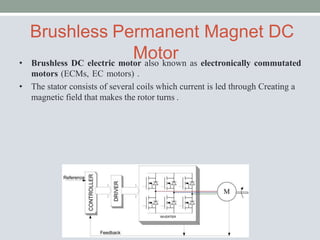
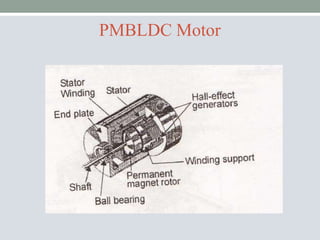
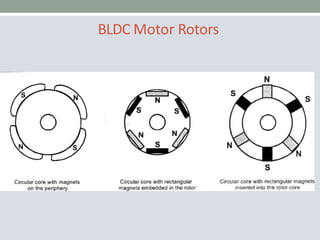
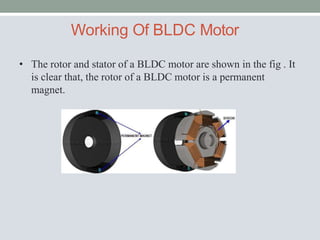
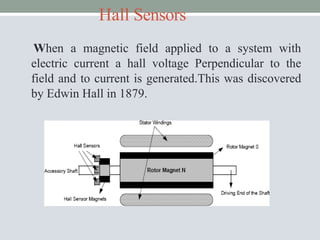
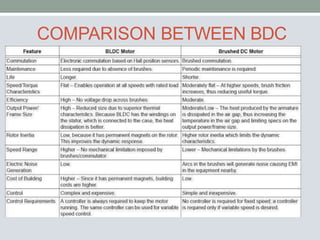
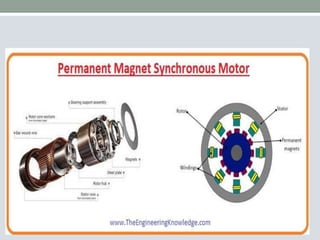
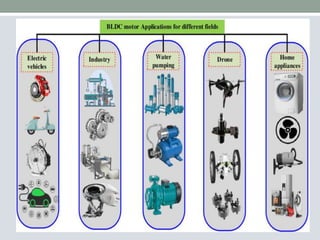
This document discusses brushless DC motors (BLDC motors) which use permanent magnets and electronic commutation instead of brushes. It describes the construction and working of BLDC motors including the stator, rotor and hall sensors. Key advantages of BLDC motors are increased reliability, efficiency and longer life compared to brushed DC motors. BLDC motors find applications in consumer goods, medical devices, vehicles and airplanes due to their precise control and high power density.