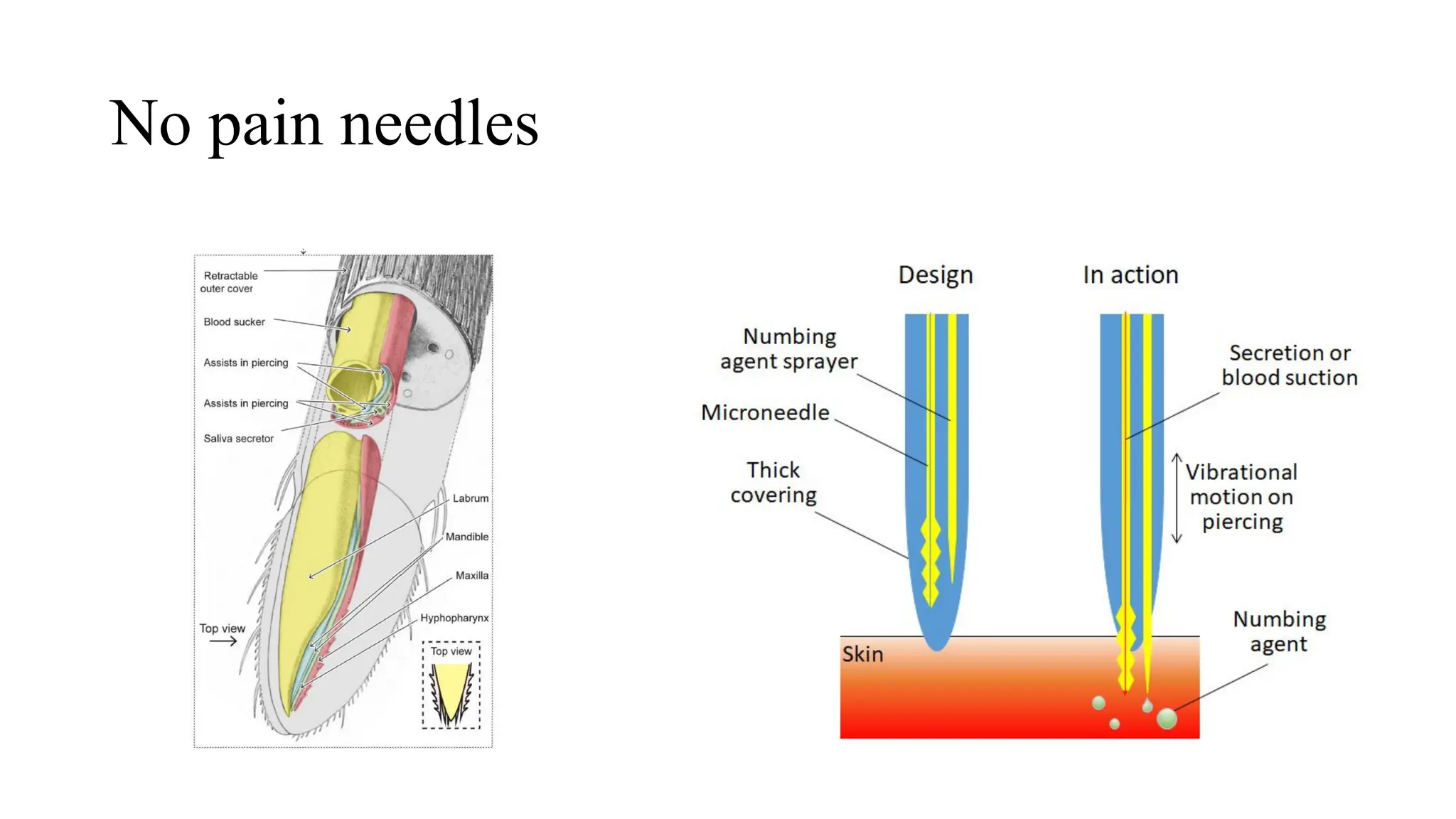
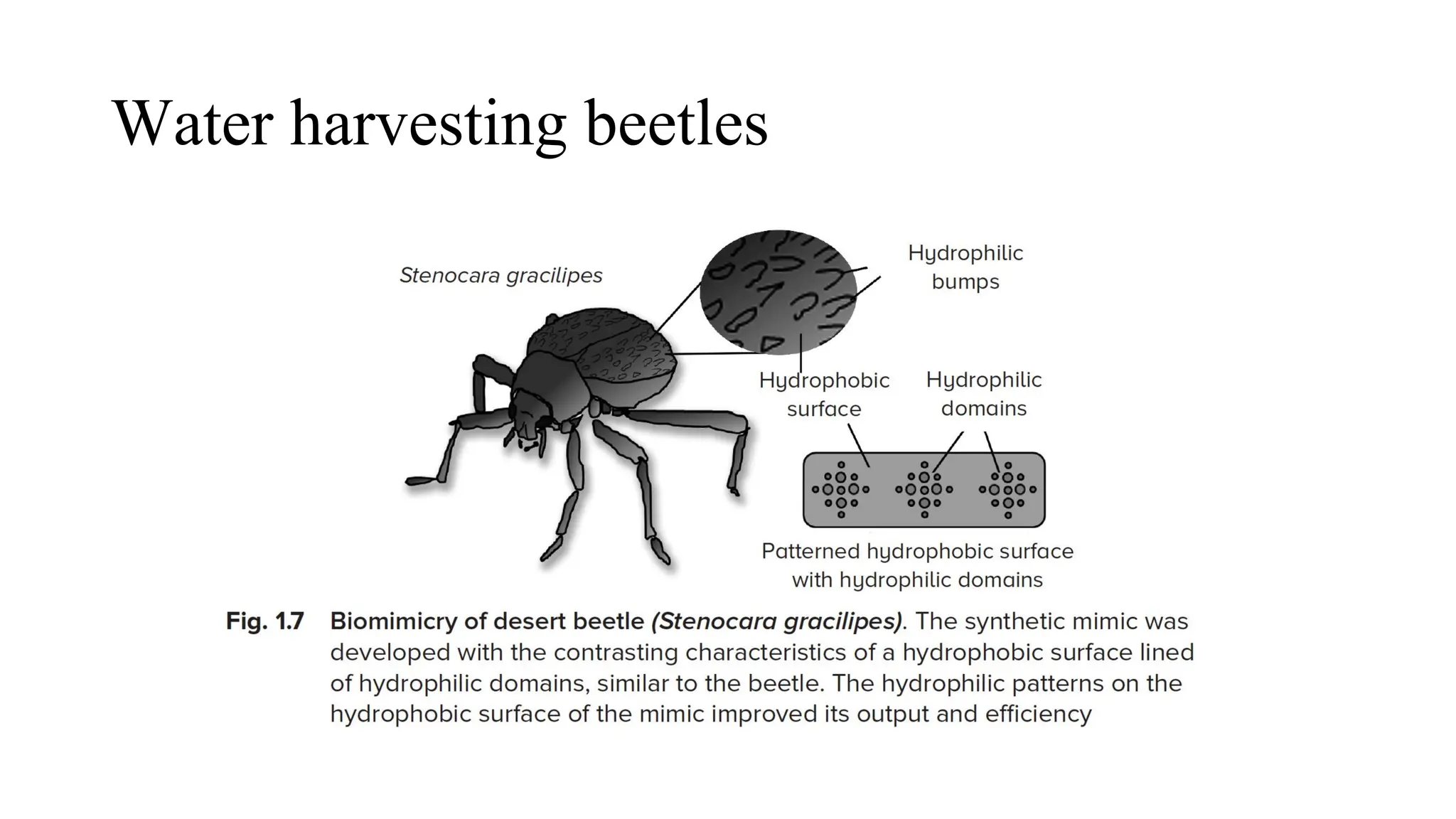
