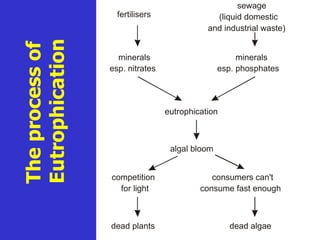
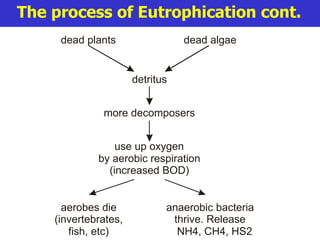
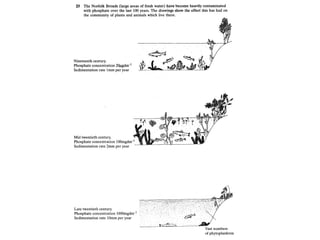
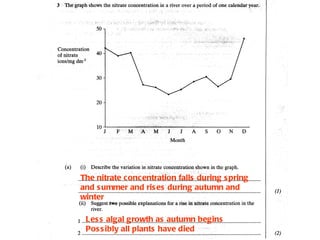
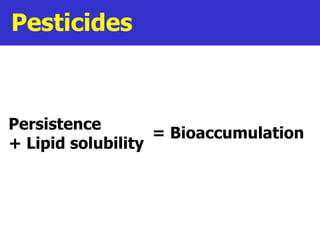
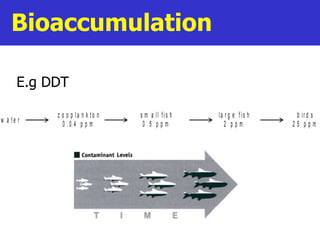
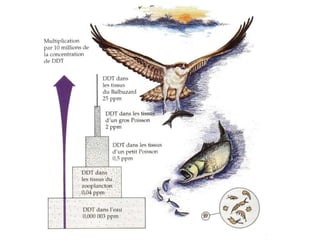
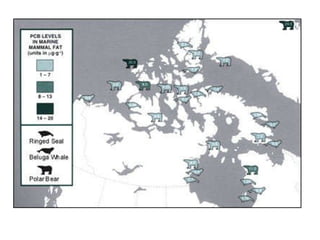
Fertilizers can cause eutrophication of water bodies. Eutrophication occurs when excess nutrients like nitrates and phosphates from fertilizers enter water, promoting algal bloom. As algae grow and then die, they are decomposed by bacteria which use up oxygen, potentially killing aquatic life. Pesticides include herbicides, insecticides, fungicides and bactericides and can persist in the environment if lipid soluble, allowing bioaccumulation in organisms over time. The key points are examined in more detail with examples of processes like eutrophication and concepts such as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).