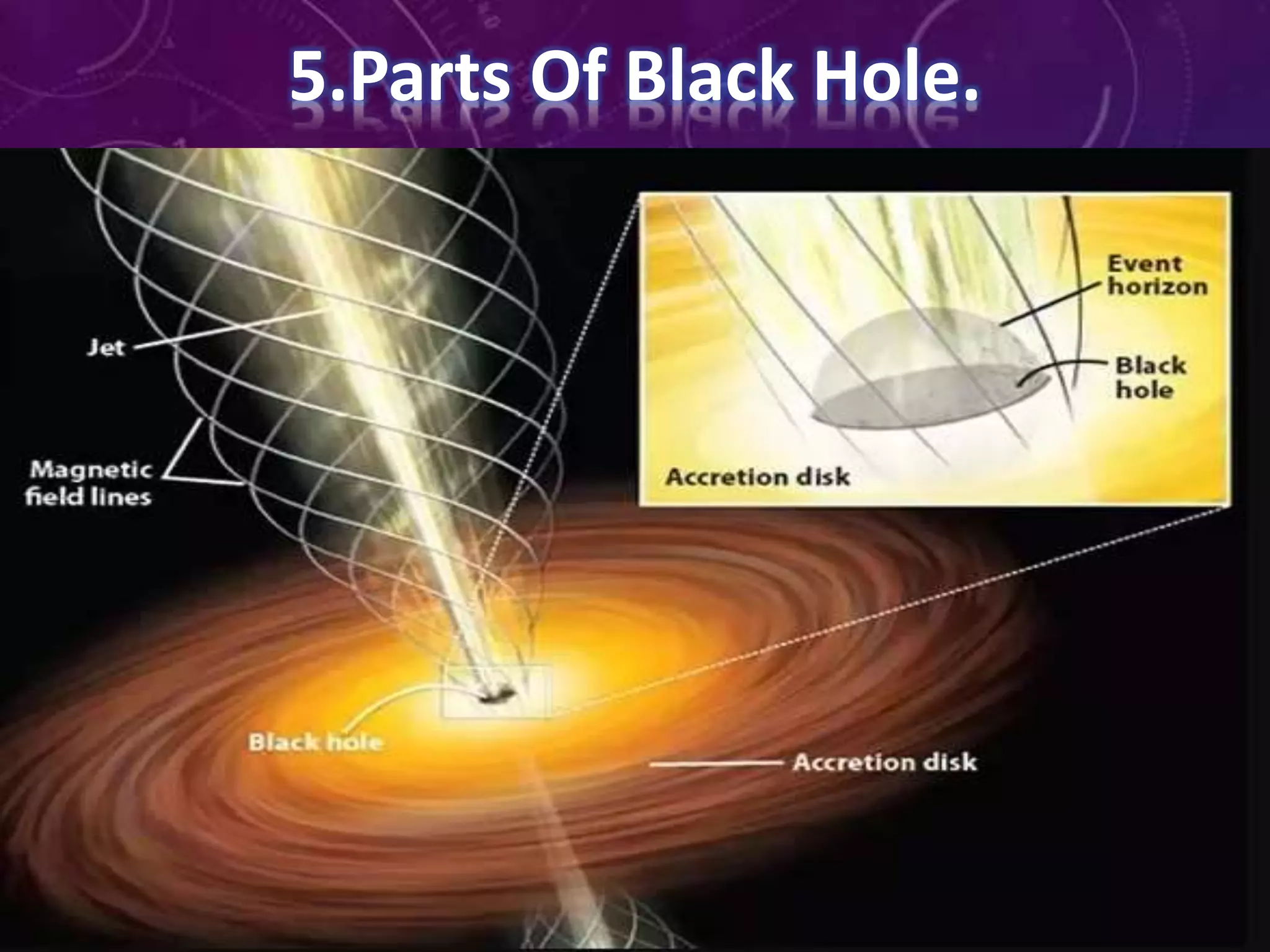
A black hole is a region of space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. They form when massive stars collapse at the end of their life cycles. There are several types of black holes including stellar black holes formed by collapsed stars and supermassive black holes millions to billions times the mass of our sun. As objects fall into a black hole's event horizon, they become "spaghettified" as the black hole's immense gravity stretches and pulls them apart.