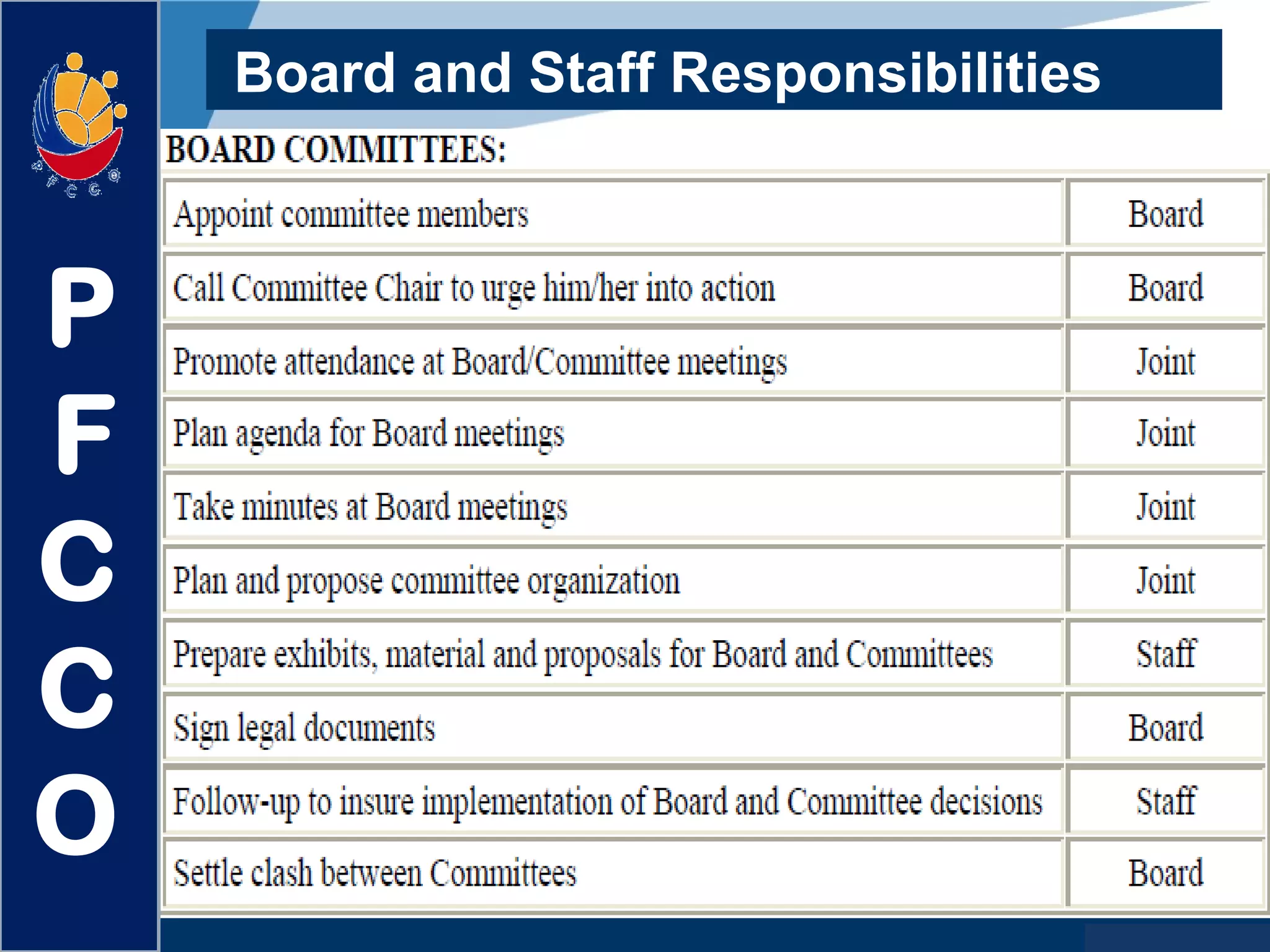
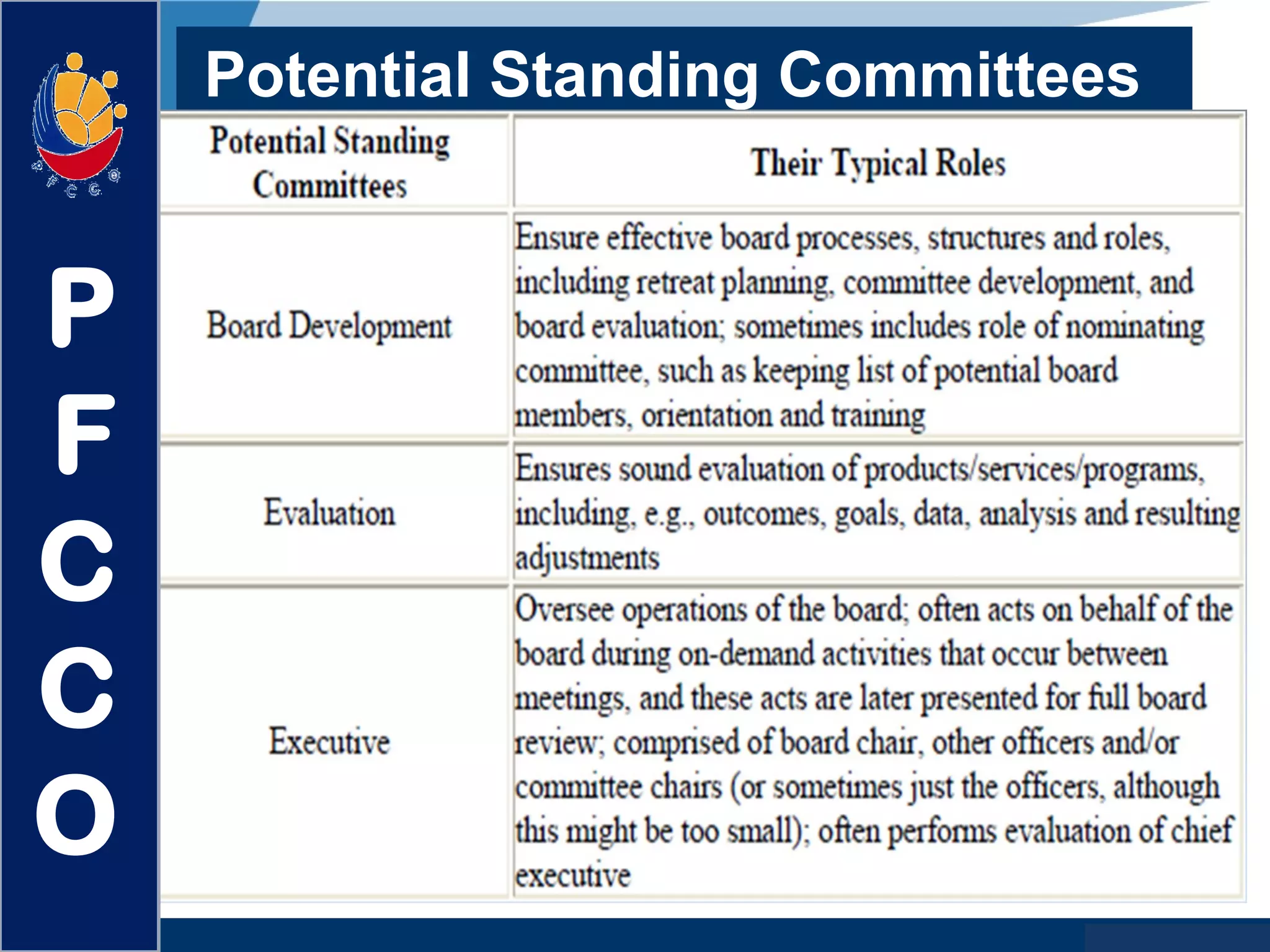
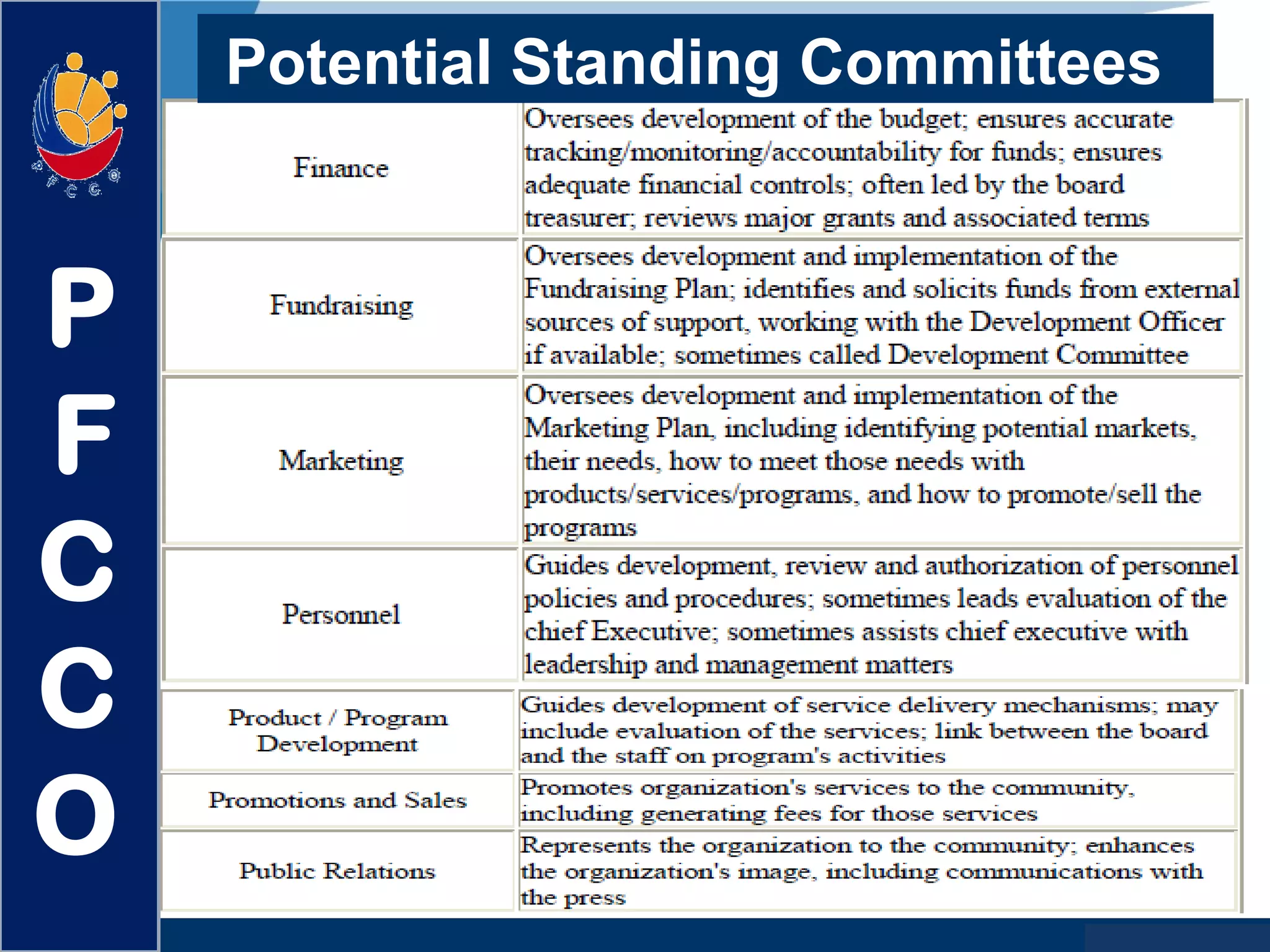