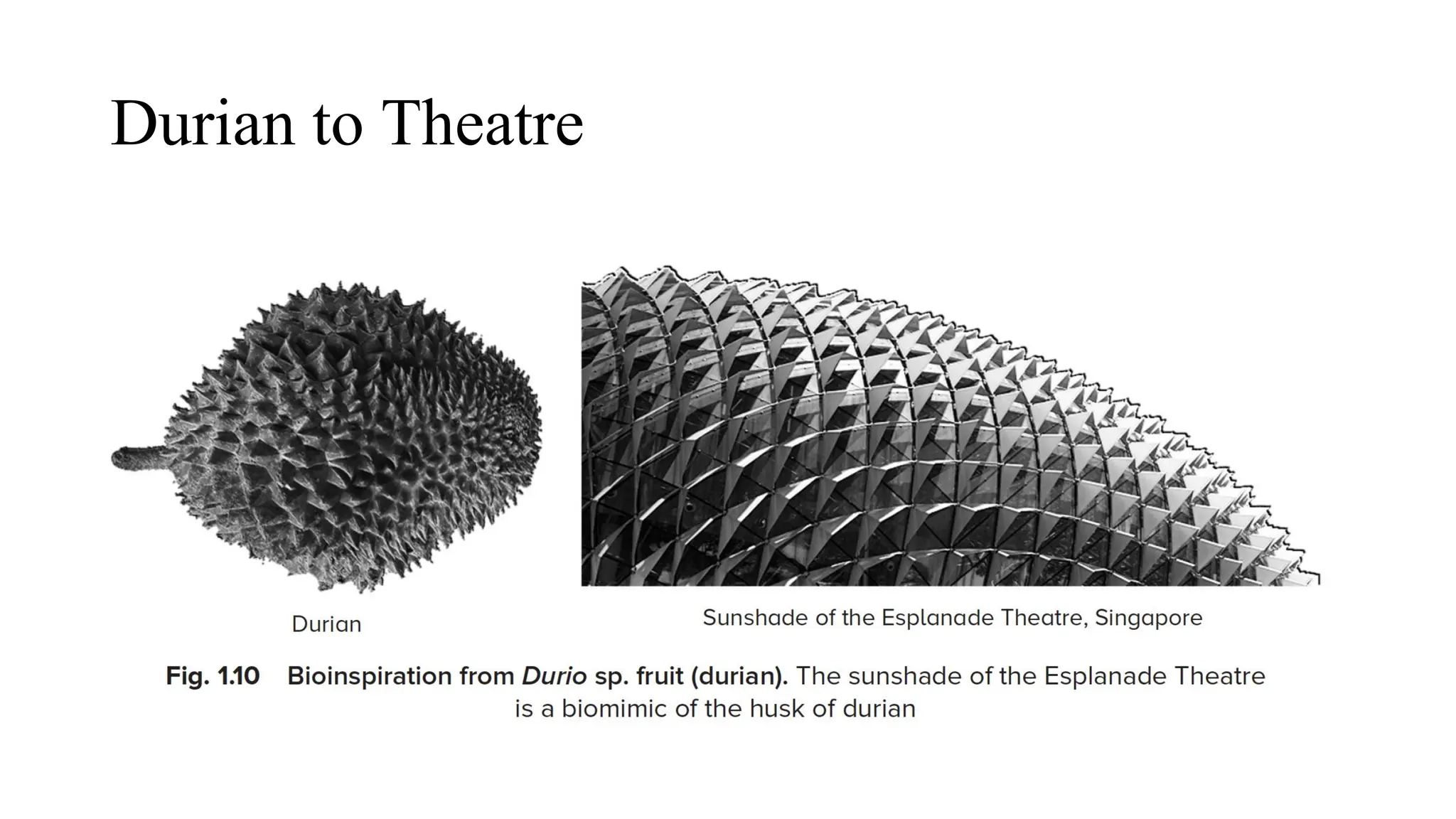
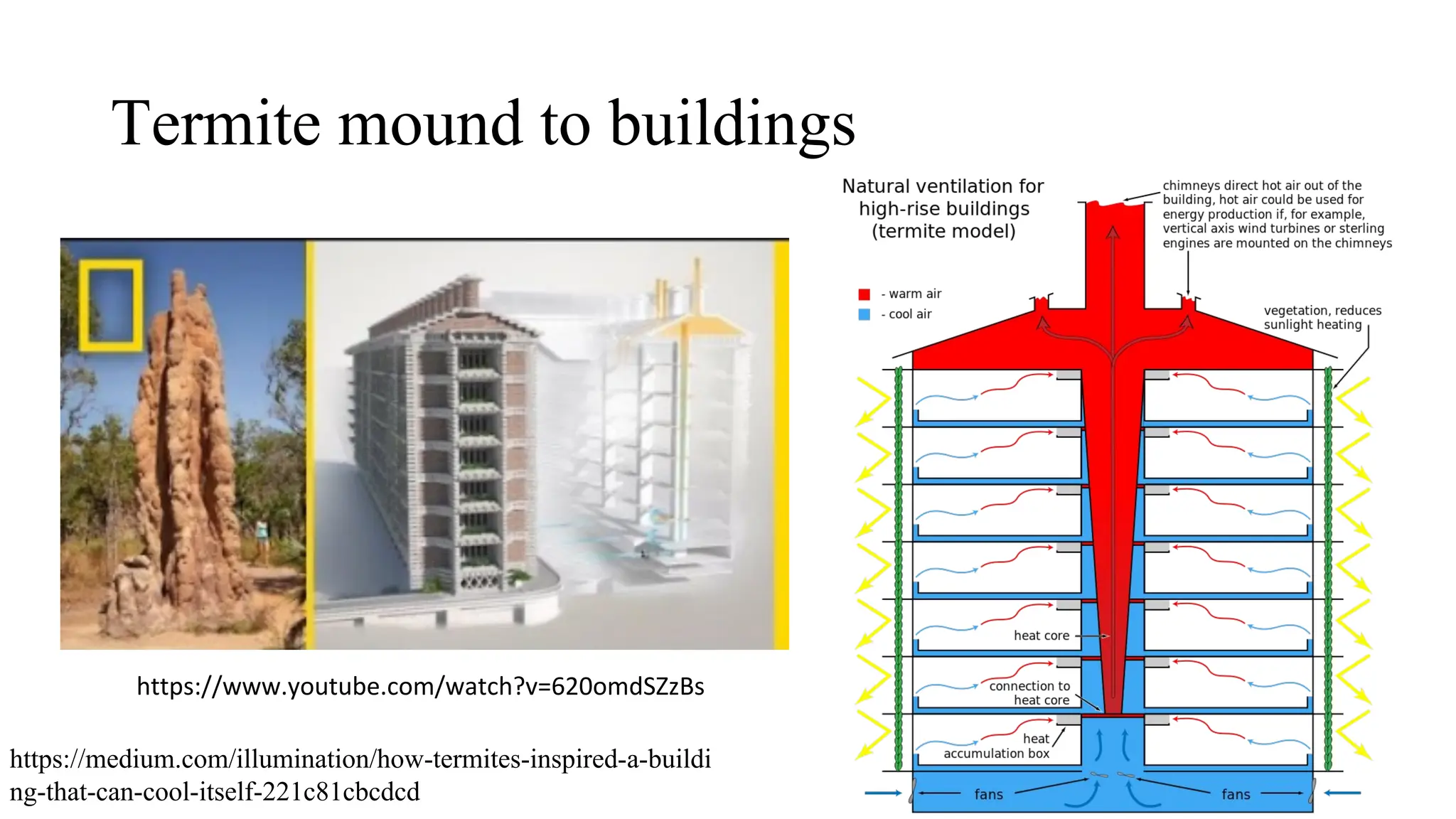
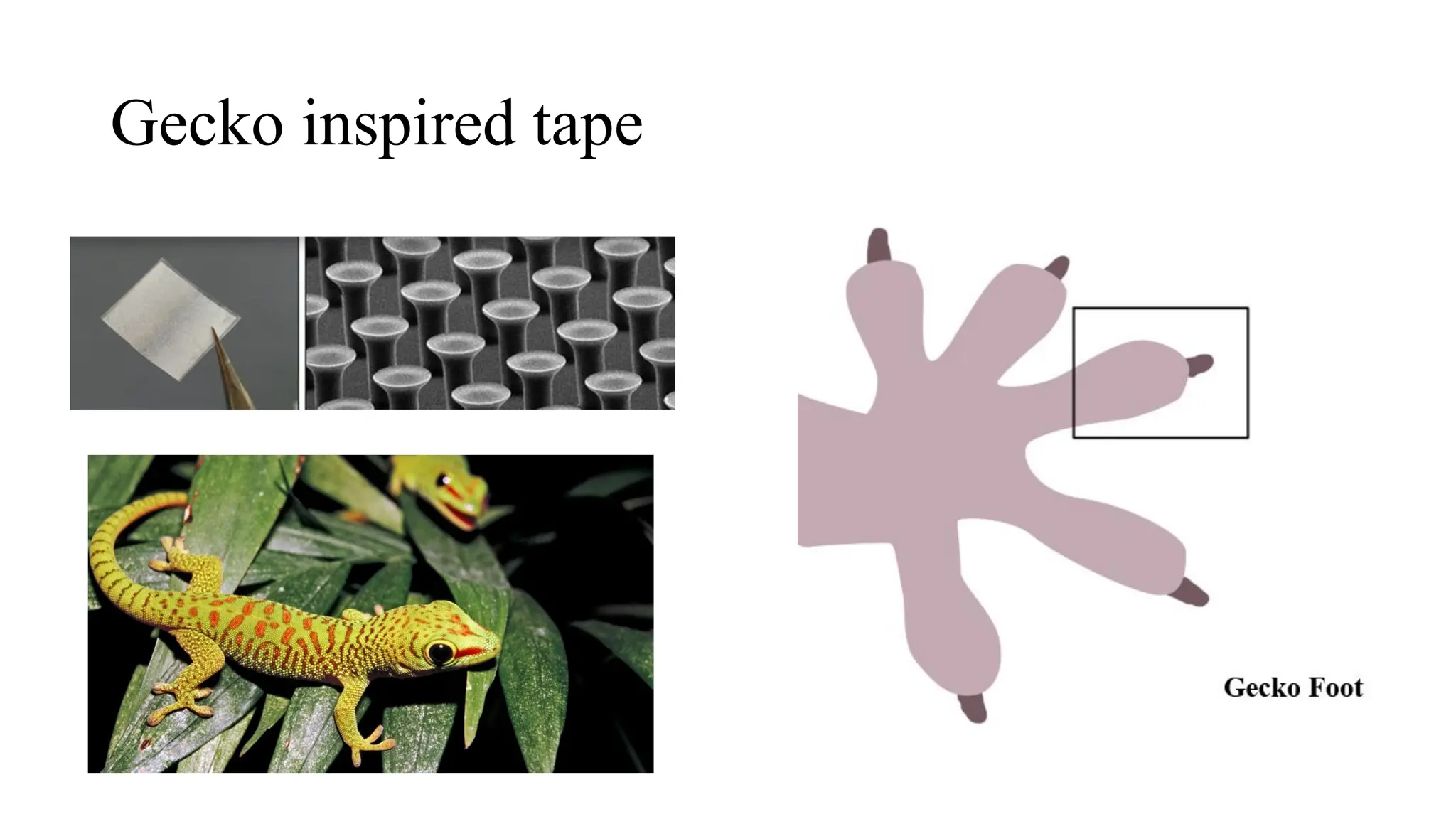
