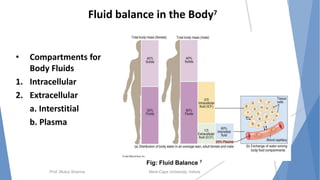
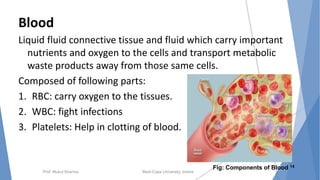
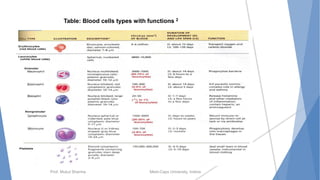
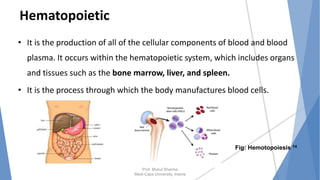
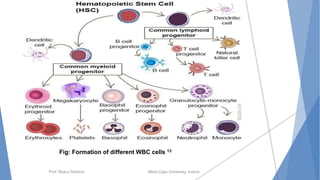
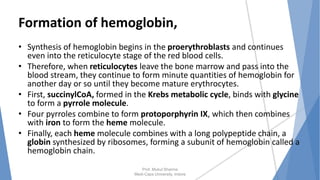
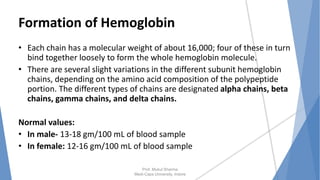
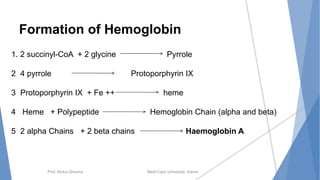
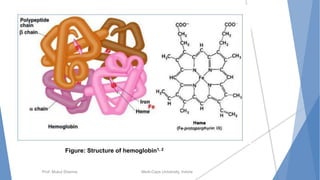
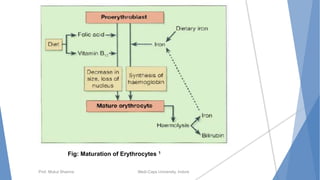
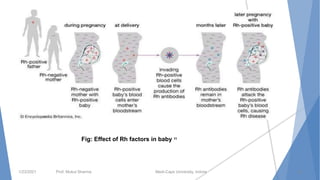
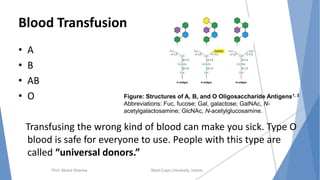
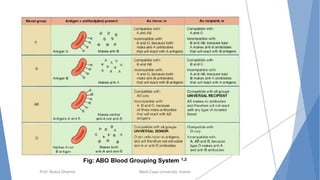
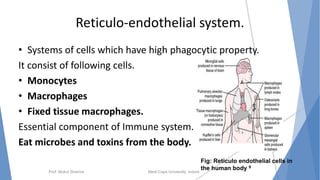
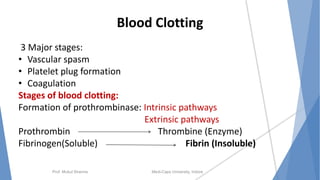
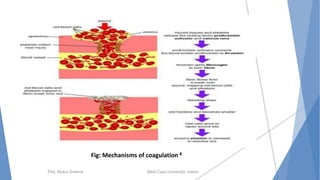
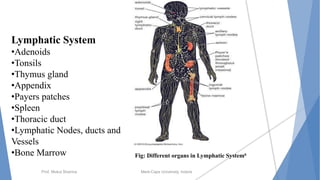
The document discusses the blood and lymphatic systems. It describes how blood is composed of plasma and formed elements like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The lymphatic system transports lymph throughout the body and contains lymph nodes and organs that help fight infection and maintain fluid balance. Both systems are vital for circulating nutrients and oxygen, removing waste, and defending against disease. Key processes covered include hematopoiesis, blood grouping, coagulation, and common blood disorders.