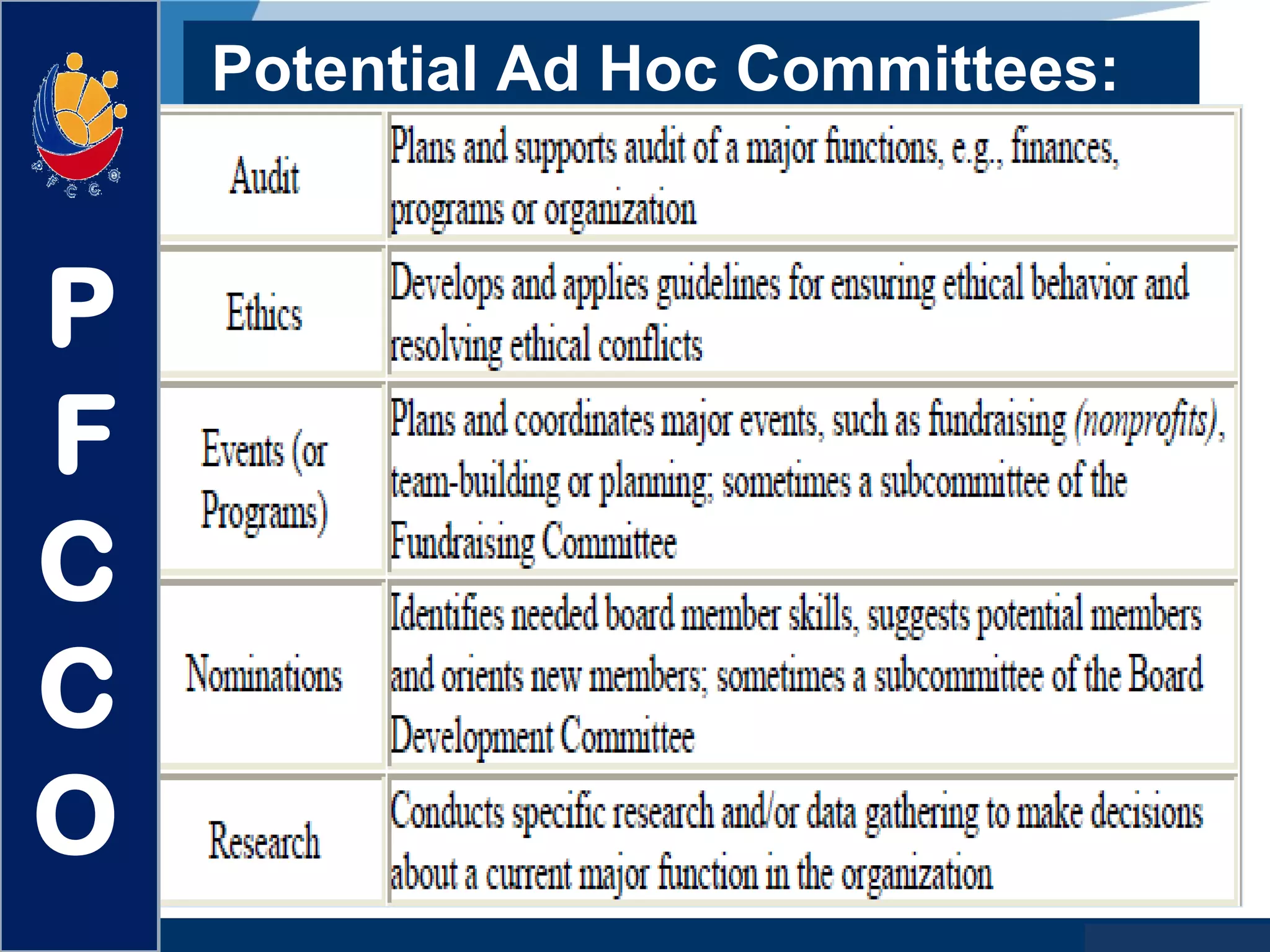
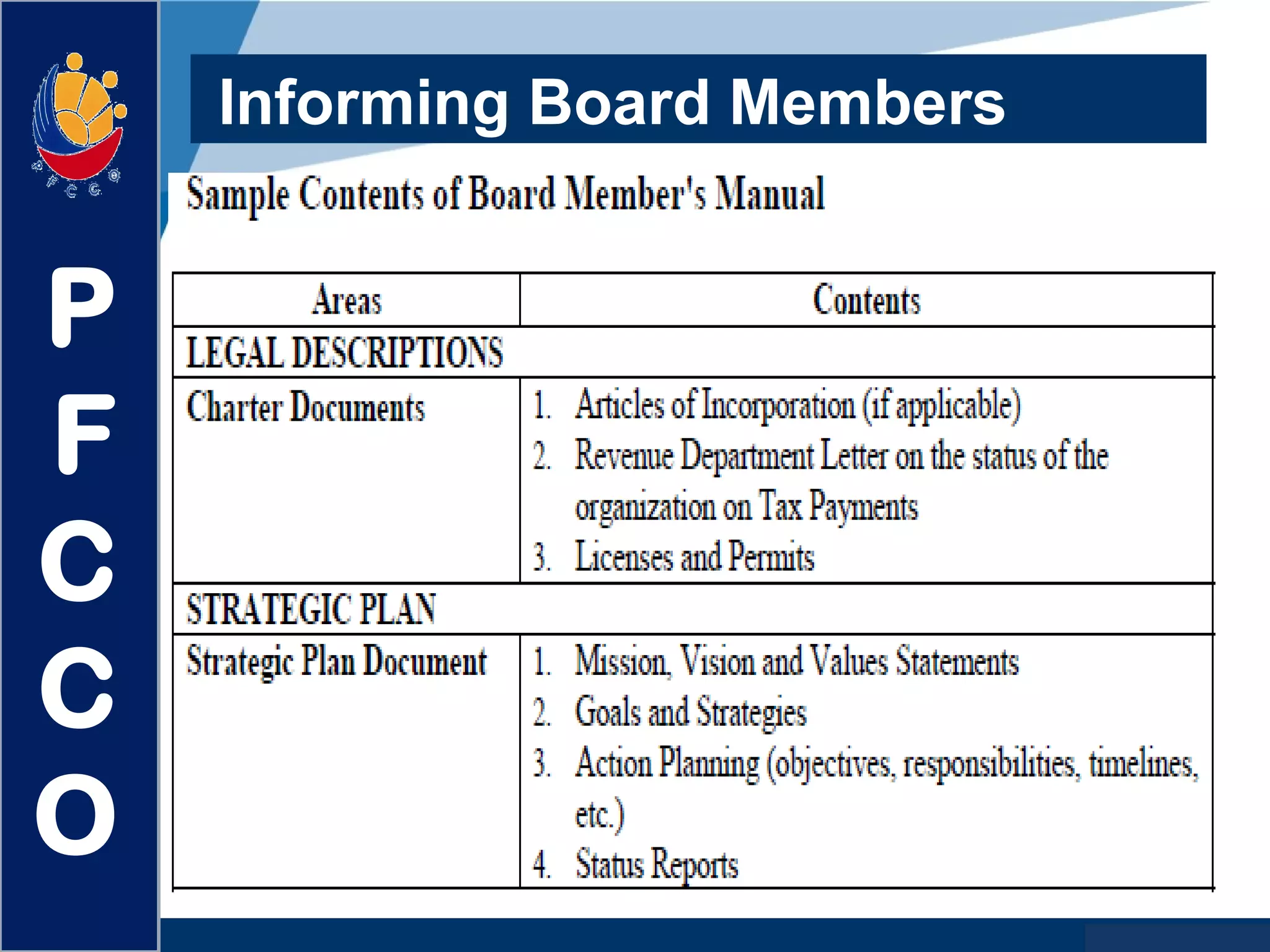