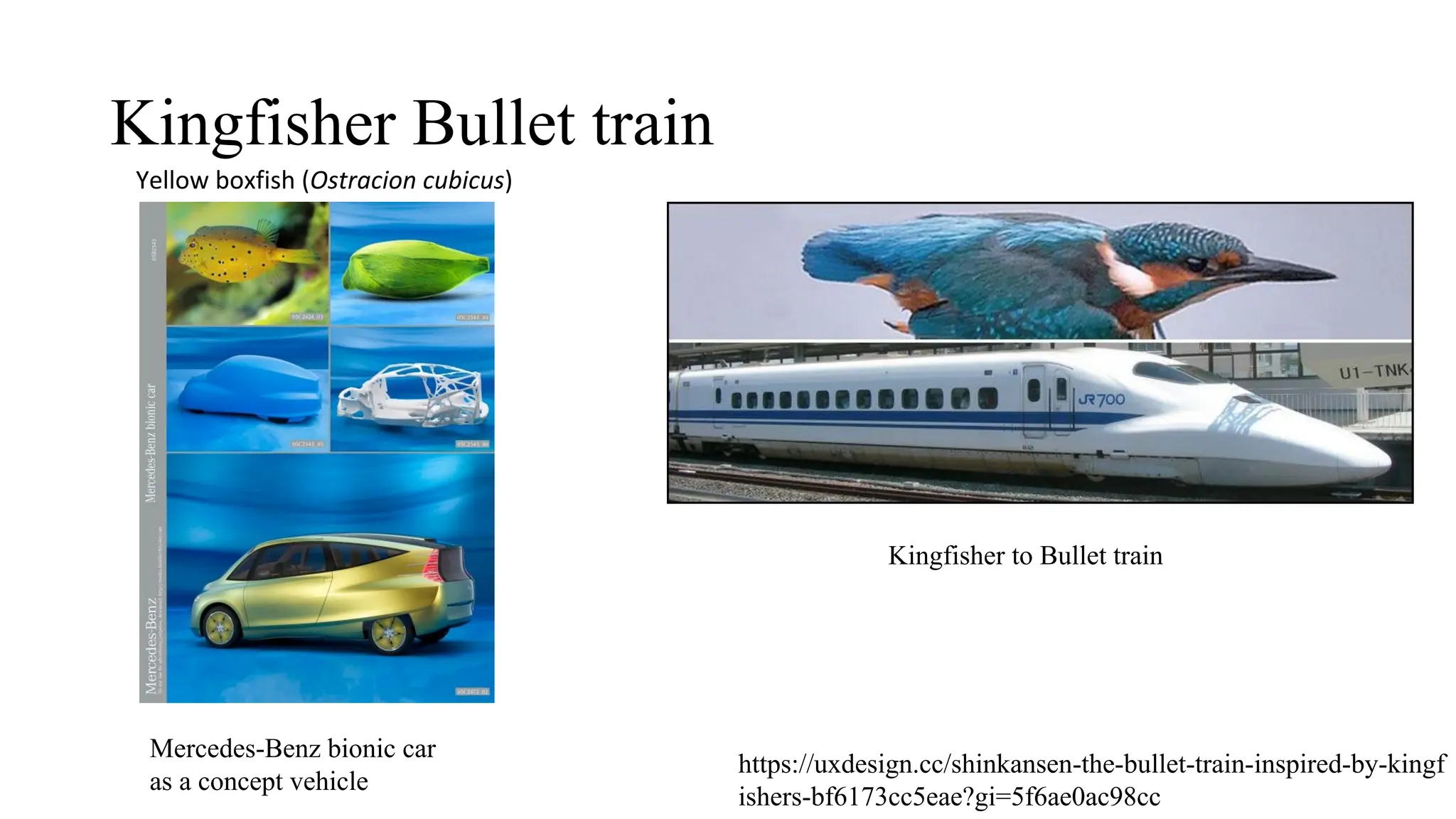
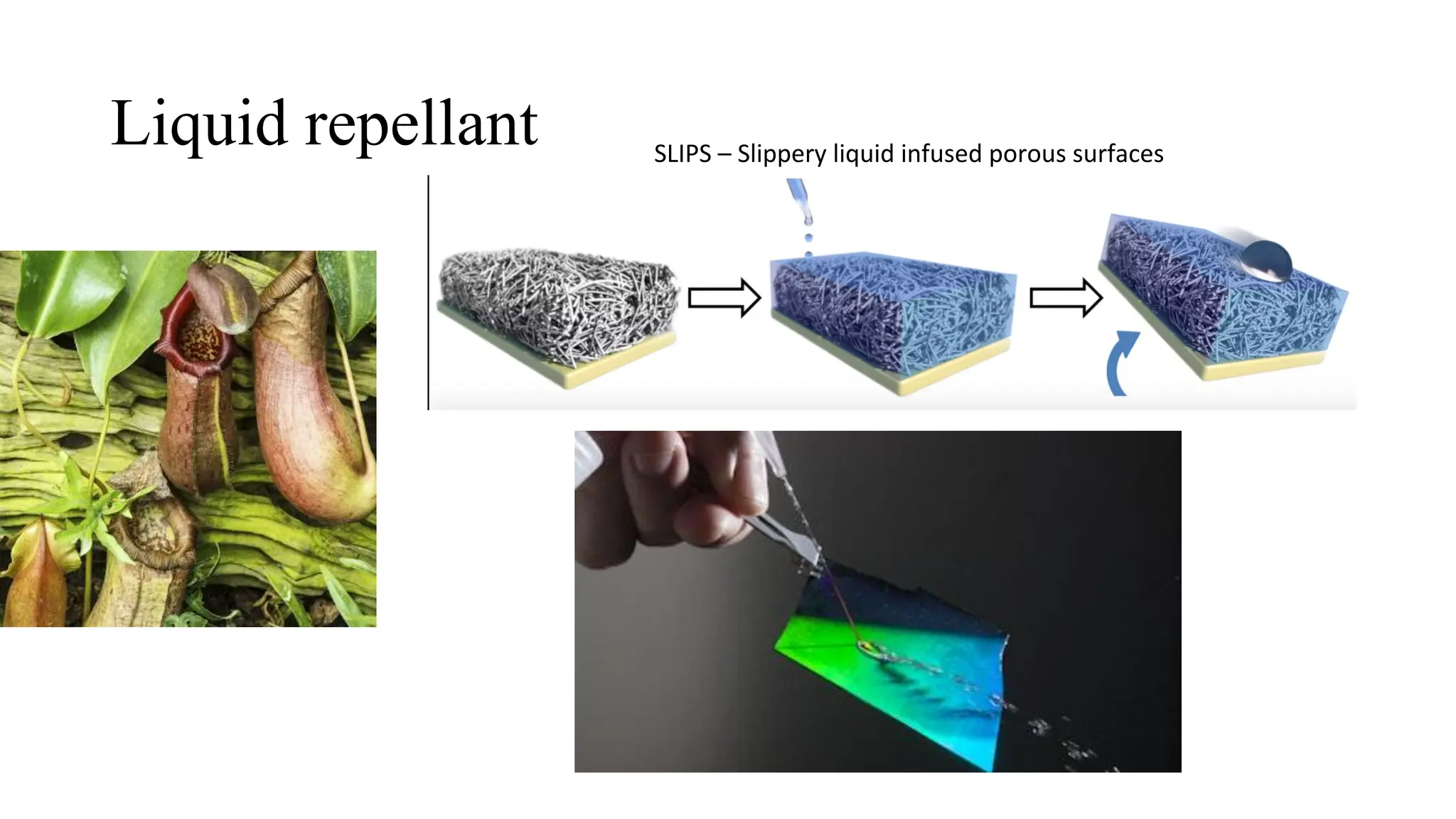
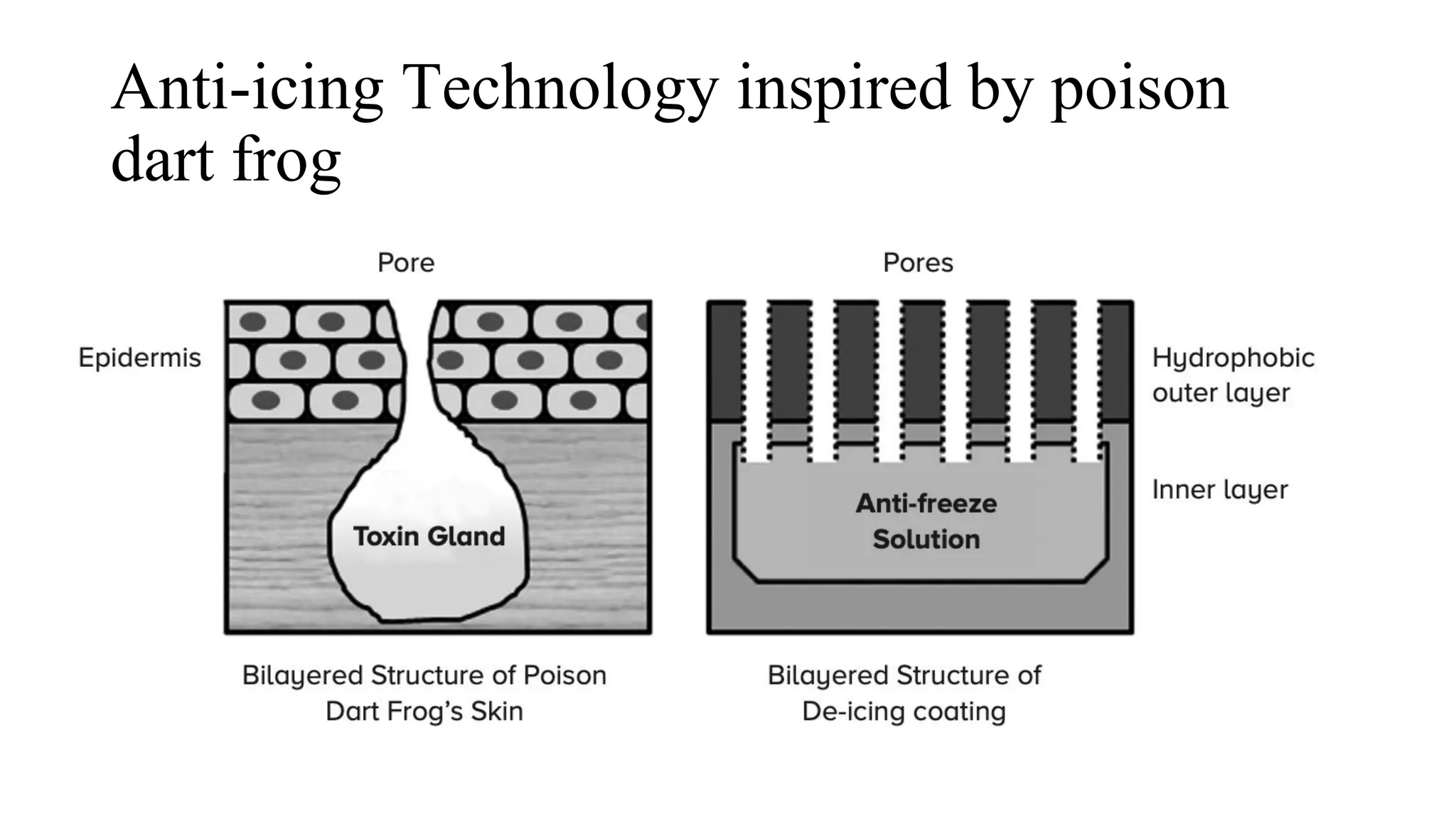
The document outlines a biology course designed for engineering students, aiming to link biological concepts with engineering applications. It covers various topics including bio-inspired engineering, cellular biology, and interdisciplinary technologies inspired by organ systems, emphasizing the importance of biology in developing human-friendly technologies. The course includes practical laboratory experiments and addresses FAQs concerning the relevance of biology to non-biology majors.