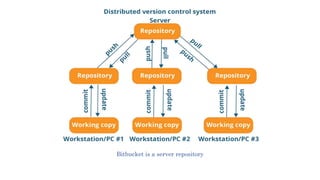
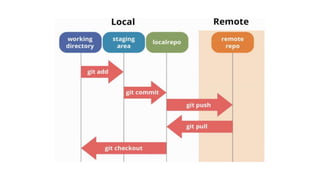
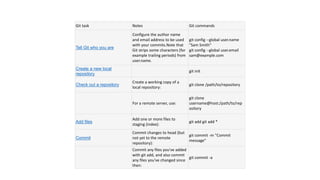
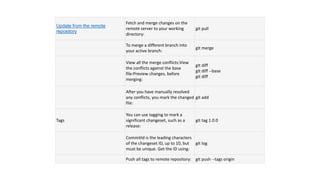
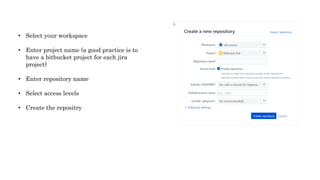
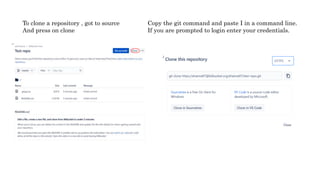
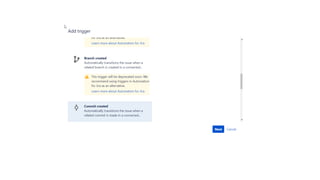
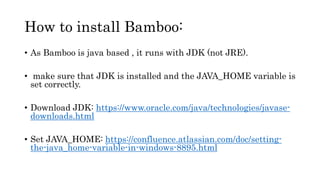
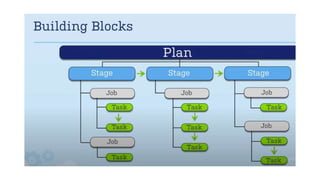
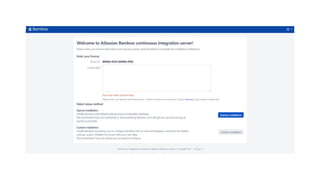
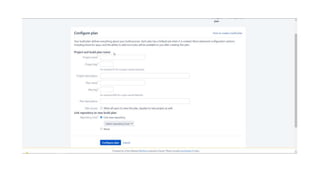
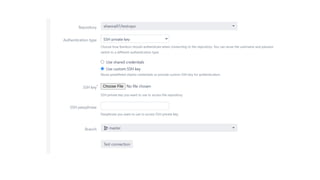
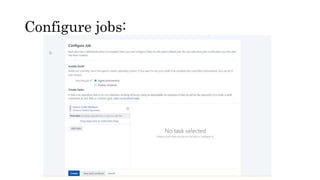
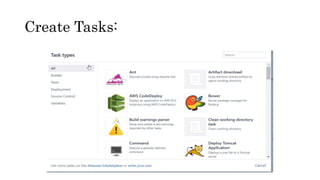
The document provides information about version control systems like Git and tools from Atlassian like Bitbucket, Bamboo, and Jira. It discusses how Git is used to manage source code changes over time. It also explains how to install and configure Git, and commonly used Git commands. The document then describes how Bitbucket can be used as a code repository and linked to Jira for issue tracking. Bamboo is introduced as a tool for continuous integration and deployment that can be linked to Bitbucket and Jira as well. Steps for installing and configuring Bamboo pipelines are also outlined.