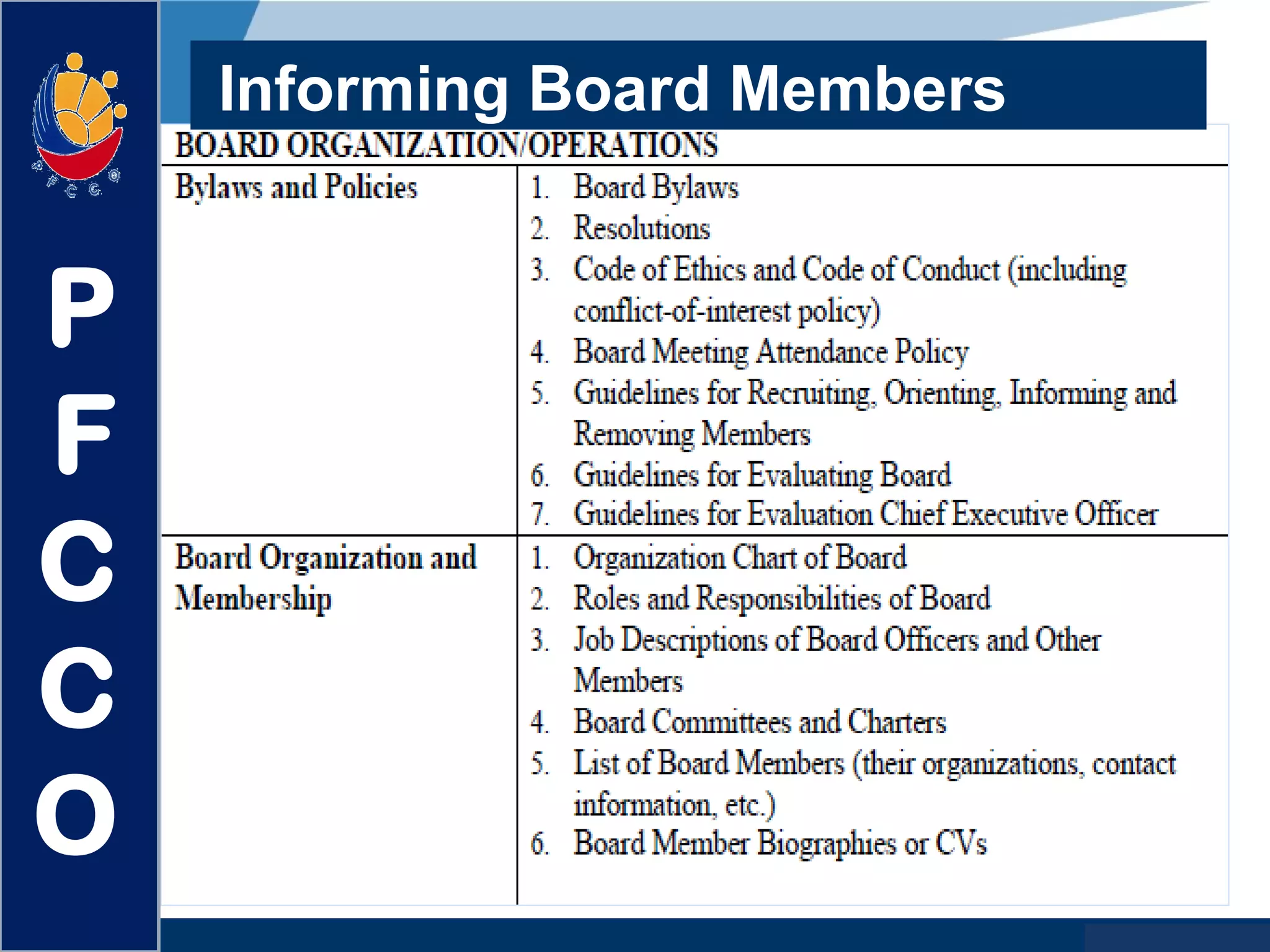
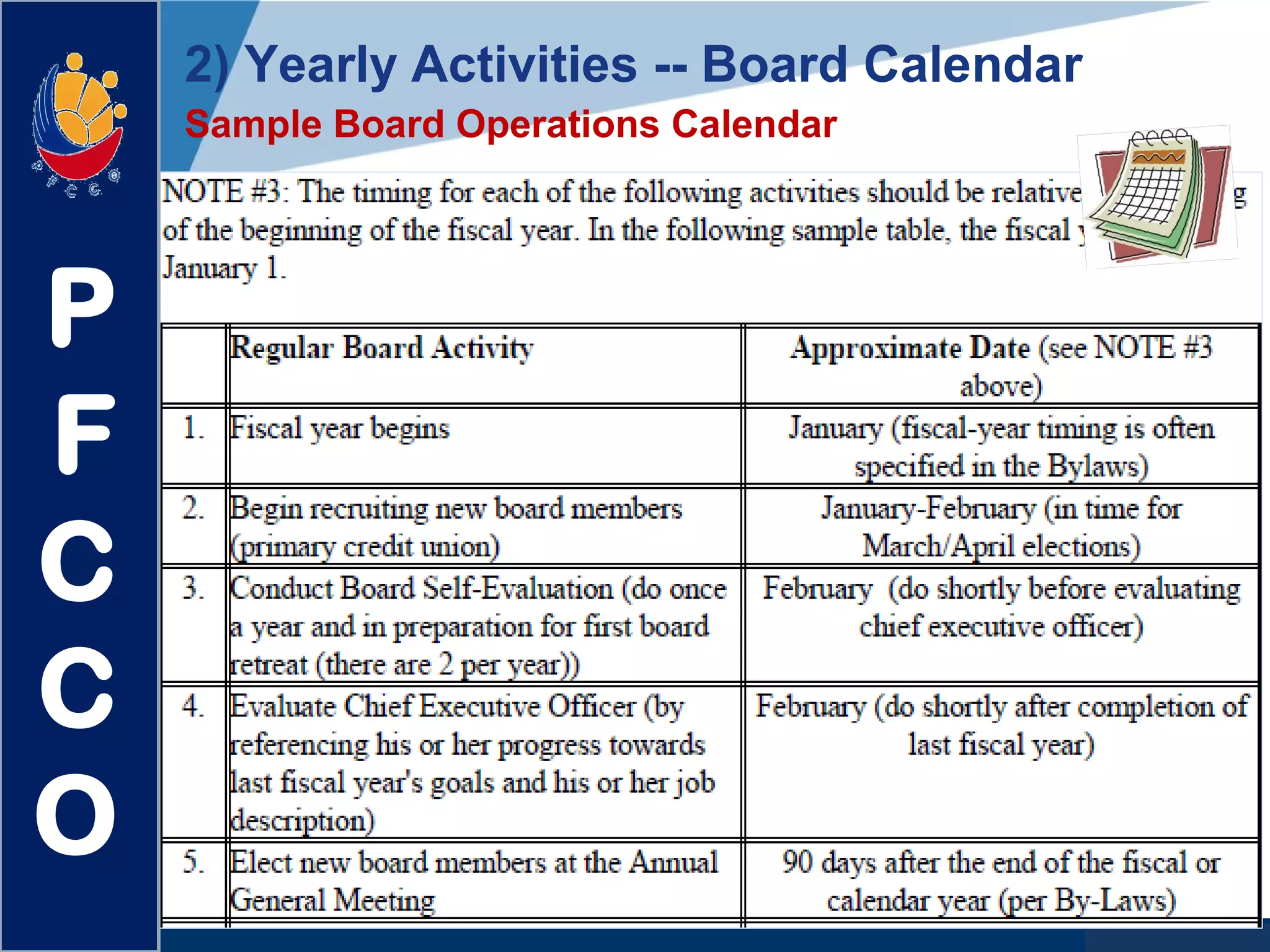
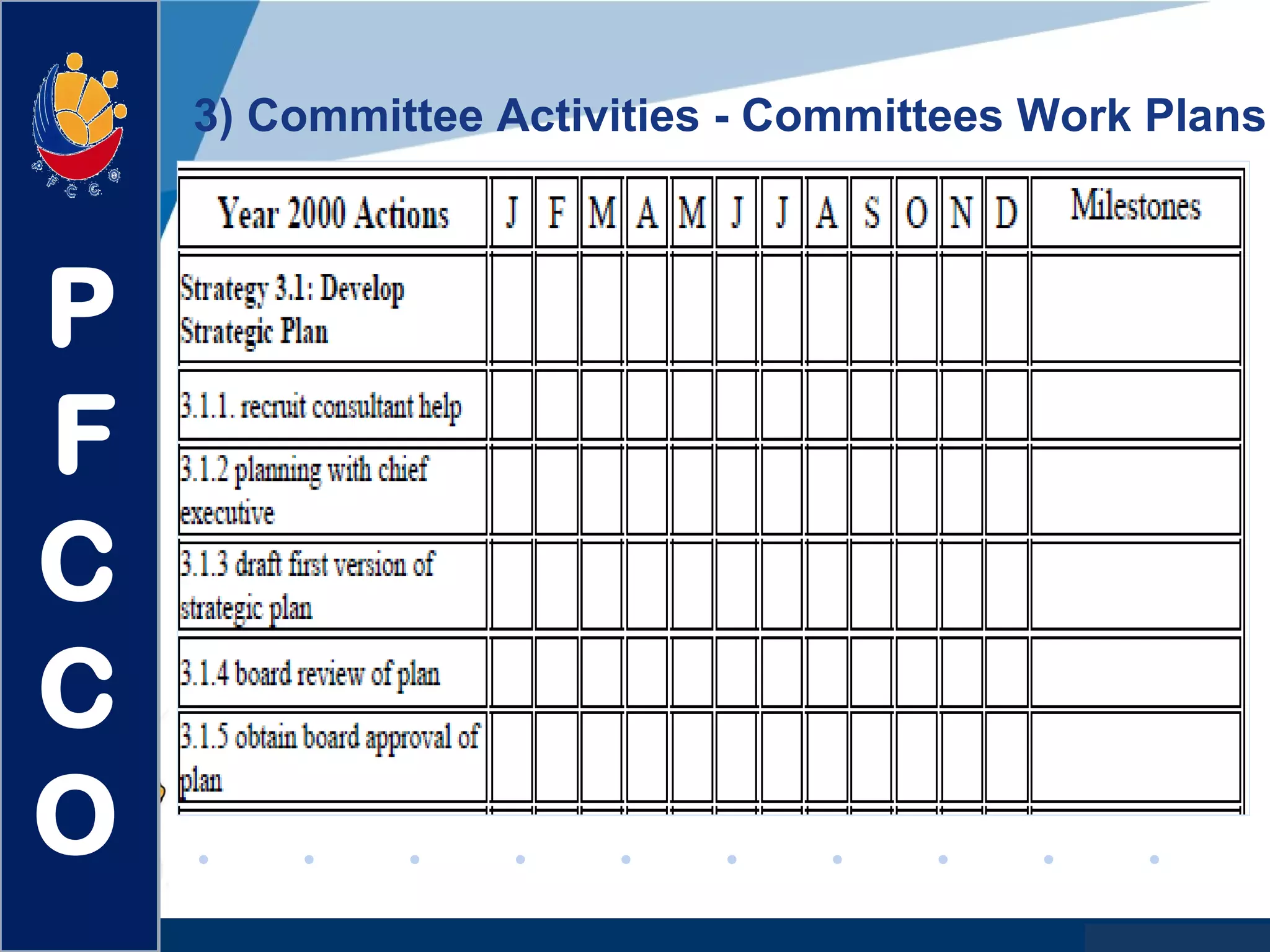
