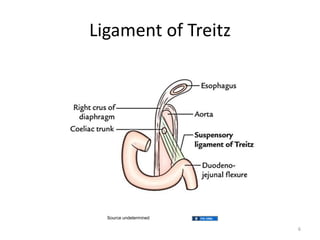
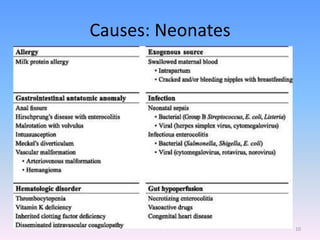
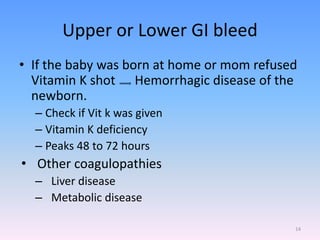
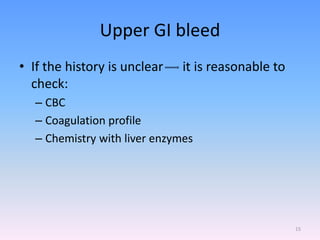
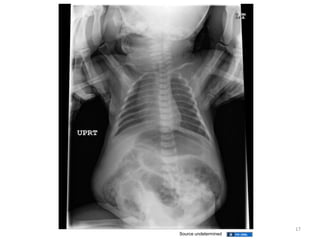
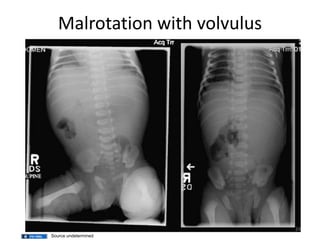
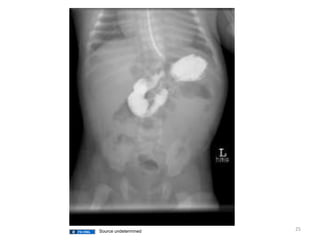
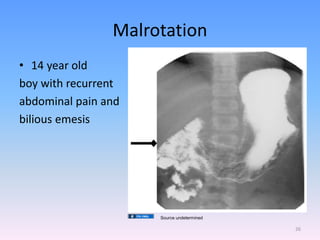
A newborn infant presenting with bloody stool requires evaluation to identify potential serious underlying causes of bleeding while reassuring parents that many cases are benign and self-limiting. Key factors to assess include the color and consistency of stool to localize bleeding origin, history of vitamin K administration at birth, and medications exposure to identify potential coagulopathies. While occult blood alone may not be significant, gross hematochezia or melena requires further workup to rule out conditions such as necrotizing enterocolitis, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, or anal fissures.