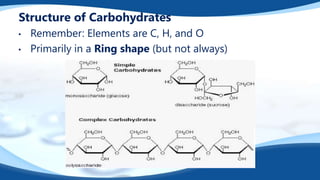
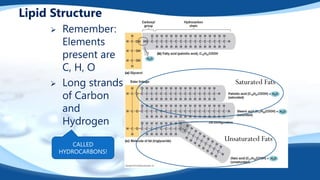
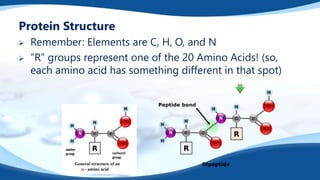
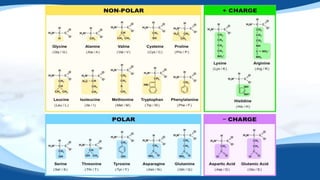
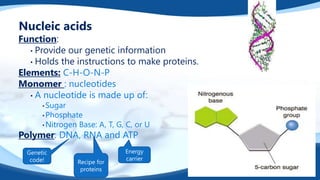
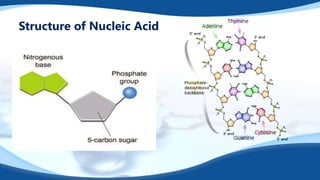
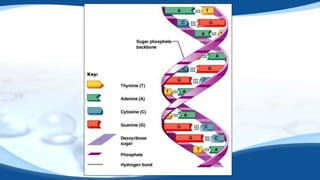
The 4 main biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates like sugars and starches provide energy, lipids like fats store energy and make up cell membranes, proteins build tissue and transport molecules, and nucleic acids like DNA and RNA contain our genetic code and instructions. These biomolecules are made up of smaller building blocks and contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen or phosphorus. We obtain biomolecules from the foods we eat like plants, meat, and oils which are necessary for life.