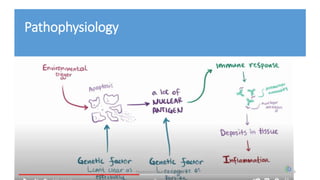
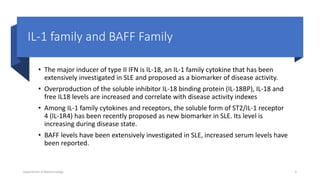
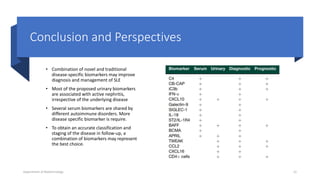
The document discusses the role of novel biomarkers in the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease characterized by the immune system attacking healthy tissues. It highlights the significance of complement levels, gene expression markers, and urinary biomarkers in understanding disease activity and progression. The conclusion emphasizes the need for a combination of disease-specific biomarkers to improve diagnosis and monitoring in SLE patients.