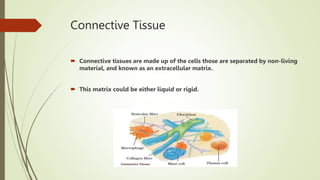
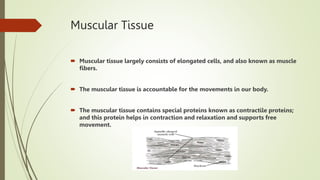
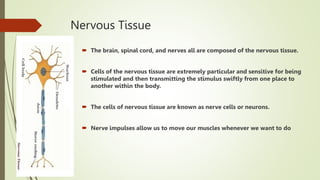
Animal tissues are divided into four main types - epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue forms protective barriers around organs and throughout the body. Connective tissue is made up of cells separated by an extracellular matrix and includes fibrous, skeletal, and fluid types such as tendons, bone, and blood. Muscular tissue consists of elongated muscle fibers that allow for body movement. Nervous tissue is composed of neurons in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves which transmit stimuli rapidly throughout the body.