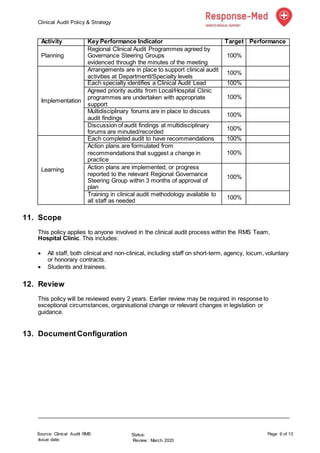
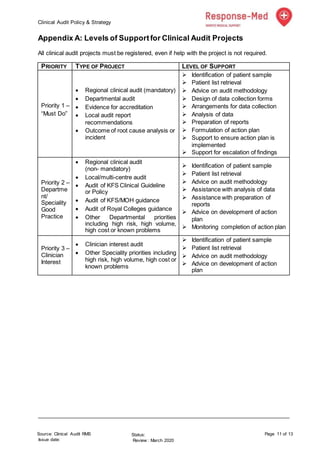
This document outlines the clinical audit policy and strategy for Response Med. It discusses statutory requirements that mandate regular clinical audits to assess quality and ensure patient safety. The purposes are to define a framework for clinical audits and clarify roles and responsibilities. The outcomes aim to provide evidence of a robust audit program, improvements based on audit findings, and adherence to best practices. The procedures describe developing an annual audit plan, conducting audits, and monitoring completion of the plan.