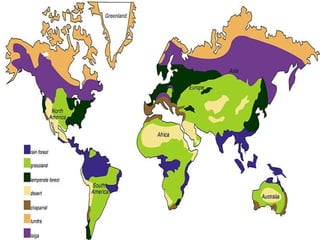
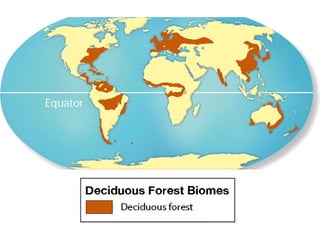
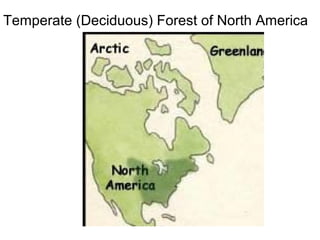
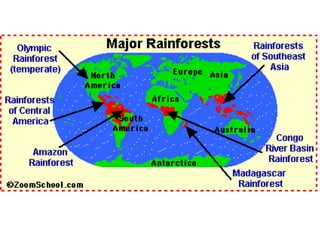
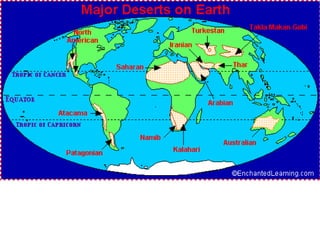
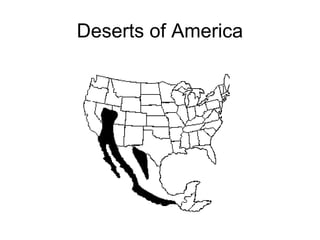
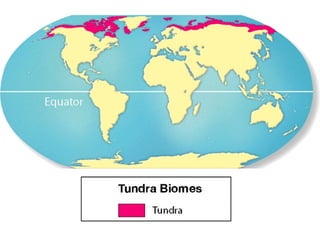
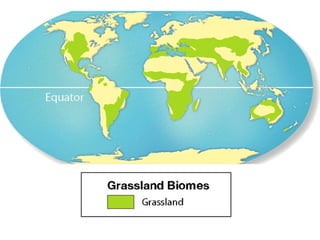
This document provides information about different biomes including temperate deciduous forests, tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, grasslands, and freshwater and saltwater biomes. It describes the key characteristics of each biome such as average precipitation, temperature, dominant plant and animal species, and adaptations organisms have for surviving in each environment. Examples are given of plant and animal species found in each biome.