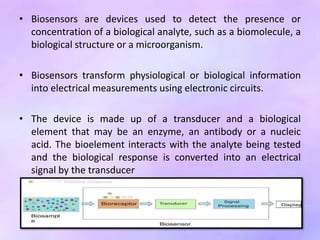
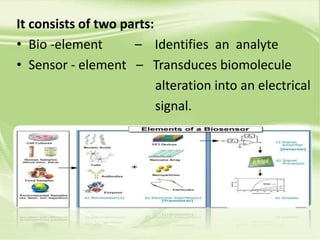
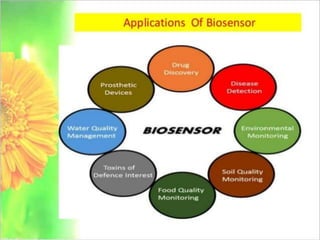
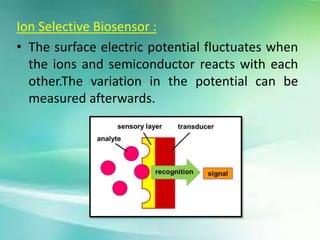
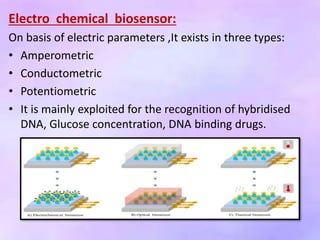
This presentation discusses biosensors, which are devices that use biological elements like enzymes or antibodies to detect analytes and transduce biological responses into electrical signals. It describes the basic components and working principle of biosensors. The presentation provides a brief history of biosensors and discusses the major types including optical, resonant, thermal, ion selective, and electrochemical biosensors. It also outlines some applications of biosensors in the pharmaceutical sector like drug discovery screening and clinical diagnostics.