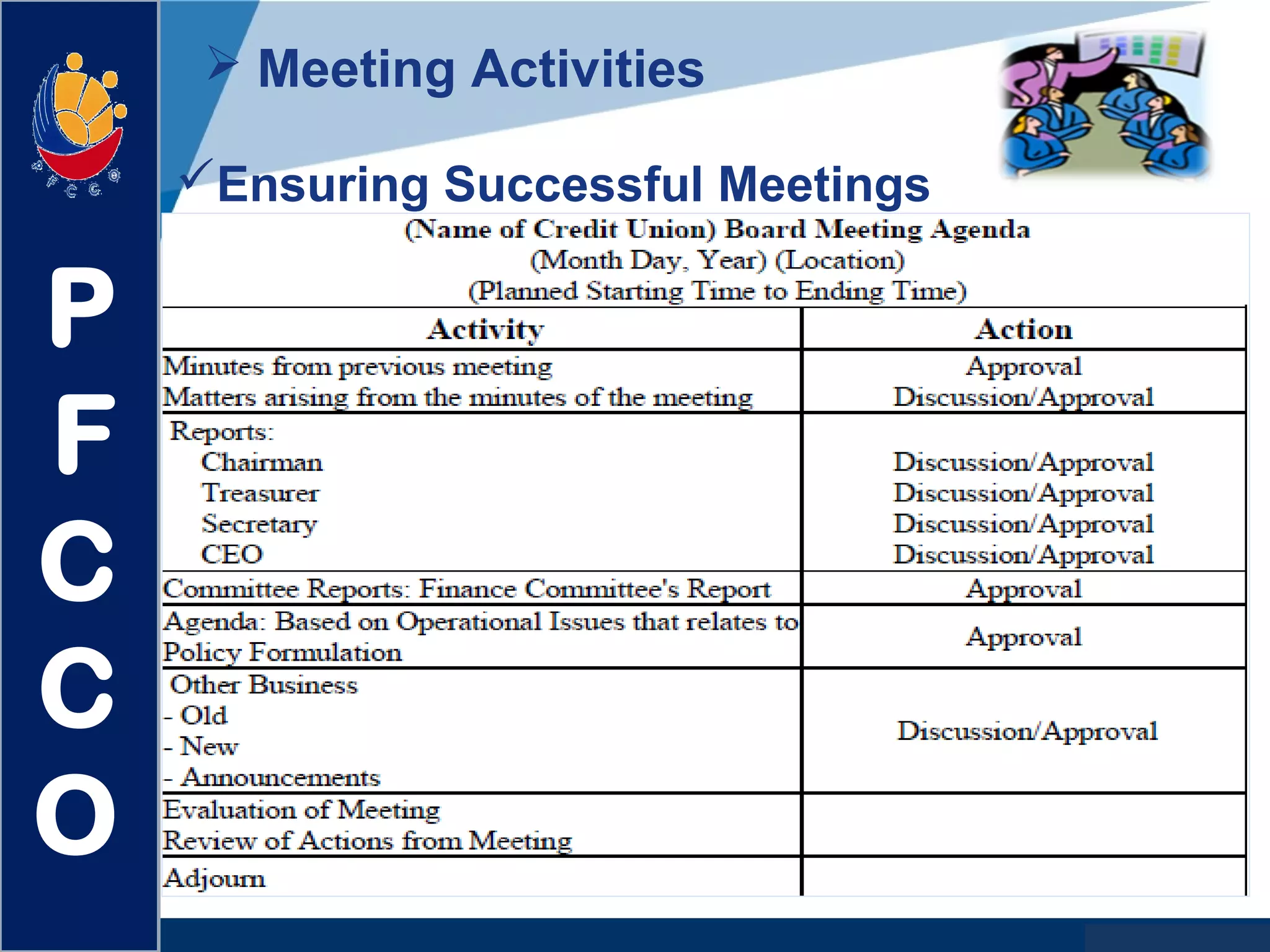
The document discusses the roles and responsibilities of boards of directors and board members. It provides descriptions for common board roles such as the board chair, vice chair, committee chairs, board members, secretary, and treasurer. It also discusses guidelines for effective board operations, which include recruiting and orienting new members, defining committees and their work, ensuring successful board meetings, and generating participation in committees.