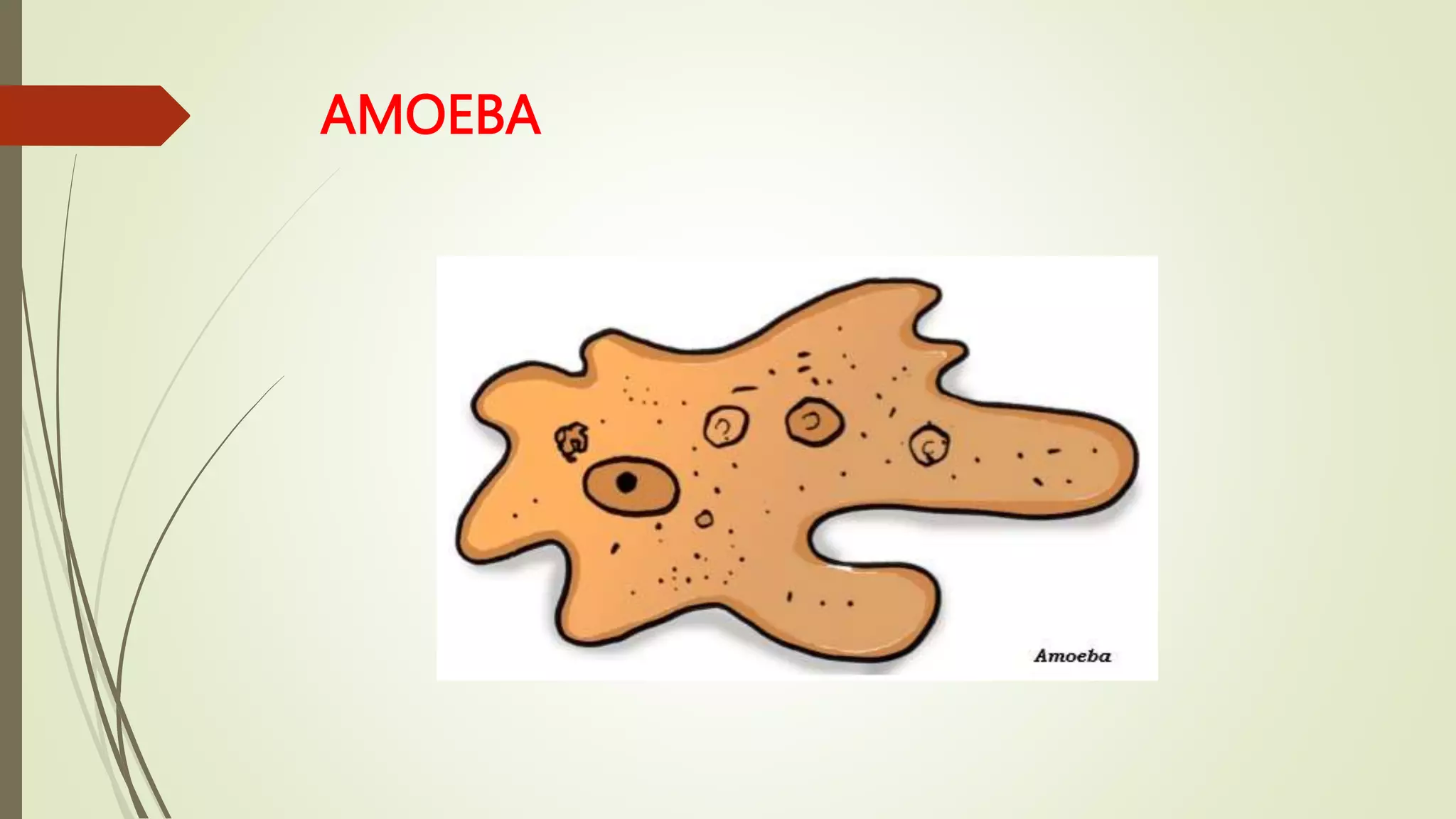
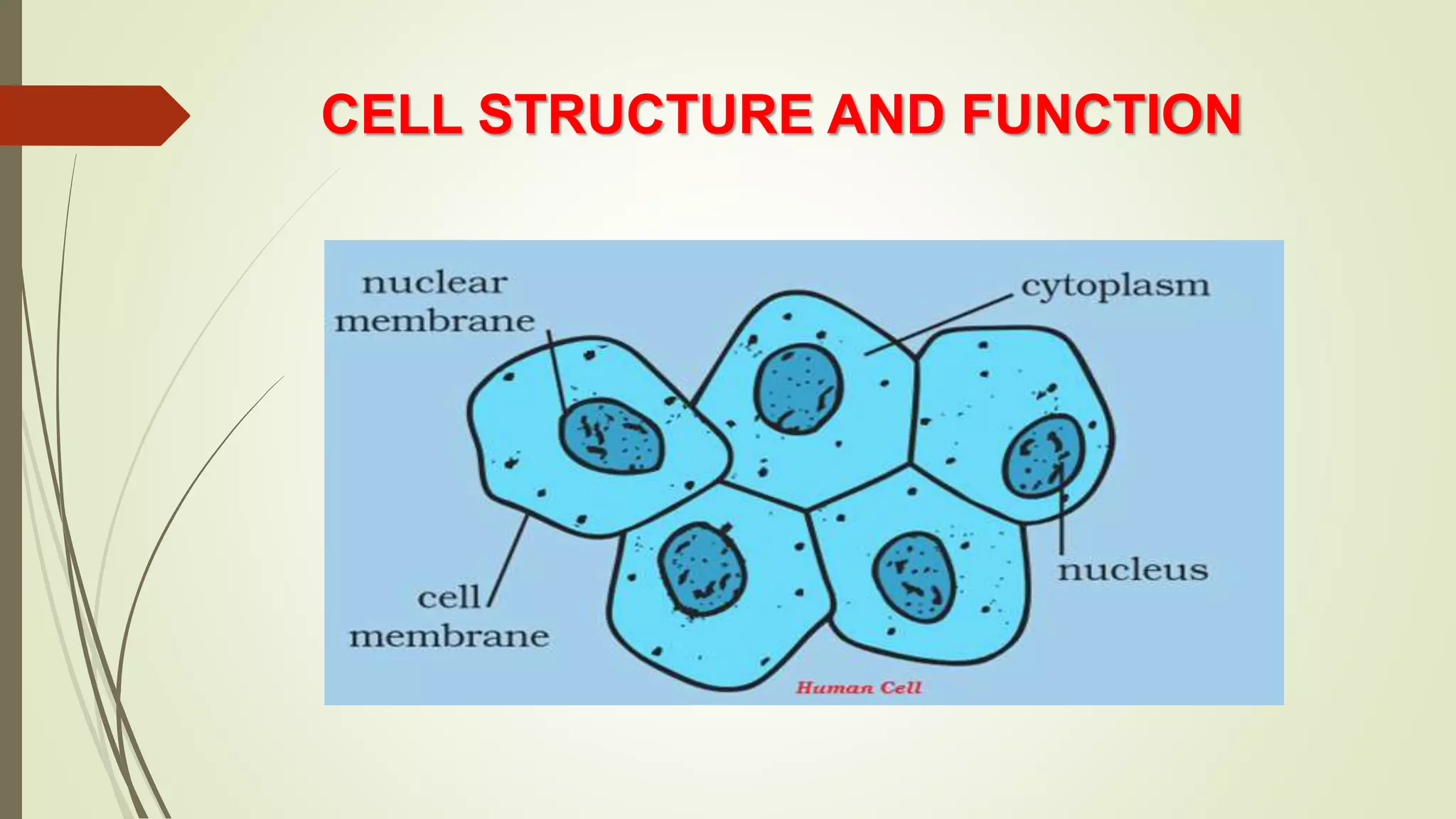
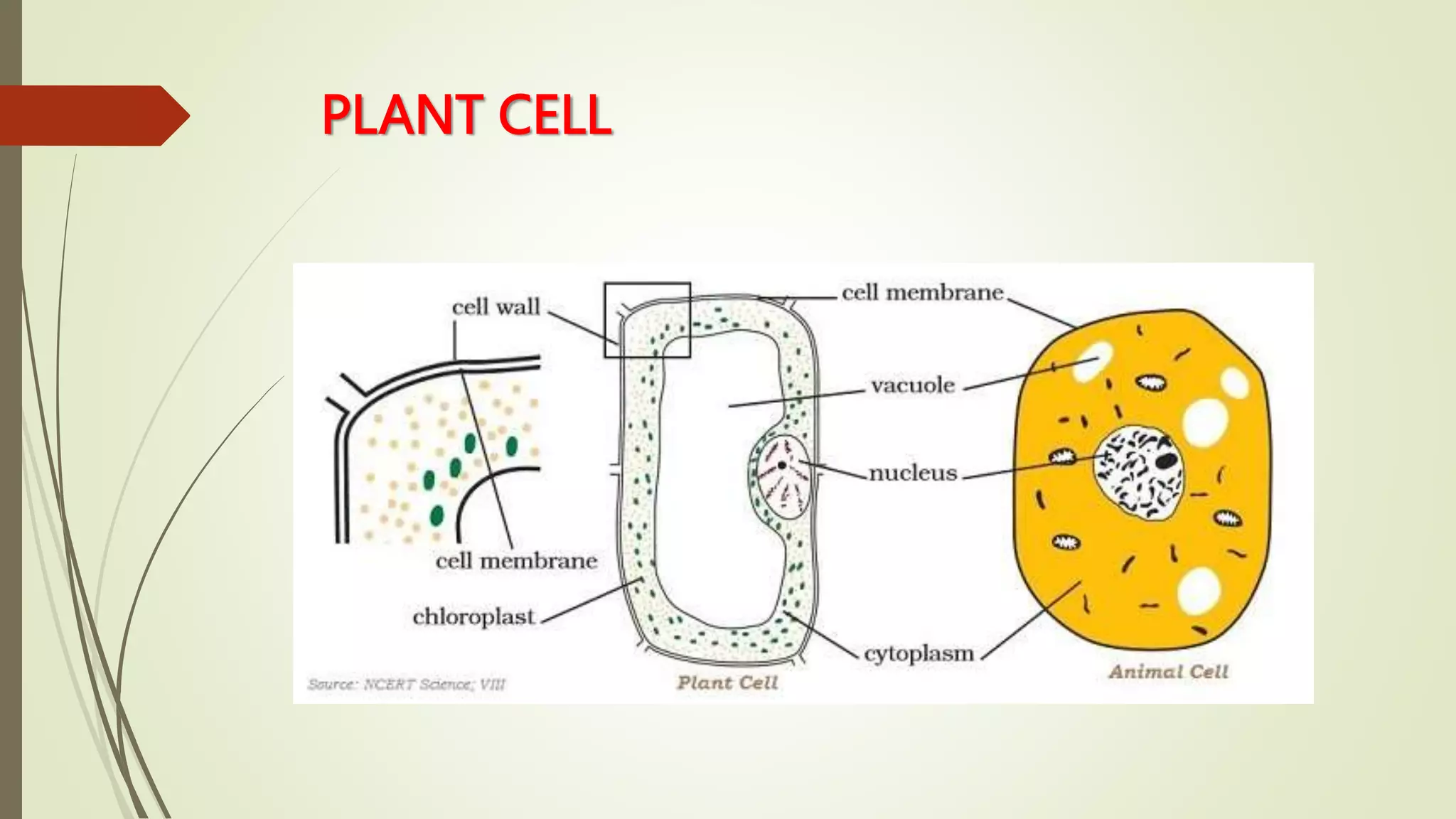
This document discusses the structure and functions of cells. It begins by introducing the basic unit of life, the cell, and defines single-celled and multicellular organisms. Specifically, it describes the amoeba as a single-celled organism that can perform all life functions. The document then explains eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It details the main parts of a cell - the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus - and some of their functions. The document also distinguishes plant cells from animal cells by noting that plant cells have a cell wall. It concludes by describing some other cellular structures like chloroplasts and their importance in photosynthesis.