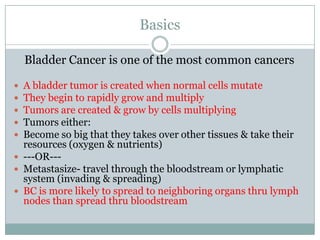
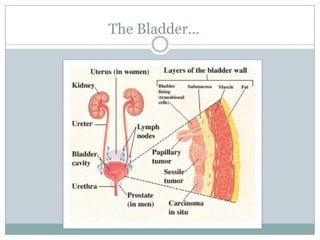
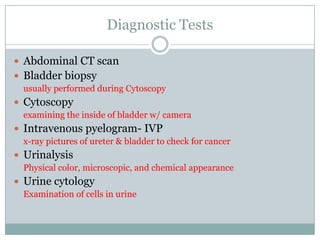
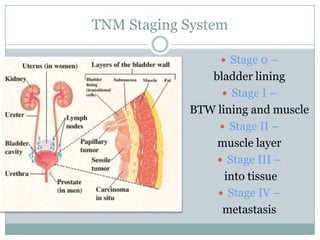
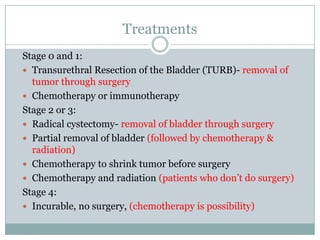
Bladder cancer is a common cancer resulting from mutations in normal cells that lead to tumor formation, primarily affecting men more than women. The major types include transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, with symptoms like blood in urine and frequent urination. Treatment varies by stage and includes procedures like transurethral resection and radical cystectomy, with significant risk factors being smoking, chemical exposure, and certain infections.